![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the testis? |
• Produces sperms (male gametes) • Produce male sex hormones e.g. testosterone. |
|
|
|
What is the scrotum? |
- Testes are held in the scrotum, which are pouch-like sac outside the body, allowing the scrotum to be at a lower temperature than body temperature, which is essential for sperm production. |
|
|
|
What is the sperm duct? |
They transport sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. |
|
|
|
What do the prostate gland, seminal vesicles and the Cowper's gland do? |
They secrete fluid that contain nutrients and enzymes which nourish and activate the sperm, allowing them to swim actively |
|
|
|
What is the urethra? |
The urethra is a tube which passes from the bladder and it is a passage for urine and semen to pass out of the body |
|
|
|
Why is an acrosome present in the head of a sperm? |
Acrosome is a vesicle containing enzymes which break down part of the egg membranes so that the sperm can penetrate the egg during fertilisation. |
|
|
|
What is the chromosome number in the nucleus of a sperms? |
Haploid (23 chromosomes) |
|
|
|
Why does the middle piece contain numerous mitochondria? |
The middle piece contains numerous mitochondria, which provides energy for the sperm to swim towards the egg. |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the flagellum? |
It carries out a beating movement to swim towards the egg |
|
|
|
What is the ovary? |
The ovaries produce ova (female gamete) and female sex hormones such as oestrogen and progesterone |
|
|
|
What is the oviduct/fallopian tubes? |
It is a narrow muscular tube where fertilisation occurs and the ovary releases the ovum into and leads to uterus. |
|
|
|
What is the uterus? |
The uterus is a thick muscular organ that is lined with uterine lining richly supplied with blood vessels. It is the site of implantation of the embryo post-fertilisation and is where the embryo develops into a fetus |
|
|
|
What is the cervix? |
• The cervix is a circular ring of muscle that enlarges during birth to allow the passage of the foetus. |
|
|
|
What is the vagina for? |
It is a birth canal through which the baby is born and is where sperm is deposited during sexual intercourse |
|
|
|
What is the chromosome number in the ovum? |
Haploid (23 chromosomes) |
|
|
|
What's puberty? |
Puberty is the stage of human growth and development in which a person becomes physically mature |
|
|
|
What happens in males during puberty? |
1) Facial hair, pubic hair and armpit hair start to grow 2) The penis and testicle increase in size 3) The larynx enlarges and voice deepens 4) The production of sperms starts |
|
|
|
What happens in females during puberty? |
1) Pubic hair and armpit hair start to appear 2) The breasts and uterus enlarge 3) The hips broaden 4) Menstruation and ovulation starts |
|
|
|
What is menstruation? |
Menstruation is the monthly discharge of blood from the uterus via the vagina |
|
|
|
How long is the menstrual period? |
5 days |
|
|
|
What is the average menstrual cycle? |
28 days |
|
|
|
What affects the menstrual cycle? |
Stress, tiredness, illness, unbalanced diet and malnutrition |
|
|
|
What are the changes in a follicle during the menstrual cycle? |
1) Primary follicle is formed
2) Graffian follicle is formed from a primary follicle
- The Graffian follicle contains an egg with haploid number of chromosomes surrounded by follicle cells and a fluid filled space
3) Ovulation
- The Graffian follicle ruptures and releases the egg into the oviduct
4) Corpus luteum
- The Graffian follicle develops into a corpus luteum after ovulation
- The Corpus luteum produces hormones that prepare the body for pregnancy
5) Break down of Corpus luteum
- The corpus luteum eventually breaks down if there is no fertilisation |
|
|
|
What are the stages in a menstrual cycle? |
- Day 1 - 5: Menstruation - Day 6 - 13: Follicle stage
- Day 14: Ovulation - Day 15 - 28: Corpus luteum stage |
|
|
|
What occurs during the menstrual flow stage? |
Day 1 - 5: Menstruation
• The endometrium breaks down and flows out of the body through the vagina.
• Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is secreted by the pituitary gland |
|
|
|
What are the effects of follicle-stimulating hormone? |
1) Stimulates development of follicles during the follicle stage 2) Stimulates the follicles in the ovaries to secrete oestrogen during the follicle stage |
2 pts |
|
|
What are the effects of oestrogen? |
- Causes repair and growth of uterine lining during the follicle stage - At a high concentration of oestrogen, it stops FSH production, preventing maturation and development of further follicles during the follicle stage - At high concentration, oestrogen stimulates pituitary gland to secrete lutenising hormone during the follicle stage |
3 pts |
|
|
What are the effects of luteinising hormone (LH)? |
- causes ovulation - causes formation of the corpus luteum from the remains of the Graafian follicle during ovulation |
2 pts |
|
|
What are the effects of progesterone? |
- Thickens uterine lining to prepare it for implantation of embryo during the corpus luteum stage - Stops ovulation and FSH production |
|
|
|
What happens if no fertilisation occurs? |
1) The egg will break down
2) Lutenising hormone production is stopped by high concentration of progesterone, causing the corpus luteum to break down
3) Progesterone is not secreted anymore as corpus luteum is broken down
4) The thickened uterine lining cannot be maintained without progesterone and so it breaks down
5) Menstruation is repeated again and the whoe cycle is repeated again with the production of FSH by the pituitary gland |
|
|
|
When is the fertile period? |
The fertile phase of the cycle is from day 11 to 17. |
|
|
|
What happens during fertilisation? |
1. During sexual intercourse, semen containing sperms is deposited into the vagina of a woman.
2. The sperms swim up the oviducts and encounter the ovum.
3. The acrosome of the sperms release enzymes to disperse the layer of cells surrounding the ovum and break down the outer membrane of the ovum.
