![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Information highway |
Spinal cord Connects brain with lower body |
|
|
Conduction |
Nerve fibers that conduct information up and down the cord connecting differ levels of trunk w/ each other and the brain |
|
|
Neural integration |
Input from multiple sources integrated and executed output |
|
|
Locomotion |
Repetitive coordinated contractions of several muscle groups in the limbs |
|
|
Reflexes |
Involuntary stereotyped reactions of glands or muscle stimulation - automatic responses to sensory input that occur without out intent or often even our awareness |
|
|
Spinal cord |
* cylinder of nervous tissue * arises from the brainstem at the foramen magnum of the skull * passes through vertebral canal *ends at L1 or beyond * rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves - first goes b/w skull and c1 rest goes through in vertebral foramina |
|
|
Cervical enlargement |
Nerves to upper limb |
|
|
Lumbar enlargement |
Nerves to pelvic region and lower limbs |
|
|
Cauda equina |
Bundle of nerve roots that occupy vertebral canal from L2 to S5 |
|
|
Meninges |
Three fibrous connective tissue membrane that encloses the brain and spinal cord - seperates soft tissues of central nervous system from bones of cranium and vertebral canal 3 layers * dura matter * arachnoid matter * pia matter |
|
|
Spina bifida |
* Congenital defect * one or more vertebrae fail to form a complete vertebral arch for enclosure of the spinal cord * common in limbo sacral region * folic acid prevents defect * defect happens first 4 weeks of development supplementation must begin 3 months before conception |
|
|
Gray matter |
Site of information processing synaptic integration |
|
|
White matter |
Carry signals from one part of central nervous system to another |
|
|
Ascending tracts |
Carry sensory information up the spinal cord |
|
|
Descending tracts |
Carry motor information down the spinal cord |
|
|
Decussation |
As the fibers pass up or down the brainstem and spinal cord they cross over from the left to the right side and vice versa |
|
|
Contralateral |
When the origin and destination of a tracts are on opposite sides of the body |
|
|
Ipsilateral |
When the origin and destination of the tract are on the same side of the body does not cross |
|
|
Sensory signals |
Travel across three neurons from origin in receptors to the destination in the sensory areas of the brain |
|
|
First order neuron |
Detect stimulus and transmit the signal to spinal cord of the brainstem |
|
|
Second order neurons |
Continues to the thalamus at the upper end of the brainstem |
|
|
Third order neurons |
Carries the signal the rest of the way to the sensory region of the cerebral cortex |
|
|
Gracile fasciculus |
* carries signals from mod thoracic and lower parts of the body * below T6 * carries signals for vibration visceral pain deep and discrimative touch and proprioception from lower limbs and lower trunk |
|
|
Proprioception |
Nonvisual sense of the position and movements of the body |
|
|
Cuneate fasciculus |
* originates T6 and up upper - chest and limb * ends in cuneate nucleus on ipsilateral side of the medulla oblongata * occupies lateral portion of posterior column * Carry signals to contralateral cerebral hemisphere |
|
|
Spinothalamic tract |
* passes up the anterior and lateral columns of the spinal cord * ends in posterior horn of spinal cord * Carry signals for pain pressure temperature light touch tickle and itch * sends signals to the contralateral cerebral hemisphere |
|
|
Spinoreticular tract |
Carries pain signal resulted from tissue injury |
|
|
Spinocerebullar tract |
Travel through lateral column * Carry proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk up to the cerebellum |
|
|
Upper motor neuron |
In cerebral cortex |
|
|
Lower motor neuron |
In spinal cord |
|
|
Corticospinal tracts |
* from cerebral cortex for precise finely coordinated limb movements *decussate in lower medulla * lateral corticospinal tract on contralateral side of spinal cord |
