![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
what is the lipoprotein is taken up by macrophages, which then invade the coronary endothelium to initiate plaque formation
|
oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL)
|
|
|
|
what is the characteristic lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme pattern in acute myocardial infarction?
|
LD1>LD2
|
|
|
|
what relative index (RI) of creatine kinase MB antigen mass (CK-MB) to total CK activity suggest AMI?
|
2%
|
|
|
|
most important laboratory test for acute coronary syndrome (ACS)?
|
cardiac troponin (cTn); both cTnI and cTnT are in use
|
|
|
|
reasons for the high specificity of cardiac troponin I and T (cTnI, cTnT)?
|
assays are specific for the cardiac forms
both cTnI and cTnT are essentially absent from the normal serum |
|
|
|
how long after an AMI does cTn peak?
|
24hours
|
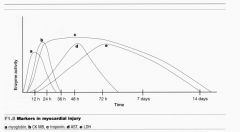
|
|
|
63 yom AMI, 12 hours later cTnI levels begin to gradually rise again. The patient denies chest pain. Does this represent a second, silent AMI?
|
no; the majority of cTn is bound to muscle fibers and is released more slowly in the week-plus after the AMI
|
|
|
|
what is the window of opportunity for using myoglobin as a marker for cardiac injury?
|
elevated serum levels are apparent within 2-3 hours after AMI, return to baseline by 24hours
|
|
|
|
hs-CRP is the current analyte of choice as an inflammatory marker for risk assessment of CHD , universal screening is not recommended
|
hs-CRP is the current analyte of choice as an inflammatory marker for risk assessment of CHD , universal screening is not recommended
|
|
|
|
when is a homocysteine measurement warranted?
|
if a person who is at low risk of CHD, based on traditional risk factors develops CHD; then a homocysteine level may provide some other useful data
|
|
|
|
BNP limitations as an analyze for HF?
|
BNP is not especially specific marker as it is elevated in other conditions of fluid imbalance such as renal failure; chronic HF patients with stable disease may have values within the reference range; intra-individual variation can be as great as 30-40% in chronic HF patients with stable disease
|
|

