![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What chemicals that affect physiology in any manner? |
Drugs |
|
|
What drugs that act against diseases? |
Chemotherapeutic Agents |
|
|
What drugs that treat infections? |
Antimicrobial Agents |
|
|
In The History of Antimicrobial Agents, who proposed the term “chemotherapy”? |
Paul Ehrlich |
|
|
What is a chemical that selectively kill the pathogens while having little or no effect on a patient? |
Chemotherapy |
|
|
What arsenic compound that killed trypanosomes and another that worked against treponemes? |
“Magic Bullets” |
|
|
Who coined Penicillin released from Penicillium and Antibiotics? |
Alexander Fleming |
|
|
What is an antimicrobial agents produced naturally by organisms? |
Antibiotics |
|
|
Who coined Sulfanilamide? |
Gerhard Domagk |
|
|
What is the first antimicrobial agent used to treat wide array of infections? |
Sulfanilamide |
|
|
Semisynthetics and synthetics |
Gerhard Domagk |
|
|
In the Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Action, key is _____. |
Selective Toxicity |
|
|
What constitute largest number and diversity of antimicrobial agents? Fewer drugs to treat eukaryotic infections. Even fewer antiviral drugs. |
Antibacterial Drugs |
|
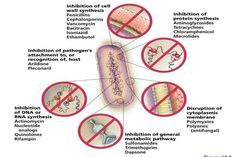
|
Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Action |
|
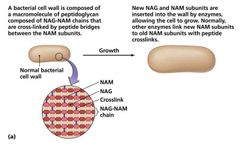
|
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis |
|
|
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis |
|
|
In the Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis, most common agents act by preventing cross-linkage of _______. |
NAM subunits |
|
|
In the Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis, what is the most prominent in this group and—functional groups are beta-lactam rings? |
beta-lactams |
|
|
What bind to enzymes that cross-link NAM subunits. Bacteria have weakened cell walls and eventually lyse? |
Beta-lactams |
|
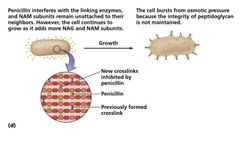
|
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis |
|
|
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis |
|
|
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis: • more stable in acidic environments • more readily absorbed • less susceptible to deactivation• more active against more types of bacteria |
Semisynthetic derivatives of beta-lactams |
|
|
What is an effective only against aerobic Gram-negatives? |
Simplest beta-lactams |
|
|
What is an effective only against aerobic Gram-negatives? |
Simplest beta-lactams |
|
|
What interfere with particular alanine-alanine bridges that link NAM subunits in many Gram-positives? |
Vancomycin and Cycloserine |
|
|
What blocks secretion of NAG and NAM from cytoplasm? |
Bacitracin |
|
|
What disrupt formation of `arabinogalactan-mycolic acid in mycobacterial species? |
Isoniazid and Ethambutol |
|
|
▪ prevent bacteria from increasing amount of peptidoglycan ▪ have no effect on existing peptidoglycan layer ▪ effective only for growing cells ▪ no effect on plant or animal cells; no peptidoglycan |
Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis |
|
|
In the Inhibition of Protein Synthesis, Prokaryotic ribosomes are _____. |
70S (30S and 50S) |
|
|
In the Inhibition of Protein Synthesis, Eukaryotic ribosomes are _____. |
80S (40S and 60S) |
|
|
Drugs can selectively target translation. Mitochondria of animals and humans contain ______; can be harmful. |
70S ribosomes |
|
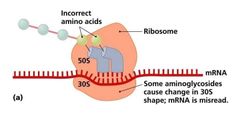
|
Inhibition of Protein Synthesis |
|
|
Some drugs become incorporated into cytoplasmic membrane and damage its integrity. |
In the Disruption of Cytoplasmic Membranes |
|
|
