![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acrosome |
Is a structure that forms a cap over most of the nucleus of the sperm cell. The main job of the acrosome is to penetrate the outer layers of the ovum so that the sperm can get inside. |
|
|
Seminiferous Tubules |
Spermatogenesis takes place in the seminiferous tubules, which are an intricate system of tubules in the testes where spermatogenesis takes place |
|
|
Sertoli Cells |
Which are somatic cells of the seminiferous tubules that support and provide nutrients to the various sperm precursors |
|
|
Spermatogenesis |
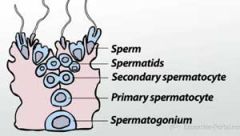
Is the process by which the male gametes, called sperm, are created. |
|
|
Germ Cells |
Are the cells that will become gametes |
|
|
Oogenesis |
Is the process by which the female gametes, or ova, are created. The female gamete is called an ovum |
|
|
Blastula |
The embryo takes the form of a hollow ball called |
|
|
Blastocyt |
Is a mammalian blastula that contains two distinct cell lineages |
|
|
Trophoblast Cells |
External cells are called trophoblast cells. The trophoblast cells will play a key role in the process of implantation in the uterine wall and will eventually become the chorion, which is the embryonic portion of the placenta. |
|
|
Morula |
An embryonic stage consisting of a solid, compact mass of 16 or more cells. The morula is the first embryonic stage where mammalian cells can be categorized as being either internal or external. |
|
|
Cleavage |
Is the process by which the zygote rapidly divides without growing to become multicellular. Cleavage uses the process of mitosis to replicate the genome and then divide the cells in half; however, unlike normal mitosis, there is no growth phase between divisions during cleavage. |
|
|
Zona Pellucida |
Which is a layer of extracellular matrix surrounding the mature oocyte, fertilized zygote and pre-implantation blastocyst. The zona pellucida surrounds the developing embryo during its entire journey down the fallopian tube and prevents the embryo from attaching prematurely to the wall of the fallopian tube. If the embryo implants in the fallopian tube, it will grow larger and cause an ectopic pregnancy outside of the uterus, which is the mammal-specific organ where prenatal development occurs. |
|
|
Protease |
Once the blastocyst reaches the uterus, it uses a protein digesting enzyme, or protease, to make a hole in the surrounding zona pellucida. It then squeezes through the hole to hatch out of the zona pellucida. Proteins on the outer surface of the blastocyst bind to the extracellular matrix of the uterine wall and allow the blastocyst to attach. The blastocyst will bury itself in the uterine wall = implantation |
|
|
Placenta |
Composite structure of embryonic and maternal tissues that supplies nutrients to the developing embryo 1. Attach fetus to uterine wall 2. Provide nutrients to fetus 3. Allow fetus to transfer waste products to mothers blood |
|
|
Intervillous Space |
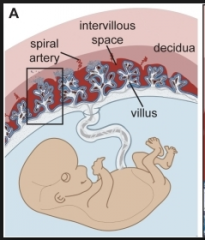
Allows nutrients to diffuse from the maternal blood, through the trophoblasts and into the embryonic bloodstream |
|
|
Chorionic Villi |
Are finger-like structures of the placenta composed of embryo-derived trophoblasts. The chorionic villi are surrounded by maternal blood which comes into direct contact with the embryonic trophoblast cells |
|
|
Chorion |
Is the embryonic-derived portion of the placenta. It is composed of trophoblasts, which you may remember are the cells that made up the outer cell layer of the blastocyst. |
|
|
Blood Flow in the Placenta |
Maternal blood flows from the mother's circulatory system, through the intervillous space and then re-enters the mother's blood vessels. Fetal blood flows from the fetus into two main arteries in the umbilical cord, through the capillary network of the chorionic villi and is returned to the fetus by the umbilical vein. The maternal blood that enters the placenta is nutrient and oxygen rich. |
|
|
Fetal Waste |
Fetal blood contains high concentrations of carbon dioxide and other waste products, while the material blood in the intervillous space contains low concentrations of these waste products. As a result, carbon dioxide and other waste products diffuse out of the fetal blood, across the trophoblasts of the chorionic villi and into the maternal blood that surrounds the villi. The mother's lungs, kidneys and liver will easily remove these waste products from her blood. Notice that in the placenta, the maternal and fetal blood does not mix. The two blood supplies remain separated by the fetal trophoblasts and endothelial cells. However, nutrients and waste products, including oxygen and carbon dioxide, are free to diffuse from one blood supply to the other down concentration gradients. |
|
|
Vertebrates have four different extraembryonic membranes |
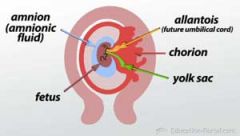
1. Chorion: is the outermost membrane and lines the inside of the eggshell 2. Allantois: is a sac-like extraembryonic membrane that removes waste from the embryo. The allantois exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide with the air outside the eggshell and serves as a disposal site for uric acid 3. Yolk sac:is the extraembryonic membrane that surrounds the egg yolk. The yolk sac has a well-developed vascular system that transports nutrients from the egg yolk to the developing embryo 4. Amnion: is the extraembryonic membrane that surrounds the developing embryo. |
|
|
Gastrulation |
Which is the process that results in the formation of three distinct germ layers in the early embryo. Primary germ layers 1. Endoderm: inner layer of cells 2. Ectoderm: outer layer of cells 3. Mesoderm: middle layer of cells |
|
|
Ectoderm Body Parts |

|
|
|
Mesoderm Body Parts |
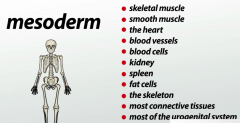
|
|
|
Endoderm Body Parts |

|
|
|
Dorsal |
Which is the back side of the animal |
|
|
Ventral |
Underbelly side, of the animal |
|
|
Anterior |
End of the animal is located at its head |
|
|
Posterior |
Located at the tip of the animal's tail, or where the tail would be if that particular animal doesn't have one |
|
|
Somatic Cell |
Non-reproductive cell |