|
|
Pyramids |
Ridges on anterior surface of medulla oblongata formed from fibers of this system |
|
|
Spinal nerves |
31 pairs * 8 cervical nerves * 12 thoracic nerves * 5 lumbar nerves * 5 sacral nerves * 1 coccygeal nerves |
|
|
Nerve |
A cord like organ composed of numerous nerve fibers (axons) bound together by connective tissue |
|
|
Mixed nerves |
Contain both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) fibers * conduct signals in two directions |
|
|
Poliomielitis |
* Caused by poliovirus * Virus spread by fecal contamination of water * Destroys motor neurons in brainstem and anterior horn of spinal cord * Signs of polio muscle pain, weakness and loss of some reflex |
|
|
Als |
* destruction of motor neurons and muscular atrophy * weakness difficulty speaking swallowing use of hands |
|
|
Sensory (afferent) neurons |
Carrys signal from sensory receptors to cns |
|
|
Motor efferent nerves |
Carry signals from cns yo muscles and glands |
|
|
Nerve plexus |
No thoracic plexus |
|
|
Cervical plexus C1-C5 |
*In neck *Supplies neck and phenix nerve to the diaphragm |
|
|
Brachial Plexus C5-T1 |
Near the shoulder * median nerve carpal tunnel syndrome |
|
|
Lumbar plexus L1-L4 |
In lower back -supplies abdominal wall, anterior thigh, genitalia |
|
|
Coccygeal plexus S4,S5,and Co |
, |
|
|
Somatosensory |
Carry sensory signals from bones,joints,muscles,and the skin |
|
|
Proprioception |
Brain receives information about body position and movements from nerve endings in muscles, tendons, and joints |
|
|
Chickenpox |
-caused by varciella-zoster virus - virus remains for life in the posterior toot ganglion |
|
|
Shingles |
Localized disease caused by the virus traveling down th sensory nerves by fast axonal transport when immune system is compromised - common after age of 50 - usually in chest and waist on one side of the body - childhood chickenpox vaccinations reducer the risk of shingles later in life |
|
|
Sciatic nerve injury |
- Sciatica : sharp pain that travels from gluteal region along the posterior side of thigh and leg to ankle - 90% cases result from herniated intervertebral disc or osteoporosis of lower spine |
|
|
Dermatone |
A specific area of the skin that receives sensory input from a pair of spinal nerves |
|
|
The nature of reflex |
- Reflexes require stimulation - Reflexes are quick - Reflexes are involuntary - Reflexes are stereotyped * they occur the same way everytime |
|
|
Somatic Reflexes |
Since they involve the somatic nervous system |
|
|
Reflexes |
Include the glandular secretion and contraction of all three types of muscle - include some learned responses : conditioned reflexes * we are dealing w/ unlearned skeletal muscle reflexes mediated by the brainstem and spinal cord |
|
|
Somatic receptors |
In skin, muscles, or tendons |
|
|
Afferent nerve fibers |
Carry information from receptors to posterior horn of spinal cord or brainstem |
|
|
Integrating center |
A point of synaptic contact b/w neurons in gray matter of spinal cord or brainstem - determines whether efferent neurons issue signal to muscles |
|
|
Efferent nerve fibers |
Carry motor impulses to skeletal muscles |
|
|
Effectors |
The somatic effectors carry out the response |
|
|
Spinal cord trauma |
-Males 16-30 highest risk group -US 10,000 to 12,000 paralyzed by spinal cord trauma each year - 55% occur in automobile or motorcycle accidents -Usually by vertebral fracture |
|
|
Babinski sign |
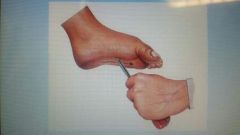
|
|
|
Paraplegia |
Paralysis of both lower limbs |
|
|
Quadriplegia |
Paralysis of all four limbs |
|
|
Hemiplegia |
Paralysis of half of the body |
|
|
Paresis |
Partial paralysis or weakness of the limbs |
|
|
Complete transection |
Complete severance of cord - immediate loss of motor control below level of injury - above C4 Poses the threat of respiratory failure -Spinal shock |
|
|
Sacral plexus L4,L5,S1-S4 |
In the pelvis * Supplies remainder of lower trunk and lower limb |

