![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Motivation refers to |
the process that leads people to behave the way they do. It occurs when a need is aroused
|
|
|
The Motivation Process (in order)
|
Unfufilled needs/wants/desires-->Tension-->Drive-->Goal or Need fulfillment (tension reduction is tension & drive)
|
|
|
Motivation is
|
the reason for behavior.
|
|
|
A motive is
|
why an individual does something.
|
|
|
Motive definition
|
Motive is a construct representing an unobservable inner force that stimulates & compels a behavorial response & provides specific direction to that response
|
|
|
Need is the same as
|
Motivation
|
|
|
When you feel a gap btwn a desired state & your actual current state, |
a need is recognized & experienced as a drive state referred to as motivation |
|
|
2 kinds of needs |
Biogenic needs: food, water, air, shelter Psychogenic needs: Status, power, affiliation |
|
|
Two useful motivation theories: |
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs and McGuire's Psychological Motives |
|
|
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs |
A macro theory designed to account for most human behavior in general terms |
|
|
Maslow's Levels (5) |
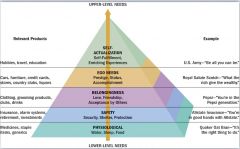
|
|
|
Maslow 1st bottom level, products, example |
Physiological (water sleep food). Medicines, staple items, generics. Quaker Oat Brand: "It's the right thing to do" |
|
|
Maslow 2nd bottom level, products, example |
Safety (security, shelter, protection). Insurance, alarm systems, retirement, investments. AllState-"You're in good hands with Allstate"
|
|
|
Maslow 3rd level middle, products, example |
Belongingness(love, friendship, acceptance by others). Clothing, grooming products, clubs, drinks. "You're in the Pepsi generation"
|
|
|
Maslow 4th top level, products, example |
Ego Needs (Prestige, Status, Accomplishment). Cars, furniture, credit cards, stores, country clubs, liquors. "What the rich give the wealthy" - scotch brand
|
|
|
Maslow 5th top level, products, example |
Self-Actualization (self-fulfillment, enriching experiences). Hobbies, travel, education. U.S Army "Be all that you can be." |
|
|
Burger Kind ad in Maslow |
Physio |
|
|
Pepsi " New generation " ad Maslow |
Belongingness |
|
|
Car ad with Logan and Swat guy: maslow |
Safety |
|
|
Rolex ad Maslow |
Ego Needs |
|
|
Nike Winning never Grows Old Maslow: |
Self Actualization |
|
|
Why people join bicycle club? I had a heart attack a few years ago, and I was told by my doctors that I really needed to step up the amount of exercise that I get-my life depend on this club. Need level? |
Physiological need |
|
|
Why people join bicycle club? I find that I learn so much from others in the club. It is really important to me to keep learning and growing in all parts of my life-including cycling. Need level? |
Self-actualization |
|
|
Why people join bicycle club? I have been cycling for a long time, and I have become quite accomplished at it. I wanted to be around other people who could fully appreciate my skill level. Need level? |
Ego needs |
|
|
Why people join bicycle club? I heard about this club and thought that it would be a great way to meet people. |
Social/Belongingness |
|
|
I used to bike alone, but I had too many close calls, where a driver didn’t see me and almost hit me. I decided it would be smarter to join a club so that I would be cycling in a large group and be more visible. Need level? |
Safety |
|
|
McGuire’s Psychological Motives |
A fairly detailed set of motives used to |
|
|
McGuire’s Psychological Motives (4) |
Need for Achievement Need for Affiliation Need for Power Need for Uniqueness |
|
|
Mcguire: Need for Achievement
|
Value personal accomplishment |
|
|
Mcguire: Need for affiliation |
Want to be with other people |
|
|
Mcguire: Need for power |
Control one’s environment |
|
|
Mcguire: Need for uniqueness |
Assert one’s individual identity |
|
|
McGuire: United Colors of Benetton Ad |
Appeal to affiliation need |
|
|
McGuire: Mercedes-Benz ad "She was riding wheels of steel before she had a learner's permit"
|
Need for achievement (important to them are power, accomplishment, and esteem) |
|
|
Personality is |
a person's unique psychological makeup and how it consistently influences the way a person responds to his/her environment. |
|
|
Nature of personality |
✽ Personality reflects individual |
|
|
Personality is also an |
individual's characteristic response tendencies across similar situations. |
|
|
Freudian Theory |
Id: primitive drives |
|
|
Multitrait approach |
Five-factor model: identifies 5 basic traits formed by genetics & early learning. These core traits interact & manifest themselves in behaviors triggered by situations. -the most commonly used by marketers |
|
|
Name the 5 traits of the 5 factor Model |
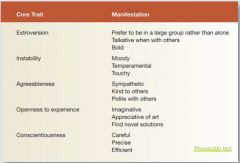
Extroversion, Instability (Neuroticism), Agreeableness, Openness to experience, Conscientiousness
|
|
|
Advatanges of 5factorModel/Multitrait approach |
the broad picture it allows of the determinants of behavior. Useful in understanding bargaining + complaining behavior and compulsive shipping. May have validity across cultures. |
|
|
Single-Trait Approach |
emphasize ONE personality trait as being particularly relevant to understanding a particular set of behaviors. |
|
|
Single Trait Approach Advantage |
While they do not suggest that other traits don't matter, they study a SINGLE trait for its RELEVANCE to a set of behaviors. (consumption-related behaviors) |
|
|
Single Trait Approach relevance |
those dealing w/ vanity, trait anxiety, sensation seeking, compulsive buying, materialism, affect intensity, self monitoring. |
|
|
Personality Trait: Consumer Ethnocentrism |
an individual difference in consumers’ |
|
|
Personality Trait: Need for Cognition (NFC) |
an individual difference in consumers’ |
|
|
Use of personality in consumer behavior |
-sometimes consumers choose products that fit their personality (homer and beer. -other times, consumers use products to bolster an area of their personality where the feel weak (Bart and a bright car) |
|
|
Brand image |
what people think of and feel when -However, A particular type of image that some brands acquire is brand personality. |
|
|
Brand personality |
-a set of human characteristics that
|
|
|
Consumers perceive brand personalities in terms of 5 basic dimensions, each with several facets: |
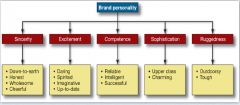
Sincerity Excitement Competence Sophistication Ruggedness
|
|
|
Communicating brand personality: 1 |
Celebrity Endorsers - Nike & Serena Williams - edgy, individualistic brand |
|
|
Communicating brand personality: 2 |
User Imagery - mountain Dew-features young, active users engaged in fun & exciting activities. |
|
|
Communicating brand personality: 3 |
Executional factors - "how" core of message is communicated. Geico - gecko accent |
|
|
Process of Emotion |
Emotion--> Drive --> Goal fulfillment |
|
|
Emotion |
|
|
|
Emotions are |
strong, relatively |
|
|
Examples of emotion |
✽ Lust, love |
|
|
Characteristics of emotion 1 |
✽ They are strongly linked to needs, motivation, |
|
|
Characteristics of emotion 2 |
|
|
|
Characteristics of emotion 3 |
✽ Personality also plays a role, e.g., some people |
|
|
Emotion & Ads |
Emotional content in ads can enhance |

