![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Urea |
made by liver from very dangerous ammonia |
|
|
Uric Acid |
from purins ( precipitates & must be removed) |
|
|
Vitamins |
filtered & removed only used to point then disposed |
|
|
Ion |
Useful to a point -> eventually have to get rid of it -not natural/viewed dangerous & rid of it aspirin, antibiotics |
|
|
Hb breakdown products: |
Polypeptides, fatty acids and creatinine (breakdown of ATP to ADP) no function, not dangerous na dget rid of it from kidneys
|
|
|
Frequency of urine formation |
CONSTANT |
|
|
Kidney Anatomy |
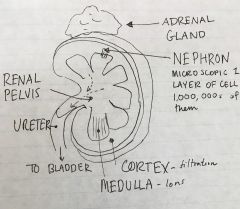
Nephron on the renal medulla in the junction with the renal cortex |
|
|
Nephron anatomy |
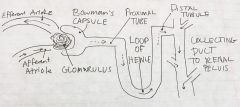
|
|
|
Afferent Arteriole Efferent Arteriole |
Afferent Atriole supplies tubule w/ with blood, efferent has blood going outwards |
|
|
Glomarulus |
Really leaky cluster of capillaries that the Bowmans capsule surrounds Leaky to filtrate* -- plasma w/o protein 20% of glomarulus leaked out a lot more than normal capillary |
|
|
Bowmans Capsule |
Structure that wraps & folds over glomerulus & hugs in place. Filtrate goes into the capsule through another level (beginning of nephron |
|
|
Proximal Tubule |
Things picked out of filtrate & back to body (reabsorption)(facilitated diffusion etc) Most occuring ~100% |
|
|
Loop of Henle |
In animals w/ risk of dehydration & concentrating of urine. More reabsorption of ions and water |
|
|
Distal Tubule |
fine tune how much water & ions reabsorbed |
|
|
Medullary collecting duct |
vasopressin (ADH) only works on aquaporins (Increase water re-absorption) |
|
|
Peritubular Capillaries |
capillaries that surround the nephron and pick up reabsorbed filtrates/ water/ ions |
|
|
Secretion/reabsorption relationship |
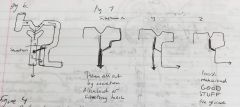
Glucose likely reabsorbed alkaloid or toxic substance (interpreted as dangerous like some medicines) 100% secretion |
|
|
Podocyte |
Foot cell interdigitations or cells that overlap making filtration slits |
|
|
GFR |
Glomerlular filtration rate based on changing diameter. Pressure in glomerular capillary into bowmans space |
|
|
Water reabsorption (proximal tubule) |
start in lumen and crosses the tight junction into interstitium then into the capillaries or can go through the epithelial cells using osmotic energy |
|
|
Glucose & Sodium reabsorption (proximal tubule) |
both Na+ and glucose get into the cell through mediated protein transports (luminal -- apical side) GLUTs & 2K+/3Na+ pumps on basolateral side of tubule towards interstitium and into the capillary leak channels (for K+) are also in the basolateral side to allow for gradient that reabsorbs sodium. Prevents elimination |
|
|
Absorbtion from the loop of henle to collecting duct Distal tubule & cortical collecting duct |
water taken up into capillaries via aquaporins on both sides (apical and basolateral) K+ eliminated on apical side while Na+ absorbed -- also leak channel for Na+ Basolateral side -- 3Na+/2K+ and aquaporins |
|
|
Aldosterone |
-steroid hormone made in adrenal cortex made in zona glumerulosa -Low sodium or high potassium or low blood pressure --> brain/ kidney triggers aldosterone |
|
|
Glomerulus/ distal tubule |
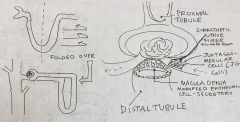
|
|
|
Renin |
Secretions from macula densa activate JG cells and produce this enzyme --> in turn causes the production of aldosterone Macula densa has Na+ sensors --> Na+ lvls affect secretion levels (has a setpoint) |
|
|
Renin Pathway |
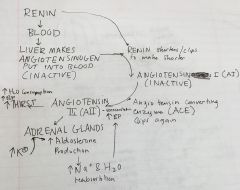
|
|
|
Effects of AII receptor blocker |
Prevents the reabsorption of Na+ and H2O --> no blood pressure increase
|
|
|
Angiotensin converting enzyme Inhibitors |
Block ACE converting enzyme --> Angiotensin I remains in this form and is not active |
|
|
K+ levels on aldosterone |
Regardless of medicine, it still has an effect. Self correcting within mechanism |
|
|
Collecting duct water absorption |
Vasopressin (ADH) through the capillary triggers vesicles with aquaporins to be placed in the luminal (apical) side of nephron. once VP decreases AQP endocytosed out or kept on vesicle then put on surface |
|
|
Time Vs. blood plasma concentration (mg/dL or mmol) |
as time passes the concentration plateaus based on substance.
|
|
|
Clearance rate |
how kidneys clear a substance -->volume/ time ml/minute how much blood is cleared & rid of solute |
|
|
Glucose clearance rate |
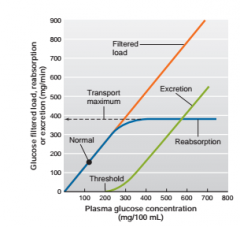
Clearance rate of glucose --> 0 ml/min positive if glucose is high @ 200-180 mg - exceed ability to recapture glucose -->380 max |
|
|
Osmotic Diuresis |
loss of fluid lots of glucose |
|
|
Polyuria |
excess fluid loss in urine |
|
|
Polydipsia |
THIRST - drinking more water because losing water |
|
|
Glucosuria |
Glucose in urine plasma/glucose conc. too high -could also indicate damage of transporters, kidneys or metabolic disorder ---> diabetes |
|
|
Excretion rate |
concentration * rate = Mg*V --> ml/min |
|
|
Clearance (Cx) |
Cx = (Vx*V)/Px Vx--> concentration of X in urine V--> Urine volume per unit time Px --> plasma concentration of S Ex: if you compare Cx to GFR (Cx=100 GFR=125) less blood is cleared than going into nephrons --> more absorption (a little bit of it) |
|
|
GFR equation |
(Vx*V)/Px |
|
|
Creatinine |
-Skeletal muscle & phosphorus processing - if everything is normal use the level to determine GFR. only secrete a little creatine/ no reabsorption |
|
|
Absorptive state |
Food in GI tract are absorbing nutients into blood |
|
|
Post-Absorptive state |
No nutrients being absorbed --> surviving on previously acquired nutrients |
|
|
Case study: Severe Kidney Disease in a Woman w Diabetes Mellitus |
Woman w diabetes gas worsening symptoms and has increase in creatinine in blood and protein in urine GFR lowered and proximal tubule not absorbing proteins back into blood Edema due to less proteins in body --> less osmotic force keeping water in blood Uremia --> urea in blood abnormal secretion of hormones -- decreased EPO and then anemia Renin increase and development of renal hypertension Treatment --ACE inhibitor to decrease blood pressure and promote better sodium and water balance. - Counselling on diet as well BUT FAILING kidneys |
|
|
Dialysis |
Separate substances using permeable membrane Hemo dialysis removes waste and excess substances from the blood |
|
|
Peritoneal Dialysis |
lining of patients abdominal cavity (peritoneum) as dialysis membrane fluid injected into this cavity and solutes diffuse, fluid is then replaced with new fluid |

