![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what does disease transmission rate vary with |
different diseases, populations and time |
|
|
was an endemic |
occurs at a relatively concentrate was in a population |
|
|
what is sporadically |
diseases that are uncommon and occur irregularly |
|
|
what is an epidemic |
increase in the number of cases of the disease within a population above normality |
|
|
what is a pandemic |
disease spread across multiple continents and throughout the world |
|
|
what are the factors that impact on transmission |
characteristics of the disease (mechanism of transmission) environmental factors (e.g. climate) characteristics of the population infected (levels of immunisation) |
|
|
what determines the extent of the disease spread |
when the factors interact |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what do some transmission methods do to the spread of disease |
restricts the spread of disease to a particular climate budget graphical area (e.g. malaria) |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - why would some modes of transmission be more likely to spread in certain groups within one population |
because behaviours or risk factors within such groups that promote disease spread a more common than in other members of the population for example hepatitis C |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what also influences disease transmission |
pathogen infectivity |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what is infectivity |
the ability of the pathogen to spread from one host to another |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what is increased infectivity mean |
means a pathogen can readily spread throughout the population |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - and what is natural history of infection |
different stages of infection and can vary with each pathogen |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what also contributes to the spread of disease |
the persistence of a pathogen within its definite host |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what is in a sympathetic carrier |
and affected by disease that can transmit to others |
|
|
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS - what can affect disease spread |
a wide variety of environmental factors including infrastructure and climate |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what's special about Dengue fever |
is more prior to transmission in urban environments as the mosquito is well adapted to bed environments and breeds an artificial water pools |
|
|
what are the 10 stages in outbreaks |
|
|
|
predicting the spread of disease - what is used for this |
mathematical modes are used to predict the spread of disease and important tools in outbreak |
|
|
predicting the spread of disease - who work works closely together and to do what |
mathematicians and biologists work closely together to produce a programme which is based upon assumptions |
|
|
predicting the spread of disease - what has enabled the development of complex models and what are these do |
developments in ICT has enabled the development of complex models which investigate disease and it spread |
|
|
PATHOGEN FACTORS THAT AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - What can changes in global temperatures do to levels of disease |
higher levels of disease for example increase in temperature and rainfall can equals the spread of disease spreading factors |
|
|
where vectors found |
hot and humid conditions - tropics |
|
|
draw the life-cycle of vectors |
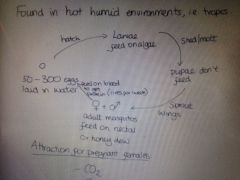
|
|
|
what is the attraction for pregnant mosquitoes |
CO2, smell and movement |
|
|
were the breeding conditions four vectors |
stagnant water natural - ponds, marshes, wetlands and swamps urban - Pool, wading Pool, buckets and drains |
|
|
HOW HOSTS CAN AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what can risk of exposure to disease be due to |
behaviours as in the example of blood-borne viruses that may also vary with age 6 or associated economic status |
|
|
HOW HOSTS CAN AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - example of people with higher susceptibility to to contracting infections |
the elderly or chronically ill |
|
|
HOW HOSTS CAN AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what else can impact on disease spread |
the proportion of the population as some of the population convenient to the disease, disease spreads rapidly due to large susceptibility of individuals |
|
|
HOW HOSTS CAN AFFECT DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what does as a large population density do |
population density large number of people living in close proximity to one another needs more opportunities for disease to spread this |
|
|
MOVEMENT OF INDIVIDUALS CAN FACILITATE DISEASE TRANSMISSION - humans have a substantial impact on the transmission of disease and what are the two categories |
intentional - quarantine and vaccination unintentional - agriculture, organisational transportation |
|
|
MOVEMENT OF INDIVIDUALS CAN FACILITATE DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what can facilitate the spread of disease and what does this allow |
the movement of individuals and population, this allows diseases to spread faster and over larger geographical areas |
|
|
MOVEMENT OF INDIVIDUALS CAN FACILITATE DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what is the morbility |
to leave act of the disease within a population, measured by the number of people affected by that disease |
|
|
MOVEMENT OF INDIVIDUALS CAN FACILITATE DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what has travelled done |
has been made easier and more affordable, which facilitates the spread of disease increasing mobility equals emerging infectious diseases now have potential to spread worldwide at alarming rates for example the 2003 stars outbreak |
|
|
MOVEMENT OF INDIVIDUALS CAN FACILITATE DISEASE TRANSMISSION - what other diseases can be spread geographically and example |
plant and animal diseases for example 2010 myrtle rust in Australia |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what is one strategy |
hand hygiene - example of this when it wasn't used hospitals during the mid-19th century West surgeons did not wash their hands, therefore increased death rates related to post operative infection |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what can hand washing do |
can significantly reduce the morality from certain infections for example diarrhoeal infections |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what is a nosocomial infection |
infections spread by health care workers |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - would is another strategy used |
immunisation - highly effective in substantially reducing worldwide morbidity and mortality for example in Australia children are vaccinated against hepatitis B, hurt choices, measles, tetanus and polio |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what do you knows action programs has the potential to do |
K disease by making a spread impossible for example smallpox was the first disease vaccine was created for and also the first to be eradicated through vaccine in 1998 |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - had as immunisation work |
if a large enough proportion of the population is mean to a disease there are too few susceptible individuals to sustain disease spread |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what is heard immunity |
once a particular proportion of the population is immune to disease, susceptible individuals are also better protected from the disease |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - hered immunity - what does it depend on |
the virulence and infectivity of a particular disease |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - immunity - groups of people object immunisation of children why and what does this cause |
reasons vary but concern has been raised by these groups about the safety vaccine for example in 1998 the small of substantial report released suggesting the MMR vaccine could cause autism in some cases levels of immunity within a population dropped so low that heard community is no longer sustained for example in 2013 measles outbreak in the UK were linked to low vaccination rates following the MMR scare |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what does quarantine do |
it stops individuals who have been exposed to infectious diseases from carrying that diseases into healthy populations |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what is quarantine used for |
used to counter the threat of spreading disease |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - how does a quarantine work |
infected individuals are kept from entering a healthy population and the incubation period of the disease has passed |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what is quarantine also used for |
use to prevent the spread of animal pathogens for example when people import cats and dogs into Australia from overseas player held in quarantine for at least 30 days |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - at how our quarantine measures to protect human health used |
captains of planes or ships are required to report passengers displaying symptoms of certain infections |
|
|
PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF DISEASE - what does Australia have |
strict quarantine laws to prevent biodiversity loss |