What attaches to ergosterol found in fungal membranes. Humans somewhat susceptible because cholesterol similar to ergosterol? |
Amphotericin B (polyene) |
|
|
Bacteria lack _____; not susceptible. |
Sterols |
|
|
What inhibit ergosterol synthesis? |
Azoles and Allyamines |
|
|
What disrupts cytoplasmic membranes of Gramnegatives; toxic to human kidneys. Some parasitic drugs act against cytoplasmic membrane? |
Polymyxin |
|
Disruption of Cytoplasmic Membranes |
Amphotericin |
|
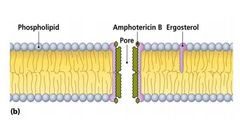
|
Disruption of Cytoplasmic Membranes |
|
|
In the Inhibition of Metabolic Pathways, when differences exist between metabolic processes of pathogen and host, _________ can be effective. |
Antimetabolic Agents |
|
|
What interfere with the metabolism of malaria parasites? |
Quinolones |
|
|
What inactivate enzymes? |
Heavy metals |
|
|
What disrupt tubulin polymerization and glucose uptake by many protozoa and parasitic worms? |
Agents |
|
|
What block activation of viruses. Metabolic antagonists? |
Drugs |
|
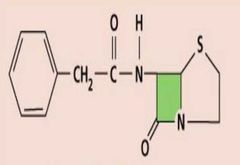
|
Pencilin G (natural) |
|
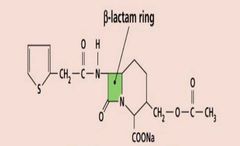
|
Cephalothin (semisynthetic) |
|
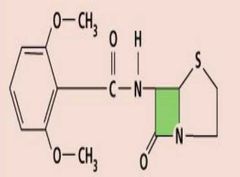
|
Methicillin (semisynthetic) |
|
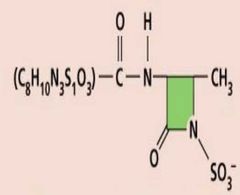
|
Aztreonam (semisynthetic) |
|
|
What are the 2 Penicillins? |
Penicillin G (natural) and Methicillin (semisynthetic) |
|
|
Cephalosporin |
Cephalothin (semisynthetic) |
|
|
Monobactam |
Aztreonam (semisynthetic) |
|
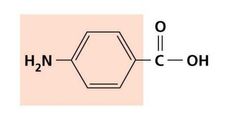
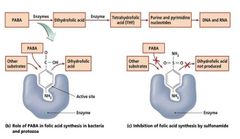
Inhibition of Metabolic Pathways |
PABA |
|
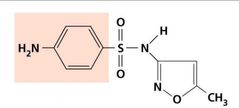
Inhibition of Metabolic Pathways |
Sulfamethoxazole |
|
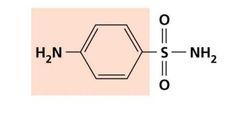
Inhibition of Metabolic Pathways |
Sulfanilamide |
|
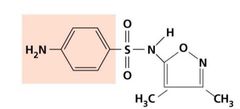
Inhibition of Metabolic Pathways |
Sulfisoxazole |
|
|
Inhibition of Metabolic Pathways |
|
|
What binds to enzyme involved in conversion of dihydrofolic acid to THF? |
Trimethoprim |
|
|
Humans obtain ______; metabolism unaffected. |
Folic acid |
|
|
What can target unique aspects of viral metabolism? |
Antiviral agents |
|
|
What neutralize acidity of phagolysosome and prevent viral uncoating? |
Amantadine, rimantadine, and weak organic bases |
|
|
What neutralize acidity of phagolysosome and prevent viral uncoating? |
Amantadine, rimantadine, and weak organic bases |
|
|
What function by blocking DNA replication or mRNA transcription? |
Several drugs |
|
|
Only slight differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA; drugs often affect both types of cells. Not normally used to treat infections; used in research and perhaps to slow cancer cell replication. |
Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis |
|
|
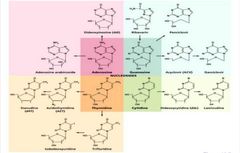
Compounds can interfere with function of nucleic acids (________). |
Nucleotide Analogs |
|
|
________ of nucleic acid molecules and prevent further replication, transcription, or translation. |
Distorted shapes |
|
|
Most often used against viruses;__________ more likely to incorporate and viral nucleic acid synthesis more rapid than that in host cells. Also effective against rapidly dividing cancer cells |
Viral DNA polymerases |
|
|
Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis |
|
|
In the Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis, what act against prokaryotic DNA gyrase; little effect on eukaryotes or viruses? |
Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones |
|
|
Other drugs bind to and inhibit action of RNA polymerase during transcription; |
rifampin |
|
|
