![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Autotroph |
"Self Feeder" Sustaining oneself without eating anything derived from other living beings Producers of the biosphere |
|
|
Photoautotroph |
Organisms that use light as a source of energy to synthesize organic substances. |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
The process of converting light energy from the sun to chemical energy that is stored in sugar and other organic molecules. |
|
|
Heterotroph |
"Other Feeding" Live on compound produced by other organisms Consumers of the biosphere |
|
|
The major site of photosynthesis in most plants |
Leaves |
|
|
Carbon dioxide enters the leaf, and oxygen exits, by way of microscopic pores called? |
Stomata (singular, stoma) |
|
|
Dense fluid that surrounds the thyloakoids? |
Stroma |
|
|
Organelles responsible for photosynthesis? |
Chloroplasts |
|
|
Chloroplasts are found mainly in the cells of the |
Mesophyll |
|
|
Stacks of thylakoid sacs are called? |
Grana (singular, granum) |
|
|
Pigment that gives leaves their color |
Chlorophyll |
|
|
Chlorophyll resides in? |
The thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts |
|
|
Sacs that segregate the stroma from the space within? |
Thylakoids |
|
|
Chemical equation of photosynthesis |
6 CO2 + 12 H2O + Light Energy -> C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O |
|
|
Fates of all atoms in photosynthesis |

|
|
|
Is photosynthesis an exergonic or endergonic reaction? |
Endergonic |
|
|
During photosynthesis, which atoms are reduced and which are oxidized? |
The 6 CO2 are reduced to C6H12O6 The 6 H2O are oxidized to 6 O2 |
|
|
The two stages of photosynthesis are? |
Light reactions (photo part) and the Calvin cycle (synthesis part) |
|
|
What occurs during the light rections of photosynthesis? |
Solar energy is converted to chemical energy H2O is split, O2 is released as a byproduct NADP+ is reduced to NADPH ATP is generated |
|
|
Photophosphorylation |
Light reactions that generate ATP using chemiosmosis to power the addition of a phosphate group to ADP |
|
|
Carbon fixation |
The incorporation of CO2 from the air into organic molecules already present in the chloroplast |
|
|
What occurs during the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis? |
CO2 from the air is incorporated into organic molecules already present in the chloroplast (carbon fixation) Fixed carbon is reduced to carbohydrate (by NADPH, powered by ATP, from the light reactions) |
|
|
Where do light reactions take place? |
The thylakoids |
|
|
Where does the Calvin cycle take place? |
The stroma |
|
|
Which phase produces sugar, the Calvin cycle or the light phases? |
Calvin cycle |
|
|
What type of energy is light? |
Electromagnetic energy |
|
|
Wavelength |
The distance between the crests of electromagnetic waves |
|
|
Electromagnetic spectrum |
The entire range of radiation |
|
|
Visible light |
Radiation that can be deteced as visible colors by the human eye (Segment most important to life) |
|
|
Photons |
Discrete particles Not tangible objects, but they act like objects in that each of them has a fixed quantity of energy. |
|
|
Shorter wavelengths have ____________ energy Longer wavelengths have _____________ energy |
Higher Lower |
|
|
Pigments |
Subtances that absorb light |
|
|
The color that we see is the _______ color |
that is reflected or transmitted (not absorbed) |
|
|
Absorption of all color |
Black |
|
|
Spectrophotometer |
A machine that directs beams of light of different wavelengths through a solution of a pigment and measures the fraction of the light transmitted at each wavelength. |
|
|
Absorption spectrum |
A graph plotting a pigment's light absorption versus wavelength |
|
|
The key light-capturing pigment that participates directly in the light reactions |
Chlorophyll a |
|
|
Action spectrum |
