![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most important test of hepatic metabolic
function? |
This is bilirubin.
|
|
|
What cellular organelle conjugates bilirubin in the liver?
|
Conjugation occurs in the smooth endoplasmic reticu lum.
|
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for conjugation of bilirubin, and what two diseases are due to mutations in the gene for this enzyme?
|
The conjugation enzyme is uridine diphosphate (UDP) glucuronyl transferase.
Different mutations result in Gilbert's and Crigler-Najjar syndromes. |
|
|
Clay-colored stool is due to the absence of what pigment?
|
This is stercobilin.
|
|
|
Review the congenital causes of hyperbilirubinemia:
Dubin-Johnson: Crigler-Najjar I: Crigler-Najjar II: Gilbert's: |
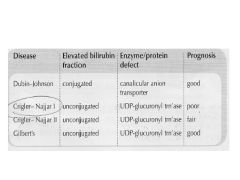
|
|
|
What reagents are used to measure total bilirubin?
|
Diazolized sulfanilic acid is the main reagent. The accelerants are caffeine or methanol.
Direct bilirubin is the measurement of bilirubin without the accelerants. |
|
|
Is arterial or venous blood the preferred specimen for the measurement of ammonia in cases of hepatic encephalopathy?
|
Arterial blood levels correlate with clinical symptoms better than do venous levels. Ammonia is a product of cellular metabolism. Specimens should be kept in ice water until separation of plasma can be performed to limit excess generation of ammonia.
|
|
|
Explain the etiology of hypertriglyceridemia in a cirrhotic patient who does not have a congenital enzyme deficiency and has provided a fasting sample?
|
The damaged liver produces decreased amounts of lipoprotein lipase, so TG are not removed from the bloodstream, and measured levels are increased.
|
|
|
What is the role of ceruloplasmin in iron metabolism?
|
Ceruloplasmin converts iron from the ferrous to the ferric state, which allows it to bind to transferrin.
|
|
|
Describe the likely patterns of elevated AST vs. ALT in acute hepatocellular injury over time by stating which is higher:
First 24 hours? After 24-48hours ? |
In the first 24 hours, AST is greater than ALT due to the higher activity of AST in the hepatocytes.
After 24-48 hours, the longer half-life of ALT makes it the predominant enzyme in serum. |
|
|
List three medications that increase gamma-glutamyl transferase levels.
|
Phenytoin, carbamazepine, and acetaminophen all raise GGT.
|
|
|
What subtype of antimitochondrial antibody is specific for primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)?
|
This is AMA M2. Other subtypes are associated with other diseases.
|
|
|
Compare and contrast type 1 and type 2 autoimmune hepatitis:
|
In type l, antinuclear (ANA) and anti-smooth muscle (ASMA) antibodies are commonly seen. This type is seen in adults and is the predominant type seen in the USA.
In type 2, ANA and ASMA are rare, but the anti-liver-kidney microsomal antibodies are seen. This type is seen in children and is much more common in Europe than in the USA. |
|
|
What is the incubation period of hepatitis A virus (HAV)?
|
HAV usually incubates 2-3 weeks, a month and a half at the most.
|
|
|
What is the incubation period of hepatitis B vims (HBV)?
|
HBV incubates 1-3 months.
|
|
|
What is the first serologic marker of HBV infection, and how soon after exposure is it detectable in most cases?
|
The first marker, seen in most infected persons, is the surface antigen, HBsAg. It shows up 2-3 months after exposure.
|
|
|
What antibody is useful in assessing recovery and clearance of HBV?
|
Anti-HBs is a good indicator of clearance of the virus.
|
|
|
What HBV marker correlates well with the amount of HBV DNA?
|
This is HBeAg.
|
|
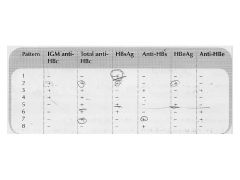
Which pattern indicates a resolved HBV infection?
What is the interpretation of pattern #2? Is the person with pattern #5 infectious to others? How likely is an elevation of ALT in patient #1? |
Which pattern indicates a resolved HBV infection?
Pattern #7 What is the interpretation of pattern #2? This is acute HBV infection. Note that IgM is still present Is the person with pattern #5 infectious to others? Yes. This is active chronic hepatitis B. Some argue that HBeAg correlates well with infectivity, particularly in pregnant women. How likely is an elevation of ALT in patient #1? Unlikely. This is the incubation period, and the person is probably asymptomatic and without transaminasemia. |
|
|
What confirmatory tests are used for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in the following situations?
Blood donor with positive anti-HCV: Chronically infected HCV patient: |
For blood donors, the recombinant immunoassay and nucleic acid test are used . In hlgh-risk populations , a confirmatory test is unnecessary, as the PPV is high. For the chronically infected, HCV RNA is used to monitor disease and assess response to treatment.
|
|
|
Which HCV genotypes are most responsive to treatment? Which type(s) is/ are most common in the USA?
|
Genotypes 2 and 3 respond best to the treatment modalities available.
Unfortunately, 65% of white people and 90-95% of black people in the USA are infected with genotype 1, which does not respond as well to treatment. |
|
|
What is the cardinal laboratory finding in acute hepatitis?
|
An elevation of the aminotransferases, frequently to levels greater than 500 IU/L is characteristic of acute hepatitis. Other parameters are often increased as well.
|
|
|
What is the most common molecular defect in hemochromatosis, and where is the HFE gene located?
|
At amino acid 282 in the gene product, tyrosine is substituted for cysteine (C282Y). The HFE gene is located on chromosome 6p.
|

