![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Integumentary |
Skin |
Epidermis |
|
|
Skeletal |
Bones |
Milk |
|
|
Muscular |
Muscles |
|
|
|
Respirtory |
Breathing (lungs/larnyx) |
12/min |
|
|
Reproductive |
Reproduction (uterus/penis) |
|
|
|
Nervous |
Nerves (spinal cord) |
|
|
|
Endocrine |
Hormones (thyroid) |
Puberty |
|
|
Cardiovascular |
Blood/heart |
|
|
|
Lyphatic |
Foreign substance filtration |
If you get strep throat |
|
|
Urinary |
Waste output (kidneys filter blood) |
|
|
|
Endogenous |
Endo (inside), originating internally |
|
|
|
Which 2 types of muscles are found in the muscular system? |
Cardiac and smooth |
|
|
|
What carries blood away from the heart? |
Artery |
Artery or vein |
|
|
What carries blood to the heart |
Vein |
Artery or vein |
|
|
What is normal body temp |
37 degrees celicus |
|
|
|
What is a negative feedback loop? |
Receptor (monitor), control centre (receives), effector (produces) Deviations trigger a minimizer |
RCE |
|
|
Give an example of a negative feedback loop |
Blood pressure regulation/hormone regulation/giving birth to a child |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
Existence and maintenance of a relatively constant environment Regulation of human body processes |
|
|
|
What is a positive feedback loop |
Mechanisms activate when deviation causes greater deviation |
|
|
|
Give an example of a positive feedback loop |
Labour (contractions)/bleeding/clotting |
|
|
|
Superior |
Toward head |
|
|
|
Inferior |
Away from head |
|
|
|
Anterior |
To front |
|
|
|
Posterior |
Toward back |
|
|
|
Cephalic |
In/relating to the head (superior) (towards head) |
|
|
|
Ventral |
Toward belly (front) |
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Towards back |
|
|
|
Supine |
Lying face up |
|
|
|
Prone |
Lying face down |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Nearer to center of body/point of attachment |
|
|
|
Distal |
Further from point of attachment/center of body |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Of/at/towards/from the side(s) |
|
|
|
Medial |
In/towards the middle |
|
|
|
Superficial |
Existing /occurring at /on the surface |
|
|
|
Deep |
Extending down from the top/surface |
|
|
|
Name the 4 regions of the body |
Central (head/neck/trunk) Trunk (thorax/ab/pelvis) Upper limb (shoulder to finger tip) Lower limb (thigh to toe tips) |
|
|
|
Name the 4 quadrants of the abdominals |
Right upper quad Left upper quad Right lower quad Left lower quad |
|
|
|
Name and point to the 9 abdominal subdivisions |
Right hypochondriac region (upper R) Epigastric region (upper middle) Left hypochondriac region (Upper L) Right lumbar region (R middle) Umbilical region (Middle Middle) Left lumbar region (L middle) Right iliac region (R lower) Hypogastric region (lower middle) Left iliac region (L lower) |
Epi = above Hypo = below |
|
|
Name and exhibit the 3 planes |
Frontal (coronal) - vertical front/back Sagittal (median) - vertical left/right Transverse-horizontal top/bottom |
|
|
|
Name and define the 3 types of cuts through an organ |
Longitudinal-cut along length Transverse-cut at right angle to length of organ Oblique-cut at any, but a right, angle |
|
|
|
What does the diaphragm body cavity contain? |
Divides body cavity into thoracic and abdominopelvic |
|
|
|
What does the thoracic body cavity contain |
Surrounded by ribs and diaphragm, Seperate by mediastinum |
|
|
|
What does the mediastinum body cavity contain? |
All structures of the thoracic cavity (except lungs) |
|
|
|
What is a serous membrane? |
Inner wall (visceral) and outer wall (parietal), space between is filled with serous fluid (clear and watery), reduces friction and movement |
|
|
|
Explain the balloon/membrane metaphor |
When you push your hand into a balloon, the outside of your balloon is the parietal membrane, while the part around your fist is the visceral. The space between is the serous fluid |
|
|
|
Define the 3 serous membrane lined cavaties in the thoracic cavity |
Pericardial (surrounds the heart) 2 pleural (each lung) |
|
|
|
What is the name of the serous membrane lined cavity in the abdominopelvic cavity? |
Peritoneal (surrounds many organs in the abdopelvic cavity) |
|
|
|
Define radiography, and does it use radiation? |