Prepared by illuminating chloroplasts with light of different colors and then plotting wavelength against some measure of photosynthetic rate, such as CO2 consumption or O2 release. |
|
|
Carotenoids |
Hydrocarbons that are various shades of yellow and orange. Responsible for photoprotection: these compounds absorb and dissipate excessive light energy that would otherwise damage chlorophyll or interact with oxygen, forming reactive oxidative molecules that are dangerous to the cell. |
|
|
Explain the isolation of isolated chlorophyll by light |
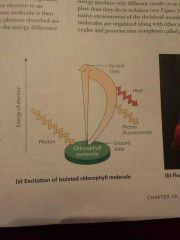
|
|
|
In their native environment of the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll molecules are organized along with other small organic molecules and proteins into complexes composed of a reaction-center complex surrounded by several light-harvesting complexes called? |
Photosystems |
|
|
Reaction-center |
An organized association of proteins holding a special pair of chlorphyll a molecules |
|
|
Light-harvesting complex |
Consists of various pigment molecules bound to proteins |
|
|
Primary electron receptor |
A molecule capable of accepting electrons and becoming reduced |
|
|
Which occurs first Photosystem I or Photosystem II? |
Photosystem II |
|
|
The reaction-center of chlorophyll a of photosystem II is known as what? Why? |
P680 This pigment is best at absorbing light having a wavelength of 680 nm |
|
|
The reaction-center of chlorophyll a of photosystem I is known as what? Why? |
P700 This pigment is best at absorbing light having a wavelength of 700nm |
|
|
Linear electron flow |
A flow of electrons through the photosystems and other molecular components built into the thylakoid membrane |
|
|
Strongest biological oxidizing agent known? |
P680+ |
|
|
Photosystem II generates? Photosystem I generate? |
ATP NADPH |
|
|
Cyclic electron flow |
An alternative path in which photoexcited electrons use photosystem I but not photosystem II |
|
|
Chloroplasts and mitochondia generate ATP by |
chemiosmosis |
|
|
What type of reaction is the Calvin cylce? |
Anabolic |
|
|
Carbohydrate produced directly from the Calvin cycle? |
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) |
|
|
What are the 3 stages of the Calvin cycle? |
Carbon fixation Reduction Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor |
|
|
The most abundant protein in chloroplasts (and thought to be the most abundant protein on Earth)? |
Rubisco [ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) carboxylase-oxygenase |
|
|
For the net synthesis of one molecule of G3P, the Calvin cycle consumes? |
3 CO2 9 ATP 6 NADPH |
|
|
2 molecules of G3P = |
Glucose |
|
|
C3 plants |
Initial fixation of carbon occurs via rubisco |
|
|
Photorespiration |
When a plant uses O2 and light to make CO2 |
|
|
Photorespiration is a seemingly wasteful process because |
It consumes ATP, instead of generating it (as in cellular respiration) It produces no sugar (actually decreases photosynthetic output |
|
|
Two most important photosynthetic adaptations? |
C4 photosynthesis crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) |
|
|
C4 plants |
Preface the calvin cycle with an alternative mode of carbon fixation that forms a four-carbon compound as its first product |
|
|
Two distinct types of photosynthetic cells in C4 photosynthesis? |
bundle-sheath cells mesophyll cells |
|
|
Bundle-sheath cells |
Arranged into tightly packed sheaths around the veins of the leaf |
|
|
PEP carboxylase is only found where? |
Mesophyll cells |
|
|
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) |
Stomata closed during the day and open at night. At night plants take up CO2 and incorporate it into a variety of organic acids. |
|
|
Overall process of photosynthesis |
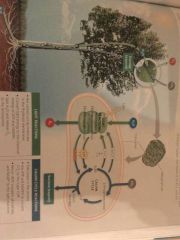
|
|
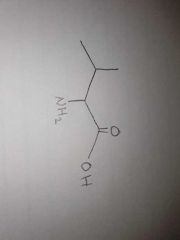
Name? Polarity? Configuration? Aromaticity? 3-Letter 1-Letter |
Valine Nonpolar (S) , L- Non aromatic Val V Strongly hydrophobic (long alkyl side chain) |

