![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
ALLELE |
Different copies of the same gene which control a certain trait (T or t) |
|
|
|
HYBRID / HETEROZYGOUS |
An individual that possesses two different alleles for a trait (ie: Tt, Bb) |
|
|
|
PURE / HOMOZYGOUS |
An individual that possesses two similar alleles for a trait (TT, tt, BB) |
|
|
|
GENOTYPE |
Genetic make-up of an individual organism. Tells us what genes are responsible for that trait. (ie: Homozygous for blue eyes (bb) |
|
|
|
GENOTYPE RATIO |
The ratio of various genotype a in a generation of offspring (TT, Tt, tt) |
|
|
|
PHENOTYPE |
The physical trait observed in an individual as a result of their genotype. (Don't use heterozygous or homozygous) ie: Blue eyes, blonde hair |
|
|
|
PHENOTYPIC RATIO |
The ratio of the various phenotype a in a generation of offspring. |
|
|
|
LAW OF SEGREGATION |
Inherited traits are determined by pairs of alleles.
(When two alleles are present the dominant allele may prevent the expression of the recessive allele.) |
|
|
|
UNIT THEORY |
Because traits are inherited as independent units Mendel's factors of inheritance are sometimes referred to as unit characters and his theory as unit theory |
|
|
|
PUNNETT |
1900s geneticist who discovered fundamentals in genetics such as sex determination, and trainers that are linked to each sex.
(Worked with traits of feather colours in chickens) |
|
|
|
COMPLETE DOMINANCE |
Both heterozygous and dominant homozygous have the same phenotype.
(TT, Tt) |
|
|
|
TEST CROSS |
When you cross an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual. Whichever is homozygous dominant all offspring will have dominant trait. If bred with heterozygous some offspring will be recessive. |
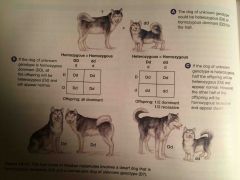
|
|
|
MENDELS 4 LAWS |
1. Law of independent characters 2. Law of segregation 3. Law of dominance 4. Law of independent assortment |
|
|
|
LAW OF INDEPENDENT UNIT CHARACTERS |
Characters (such as height, color, etc.) are inherited separately as units |
|
|
|
LAW OF SEGREGATION |
Body cells & primordial germ cells contain pairs of unit characters.
When gametes are produced each gamete receives one member from each pair. |
|
|
|
LAW OF SEGREGATION |
Body cells & primordial germ cells contain pairs of unit characters.
When gametes are produced each gamete receives one member from each pair. |
|
|
|
LAW OF DOMINANCE |
If the factors are heterozygous and contain recessive & dominant, the recessive character can only appear when two dominant is present. |
|
|
|
LAW OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT |
Any one pair of characters is inherited independently |
|
|
|
CHROMOSOME THEORY |
-Mendel's factors are carried on chromosomes - it is the segregation and independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis that accounts for the patterns of inheritance. |
|