Shadowy negative of internal body structures, mainly bones (goes through soft tissue), ex. Pneumonia (dense fluid) Ionizing radiation |
|
|
|
Define ultrasound, and does it use radiation? |
Computer analyzed sound waves bounce off a structure in the body (baby/tumour) No radiation |
|
|
|
Define computerized tomography, and does it use radiation? |
CAT (computerized axial tomography) Computer analyzed composite of radiograph, shows slices of body X-rays in a spiral Radiation used |
|
|
|
Define dynamic spatial reconstruction, and does it use radiation? |
3D version of CT using multiple slices CT had radiation, so this does as well |
|
|
|
Define digital subtraction angiography, and does it use radiation |
Comparison of radiographs w/ and w/o dye, used in blood vessel studies (fancy angiogram) Heart/brain blockage Radiation used |
|
|
|
Define magnetic resonance imaging, and does it use radiation |
MRI Uses magnetism and radio waves to look for varying alignment of protons in soft tissues Brain/spine No radiation |
|
|
|
Define position emission tomography, and does it use radiation? |
PET scan Radioactivly enabled glucose to calculate metabolic activity of cells Hypermetabolic tissues (cells in overdrive) Gamma cameras and radiation *Cancer cells are glucose hungry* |
|
|
|
Define frontal |
Forehead |
|
|
|
Define orbital |
Eye |
|
|
|
Define nasal and oral |
Nose and mouth |
|
|
|
Define otic |
Ear |
|
|
|
Define buccal and mental |
Cheek and chin |
|
|
|
Define inguinal |
Groin |
|
|
|
Define axillary |
Armpit |
|
|
|
Define brachial |
Arm |
|
|
|
Define antecubital |
Front/inner of elbow |
|
|
|
Define antebrachial |
Forearm |
|
|
|
Define carpal |
Wrist |
|
|
|
Define manual |
Hand |
|
|
|
Define palmar |
Palm |
|
|
|
Define digital |
Fingers/toes |
|
|
|
Define coxal |
Hip |
|
|
|
Define femoral |
Thigh |
|
|
|
Define crural |
Leg |
|
|
|
Define talus |
Ankle |
|
|
|
Define dorsum |
Top of foot |
|
|
|
Define occipital |
Base of skull |
|
|
|
Define nuchal |
Back of neck |
|
|
|
Define sacral |
Between the hips |
|
|
|
Define scapular |
Shoulder blade |
|
|
|
Define vertebral |
Spinal column |
|
|
|
Define lumbar |
Loin (lower r/l side of back) |
|
|
|
Define perineal |
Perineum |
|
|
|
Define cranial |
Skull |
|
|
|
Define acromial |
Point of shoulder |
|
|
|
Define olecranon |
Point of elbow |
|
|
|
Define dorsum |
Back of hand |
|
|
|
Define popliteal |
Hollow behind knee |
|
|
|
Define sural |
Calf |
Moo |
|
|
Define plantar |
Sole |
Plantar fasciitis |
|
|
Define calcaneal |
Heel |
Achilles |
|
|
Where is the carotid artery? |
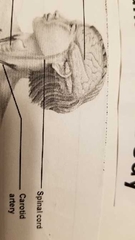
On either side of the trachea |
|
|
|
Where is the larnyx? |
Middle of the throat, voice box |
|
|
|
Where is the trachea |
Long tube that continues from the larnyx |
|
|
|
Where is the esophagus? |
Behind the larnyx |
|
|
|
Where is the aortic arch? |
Attached/above the heart |
|
|
|
Where is the liver |
R side, just under lung |
|
|
|
Where is the spleen |
L side, behind stomach, under lung, outer edge |
|
|
|
Where is the pancreas? |
Behind the stomach |
|
|
|
Where is the gallbladder? |
Under liver, middle of it |
|
|
|
What does the mediastinum consist of? |
Esophagus, trachea, blood vessels, thymus, heart |
|
|
|
What does the integumentary system do |
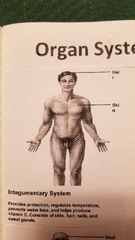
|
|
|
|
What does the muscular system do |
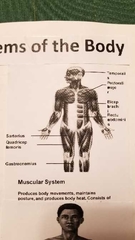
|
|
|
|
What does the skeletal system do? |
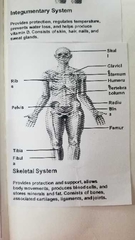
|
|
|
|
What does the male reproductive system do? |
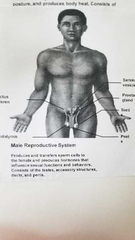
|
|
|
|
What does the female reproductive system do? |
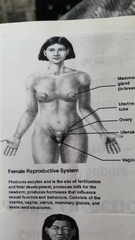
|
|
|
|
What does the endocrine system do? |
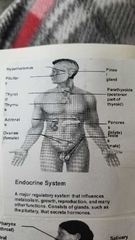
|
|
|
|
What does the Urinary System do? |
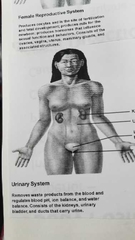
|
|
|
|
What does the digestive system do? |
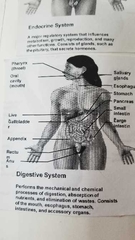
|
|
|
|
What does the respiratory system do? |
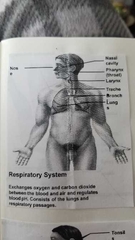
|
|
|
|
What does the cardiovascular system do? |
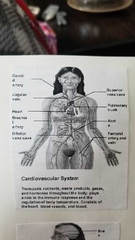
|
|
|
|
What does the lymphatic system do? |
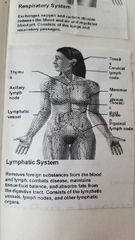
|
|
|
|
What does the nervous system do? |
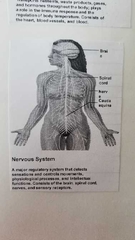
|
|