What are the 6 Ideal Antimicrobial Agent? |
• Readily available• Inexpensive • Chemically stable• Easily administered• Nontoxic and nonallergenic• Selectively toxic against wide range of pathogens |
|
|
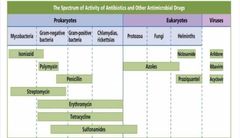
▪ Spectrum of action▪ Efficacy Dosages required to be effective Routes of administration Overall safety▪ Side effect |
Evaluation of Antimicrobial |
|
|
Spectrum of Action |
|
|
What may allow for secondary or superinfections to develop? |
Broad-spectrum Antimicrobials |
|
|
What may allow for secondary or superinfections to develop? |
Broad-spectrum Antimicrobials |
|
|
Killing of _______ reduces microbial antagonism. |
normal flora |
|
|
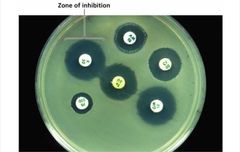
Ascertained by• Diffusion susceptibility tests• Minimum inhibitory concentration test• Minimum bactericidal concentration test |
Efficacy |
|
|
Diffusion Susceptibility Test |
|

|
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Test |
|

|
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Test |
|
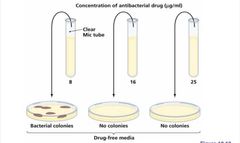
|
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MIC) Test |
|
|
Routes of Administration |
|
|
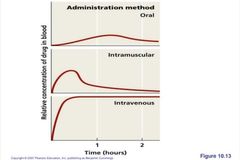
What are the 4 Routes of Administration? |
• Tropical • Oral • Intramuscular • Intravenous |
|
|
What is the application of drug if infection is external? |
Topical |
|
|
What is the simplest; lower drug concentrations; no reliance on health care provider; patients do not always follow prescribing information? |
Oral |
|
|
What requires needle for administration; concentration never as high as IV administration? |
Intramuscular |
|
|
What requires needle or catheter; drug concentration diminishes as liver and kidneys remove drug from circulation. A must know how antimicrobial agent will be distributed to infected tissues? |
Intravenous |
|
|
In the Safety and Side Effects, what are the 3 main categories of side effects? |
1. Toxicity 2. Allergies3. Disruption of normal microbiota |
|
|
Exact cause of many adverse reactions poorly understood. Drugs may be toxic to kidneys, liver, or nerves. Considerations needed when prescribing drugs to pregnant women. |
Toxicity |
|
|
Although allergic reactions are rare, they may be life threatening. Anaphylactic shock |
Allergies |
|
|
May result in secondary infections Overgrowth of normal flora – superinfections. One of the greatest concern for hospitalized patients. |
Disruption of Normal Microbiota |
|
|
Overgrowth of normal flora. |
Superinfections |
|
|
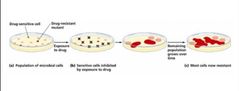
In The Development of Resistant Organisms in Populations, some are naturally partially or completely resistant. Resistance by bacteria acquired in 2 ways, what are those? |
• New mutations of chromosomal genes • Acquisition of R-plasmids via transformation, transduction, and conjugation |
|
|
The Development of Resistant Organisms in Populations |
|
|
In Multiple Resistance and Cross Resistance. Pathogen can acquire resistance to more than one drug at a time. Common when _______ exchanged. |
R-plasmids |
|
|
Develop in hospitals and nursing homes; constant use of drugs eliminates sensitive cells. |
Superbugs and Cross resistance |
|
|
High concentrations of drug maintained in patient for long enough time to kill all sensitive cells and inhibit others long enough for immune system to destroy. Limit use of antimicrobials to necessary cases. |
In Retarding Resistance |
|
|
Use antimicrobial agents in combination; |
synergism vs. antagonism |
|
|
Development of new variations of existing drugs (novel side chains added to original molecule). |
• Second-generation drugs • Third-generation drugs |

