![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Physiology
|
How the body functions
|
|
|
Anatomy
|
Study of the body structure
|
|
|
Protection support and movement
|
Integumentary system, skeletal system, The muscular system
|
|
|
Coordination and control
|
The nervous system the endocrine system
|
|
|
Circulation and immunity
|
The cardiovascular system the lymphatic system the respiratory system the digestive system the urinary system
|
|
|
Production of offspring
|
The reproductive system
|
|
|
The nervous system
|
The brain and spinal cord and the nerves make up the nervous system
|
|
|
The endocrine system
|
The endocrine system produces special substances called hormones which regulate such body activities as growth nutrient utilization and reproduction
|
|
|
The cardiovascular system
|
The heart and blood vessels make up the system that pumps blood to all the body tissues bringing with in nutrients oxygen and other needed subsistence
|
|
|
The lymphatic system
|
Lymphatic vessels assistant circulation by returning fluids from the tissues to the blood vatic organs such as tonsils ,thyroid glad and spleen play a role in immunity protecting and disease
|
|
|
The respiratory system
|
The system takes it and air and conducts it to the areas in the lungs design for gas exchange
|
|
|
The digestive system
|
The digestive system components of all organs that are involved with taking in nutrients controverting them into form that body cells can use and absorbing them into circulation organs of the digestive system include the mouth esophagus stomach small large intestine liver gallbladder pancreas
|
|
|
The urinary system
|
The chief purpose of the inner system is the rid body of waste products and Excess water this system main components are the kidneys ureters the bladder and urethra
|
|
|
Catabolism
|
When substances are broken down
|
|
|
Anabolism
|
Simple compounds are used to manufacture materials needed for growth tissue repair
|
|
|
Adenosine triphosphate
|
Energy obtained from the breakdown of nutrients is used to form a compound often described as the cells energy currency
|
|
|
Homeostasis
|
Steady-state within the organisms
|
|
|
Extracellular
|
Body fluid outside the cells
|
|
|
Intracellular fluid
|
Fluid within the cells
|
|
|
Negative feedback
|
The main method for maintaining homeostasis is negative feedback they control system based on information returning to the source
|
|
|
Anatomic position
|
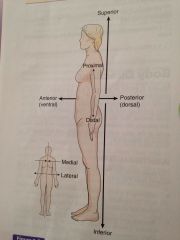
In this posture the subject is standing upright with face front arms at sides with palms forward and feet parallel
|
|
|
Superior
|
Above or higher
|
|
|
Anterior and ventral
|
Located toward the belly surface or the front of the body
|
|
|
Posterior and dorsal
|
Refer to locations near the back
|
|
|
Medial
|
An imaginary plane that passes through the midline of the body dividing it into left and right portions
|
|
|
Lateral
|
Away from midline towards the sides
|
|
|
Proximal
|
Means near to the origin of the structure
|
|
|
Distal
|
Means farther from the point
|
|
|
Frontal plane
|
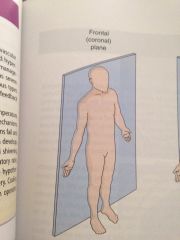
The CUT were made in line with the ears and down the middle of the body
|
|
|
Sagittal
|
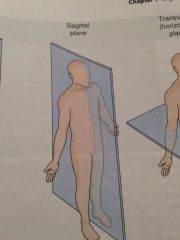
If you were to cut the body in two from front to back separating it into right and left portions sections you would have sagittal
|
|
|
Mid sagittal plane
|
They cut exactly down the midline of the body separating it into equal right to left house
|
|
|
Transverse plane
|
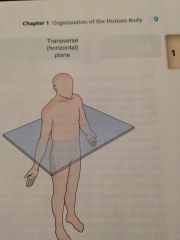
cut that is made horizontally across the two other planes divides the body into superior and inferior
|
|
|
Dorsal cavity
|
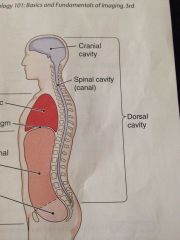
Has to subdivisions the cranial cavity containing the brain and the spinal cavity enclosing the spinal cord
|
|
|
Ventral cavity
|
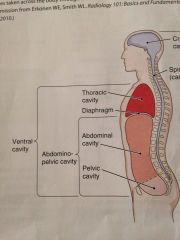
It has two main subdivisions which are separated by the diaphragm muscle use for breathing
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity
|
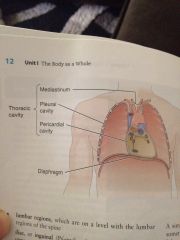
It is superior to the diaphragm. It includes the heart belongs in the large blood vessels that joint apart
|
|
|
The mediastinum
|
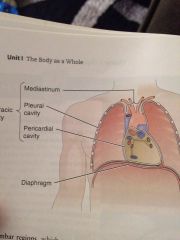
Is a space between the lungs including the organs and vessels contained in that space
|
|
|
The abdominopelvic cavity
|
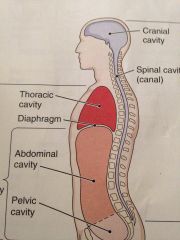
Below the diaphragm
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity
|
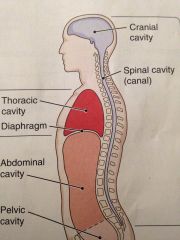
Contains the stomach most of the intestine the liver , the gallbladder the pancreas and the spleen
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity
|
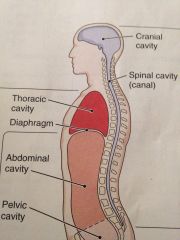
This cavity contains the urinary bladder , the rectum,the internal parts of the
Reproductive system |
|
|
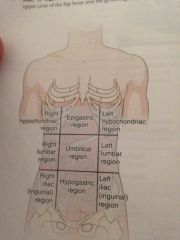
Epigastric
|
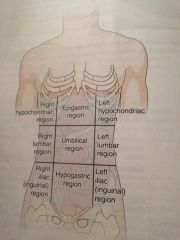
Located just inferior to the breast bone
|
|
|
Umbilical region
|
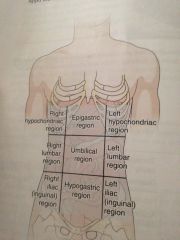
Around the navel
|
|
|
Hypo gastric region
|
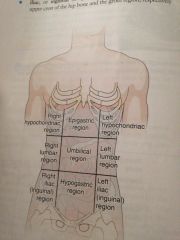
Just inferior to the ribs
|
|
|
Hypochondriac regions
|
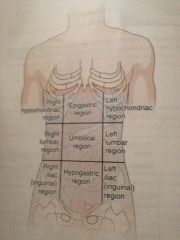
Just inferior of the ribs
|
|
|
Lumbar regions
|
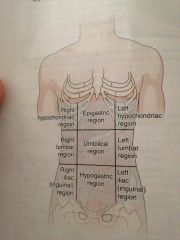
Which are on a level with the lumbar regions of the spine
|
|
|
Iliac or iguinal
|
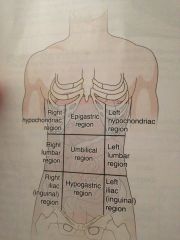
Upper crest of the hipbone and the groin region
|
|
|
Quadrants of the abdomen
|
Right and left upper quadrant
Right and left lower quadrant |
|
|
Body cavities
|
dorsal has cranial and spinal
Ventral has thoracic, abdominal regions , abdominal quadrants , pelvis |