4. The sperm nucleus fuses with the egg nucleus. This process is called fertilisation, forming zygote
5. The plasma membrane of the egg undergoes a change as soon as a single sperm has entered, preventing other sperms from entering.
6. The remaining sperms eventually die.
7. The zygote develops into an embryo, and embeds itself in the uterine lining
8. The embryo secretes a hormone that prevents the corpus luteum from break down until the placenta is formed
9. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and oestrogen until the placenta is developed and is able to take over the production or progesterone and oestrogen
10. After 10 to 12 weeks, the embryo becomes a fetus and it continues to develop |
10 pts |
|
|
What are the stages during the development of an embryo? |
1) Implantation
2) Development of the placenta
3) Development of amniotic sac |
|
|
|
What occurs during implantation? |
1. Cilia lining the oviduct sweep the fertilised egg or zygote along the oviduct. 2. Peristaltic movement of the oviduct also help the zygote move towards the uterus. 3. The zygote divides by mitosis to form a hollow ball of cells called the embryo. 4. It takes about five days for the embryo to reach the uterus. 5. The developing embryo moves down the uterus and eventually embeds itself in the uterine lining. |
5 pts |
|
|
What occurs during the development of the placenta? |
• After implantation, finger-like tissues known as villi grow out from the embryo and into the uterine lining, forming the placenta. • A tube known as the umbilical cord attaches the embryo to the placenta |
|
|
|
What occurs during the development of the amniotic sac? |
Amniotic sac develops at the same time as the placenta. • The membrane encloses the embryo in a fluid-filled space known as the amniotic cavity. • It secretes fluid known as amniotic fluid |
|
|
|
Why is the fetal blood system not continous with the mother's blood system? |
- The blood pressure of the mother would kill the fetus as it is much higher than that of the fetus - The blood group of the fetus may not be the same as the mother's and agglutination may occur if both blood systems are continous, causing harm to both mother and child |
|
|
|
What are the functions of the placenta? |
(a) Provide nutrients such as glucose, amino acids and mineral salts and oxygen from maternal blood to the embryo (b) Remove waste materials such as urea and carbon dioxide from the foetus (c) Allows protective antibodies to diffuse from maternal blood into embryonic blood (d) Produces progesterone which maintains the uterine lining during pregnancy |
4 pts |
|
|
What are the functions of the umbilical cord? |
The umbilical cord attaches the embryo to the placenta. • One umbilical vein transports oxygenated blood and food substances from the placenta to the foetus. • Two umbilical arteries transport deoxygenated blood and metabolic waste products from the foetus to the placenta. |
|
|
|
What are the functions of the amniotic fluid? |
• Acts as a cushion to absorb shock and protect the fetus against mechanical injury. • Allows the foetus to move freely. • Prevents the foetus from dehydration. • Maintains a constant temperature for optimum development of the fetus. • Acts as lubricating fluid for the passage of the baby during birth. |
5 pts |
|
|
What does the umbilical vein transport? |
It transports oxygenated blood and food substances from the placenta to the fetus |
|
|
|
What does the umbilical artery transport? |
It transports deoxygenated blood and metabolic waste products from the fetus to the placenta |
|
|
|
What happens during the follicle stage? |
Day 6 - 13: Follicle stage - FSH stimulates the development of the follicles and the development of a Graffian follicle
- Once a Graffian follicle is developed, the follicles in the ovaries are stimulated to secrete oestrogen
- Secretion of luteinising hormone (LH) is stimulated, causing ovulation
- The uterine lining is repaired and becomes thick and spongy
- The maturation and development of more follicles are presented due to the high concentration of oestrogen |
5 steps |
|
|
What happens during ovulation? |
Day 14: Ovulation • A corpus luteum is formed from the remains of a Graffian follicle
• The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and some oestrogen |
2 steps |
|
|
What happens during corpus luteum stage? |
- The uterine lining is thickened further by progesterone and is prepared for implantation of embryo
- Ovulation and FSH production is inhibited (stopped) |
|
|
|
Male reproductive system |
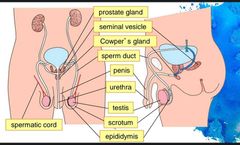
|
|
|
|
Female reproductive system |
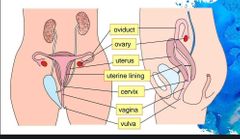
|
|
|
|
what are the 2 functions of the ovaries in a healthy woman who is not pregnant? |
1. Produce oestrogen and progesterone to repair and grow uterine lining and maintain thickness of it respectively 2. Produce ova which is the female sex gamete |
|

