![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
167 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Body Membrane |
-Functions of body membranes -cover body surfaces -line body cavities -form protective sheets around organs |
|
|
Classification of Body Membranes |
•Epithelial membranes -cutaneous membranes -mucous membranes -serous membranes •Connective Tissue -stnovial membranes |
|
|
Cutaneous Membranes (integumtary system) (skin) |
-Dry membrane -Outermost protective boundary •Superficial epidermis is composed of kerantinized stratified squamous epithelium •Underlying dermis is mostly dense connective tissue |
|
|
Mucous Membrane |
•Surface epithelium type depends on site -stratified squamous epithelium (mouth, esophagus) -simple columar epithelium (rest of digestive tract) •Underlying loose connective tissue (lamina propria) •Lines all body cavities that open to the exterior body surface •often adapated for absorption or secreation |
|
|
Serous Membrane |
•surface is a layer of simple squamous epithelium •Underlying layer is a thin layer of areolar connective tissue •lines open body cavities that are closed to the exterior of the body •serous membrane occur in pairs separated by serous fluid -visceral layer cover the outside of the organ -parietal layer lines a portion of the wall of ventral body cavitiy. |
|
|
Specific Serous Membrane |
-peritoneous -abdominal cavity -pleura -around the cavity -pericadium -around the heart |
|
|
Connective tissue membrane |
-synovial membrane -connective tissue only -lines fibrous capsules surrounding joints -secretes a lubricanting fluid |
|
|
Integumentary system |
•skin (cutaneous membrane) •skin derivatives -sweat glands -oil glands -hair -nails
|
|
|
Integumentary system |
•skin (cutaneous membrane) •skin derivatives -sweat glands -oil glands -hair -nails
|
|
|
Epidermis- outer layerDermis |
-stratified squamous epithelium -often kerantinized (hardened by keratin) |
|
|
Dermis |
-dense connective tissue |
|
|
Integumentary system |
•skin (cutaneous membrane) •skin derivatives -sweat glands -oil glands -hair -nails
|
|
|
Epidermis- outer layerDermis |
-stratified squamous epithelium -often kerantinized (hardened by keratin) |
|
|
Dermis |
-dense connective tissue |
|
|
Subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is deep to dermis |
-not part if the skin -anchors skin to underlying organs -composed mostly of adipose tissue |
|
|
Integumentary system |
•skin (cutaneous membrane) •skin derivatives -sweat glands -oil glands -hair -nails
|
|
|
Epidermis- outer layerDermis |
-stratified squamous epithelium -often kerantinized (hardened by keratin) |
|
|
Dermis |
-dense connective tissue |
|
|
Subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is deep to dermis |
-not part if the skin -anchors skin to underlying organs -composed mostly of adipose tissue |
|
|
Layers of the epidermis |
Stratum basale (deepest layer of epidermis) Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum (formed form dead skin cells) Stratum corneum (outermost layer of epidermis) |
|
|
Melanin |
-pigment (melanin) produced by melanocytes -melanocytes are mostly in the stratum basale -color is yellow to brown to black -amount of melanin produced depends upon genetics and exposure ot sunlight |
|
|
1st layer of dermis |
Papillary layer(upper dermal region) -some contain capillary loops -projectiond called dermal papillea -other house pain receptors and touch recepotors
|
|
|
2nd layer of dermis |
Reticular layer (deepest skin layer) -blood vessels -sweat and oil glands -deep pressure receptors |
|
|
Overall dermis structure |
-collagen and elastic fibers located throughout the dermis -elasticity fibers give skin elasticity -blood vessels play a role in body temperature regulation |
|
|
Normal skin color determines |
Melanin -yellow, brown, or black pigments Carotene -orange, yellow pigment from some vegetables Hemoglobin -red coloring from blood cells in dermal capillaries -oxygen content determines the extent of red coloring |
|
|
skin appendages |
Cutaneous glands are all exocrine glands -sebaceous glands -sweat glands Hair Hair follicles Nails |
|
|
Sebaceous glands |
-produces oul -lubricant for skin -prevents brittle hair -kills bacteria -Most have ducts that empty into hair follicles, other open directly onto skin surface -Glands are activated st puberty |
|
|
Sweat glands |
-produce sweat -widely distributed in skin Two types -eccrine -open via duct to pore on skin surface -aprocrine -ducts empty into hair follicles |
|
|
Swaet and its Function |
-Composition -mostly water -salt and vitamin c -some metabolic waste -fatty acids and proteins (aprocrine only) Function -helps dissipate excess heat -excretes waste products -acidic nature inh |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Rule Of Nines |
Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Rule Of Nines |
Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area |
|
|
First degree burn |
only epidermis is damaged skin is red swollen |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Second degree burn |
epidermis and upper dermis are damaged skin is red with blisters |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Rule Of Nines |
Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area |
|
|
First degree burn |
only epidermis is damaged skin is red swollen |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Second degree burn |
epidermis and upper dermis are damaged skin is red with blisters |
|
|
Third degree burns |
destorys entire skin layer burn is gray- white or black |
|
|
Critical burns |
Burns are considered critical if: -over 25% of the body had second degree burns -over 10% of the body has third degree burns -there are third degree burns on face, hands or feet |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Rule Of Nines |
Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area |
|
|
First degree burn |
only epidermis is damaged skin is red swollen |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Second degree burn |
epidermis and upper dermis are damaged skin is red with blisters |
|
|
Third degree burns |
destorys entire skin layer burn is gray- white or black |
|
|
Critical burns |
Burns are considered critical if: -over 25% of the body had second degree burns -over 10% of the body has third degree burns -there are third degree burns on face, hands or feet |
|
|
Classification of skin cancer |
Benign -does not spread (encapsulated) |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Rule Of Nines |
Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area |
|
|
First degree burn |
only epidermis is damaged skin is red swollen |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Second degree burn |
epidermis and upper dermis are damaged skin is red with blisters |
|
|
Third degree burns |
destorys entire skin layer burn is gray- white or black |
|
|
Critical burns |
Burns are considered critical if: -over 25% of the body had second degree burns -over 10% of the body has third degree burns -there are third degree burns on face, hands or feet |
|
|
Classification of skin cancer |
Benign -does not spread (encapsulated) |
|
|
Classification of skin cancer |
Malignant -metastatized (moves) to other part of the body •skin cancer is the most common type if skin cancer |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Rule Of Nines |
Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area |
|
|
First degree burn |
only epidermis is damaged skin is red swollen |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Second degree burn |
epidermis and upper dermis are damaged skin is red with blisters |
|
|
Third degree burns |
destorys entire skin layer burn is gray- white or black |
|
|
Critical burns |
Burns are considered critical if: -over 25% of the body had second degree burns -over 10% of the body has third degree burns -there are third degree burns on face, hands or feet |
|
|
Classification of skin cancer |
Benign -does not spread (encapsulated) |
|
|
Classification of skin cancer |
Malignant -metastatized (moves) to other part of the body •skin cancer is the most common type if skin cancer |
|
|
Basel cell carcinoma (skin cancer type) |
-least malignant -most common type -arises from stratum basale |
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma (skin cancer type) |
-metastasizes to lymph nodes if not removed -early removal allows a good chance of cure -believed to be sun- induced -arises from stratum spinosum |
|
|
Malignant melanoma (skin cancer type) |
-most deadly of skin cancers -cancer of melanocytes -metastasizes rapidly to lymph and blood vessels -detection uses ABCS rule |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Rule Of Nines |
Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area |
|
|
First degree burn |
only epidermis is damaged skin is red swollen |
|
|
Hair |
-produced by hair follicles -consists of hand kerantinized epithelial cells -malencytes provide pigment of hair color |
|
|
Second degree burn |
epidermis and upper dermis are damaged skin is red with blisters |
|
|
Third degree burns |
destorys entire skin layer burn is gray- white or black |
|
|
Critical burns |
Burns are considered critical if: -over 25% of the body had second degree burns -over 10% of the body has third degree burns -there are third degree burns on face, hands or feet |
|
|
Classification of skin cancer |
Benign -does not spread (encapsulated) |
|
|
Classification of skin cancer |
Malignant -metastatized (moves) to other part of the body •skin cancer is the most common type if skin cancer |
|
|
Basel cell carcinoma (skin cancer type) |
-least malignant -most common type -arises from stratum basale |
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma (skin cancer type) |
-metastasizes to lymph nodes if not removed -early removal allows a good chance of cure -believed to be sun- induced -arises from stratum spinosum |
|
|
Malignant melanoma (skin cancer type) |
-most deadly of skin cancers -cancer of melanocytes -metastasizes rapidly to lymph and blood vessels -detection uses ABCS rule |
|
|
ABCD rule |
A- asymmetry -two sides of pigmented mole do not match B-border irregularity -bordersof mole are not smooth C-color -different colors in pigmented area D- diameter -spot is larger than 6 mm in diameter |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
-central medulla -cortex surrounds -cuticle on outside of cortex |
|
|
Associated hair structures |
-hair follicle -dermal and epidermal sheath surround haircut -arrector pilimuscle -smooth muscle -pulls hairs upright when cold or frightened -sebaceous glands -sweat glands |
|
|
Nails |
-scale-like modifications of the epidermis -heavily kerantinized -stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed -responsible for growth -lack of pigment makes them colorless
|
|
|
Nail Structure |
-Free edge -body is the visible attached portion -root of nail embedded in skin -cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body |
|
|
Infections |
Athletes foot (tinea pedis) -caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles -caused by bacterial infection Cold sores -caused by virus |
|
|
Infections and allergies |
-contact dermatitis -exposures cause allergic reaction -impetigo -caused by bacterial infection -psoriasis -cause is unknown -triggered by trauma, infection, stress |
|
|
Burns |
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,electricity,UV radiation, or chemicals Assoicated dangers -dehydration -eletrolyte imbalance -circulatory shock |
|
|
Rule Of Nines |
Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area |
|
|
First degree burn |
only epidermis is damaged skin is red swollen |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
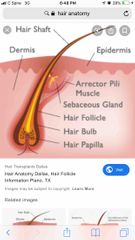
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Hair Anatomy |
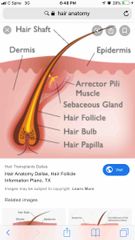
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Nail Anatomy |
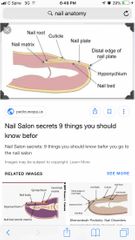
Back (Definition) |

