![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Main advantage of the metric system |
Multiples of its basic units are expressed in factors of 10 using prefixes attached to the basic unit |
|
|
Work |
Product of force and the distance through which that force acts. Work= force x distance |
|
|
In the calculation of work, what unit represents force |

Kp=kilopond The effect of gravity on a mass of 1 kilogram |
|
|
Power |
How much work is accomplished per unit of time Describes the rate at which work is being performed |
|
|
Percent grade |
Amount of vertical rise per 100 units of belt travel I.g: 10% grade Diatance=10 m 10x10=100 m of the belt travel |
|

What's this calculation? |
Total amount of work output |
|
|
Power is defined as |
Work /time |
|
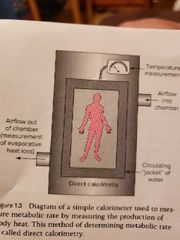
Measuring a person's metabolic rate via the measurement of heat production |
Persons body heat raises the temperature of the circulating water around the chamber Temperature change per unit of time The evaporation of water represents the heat loss from the person. And is then added to the total heat picked up by the water |
|
|
Open circuit spirometry |
Used to measure oxygen consumption |
|
|
Direct calorimetry |
Measurement of heat production as an indication of metabolic rate |
|
|
Indirect calorimetry |
Estimates metabolic rate via the measurement of oxygen consumption |
|
|
Yo |
Yo |
|

Finding metabolic rate |
Convert the vo2 max into ml first |
|
|
The capacity to convert energy expenditure into work |
Efficiency |
|
|
Steady state |

|
|

Explain |
Serves to restore normal values odd a variable to maintain homeostasis |
|

|
Responds in the same direction as the stimulus |
|
|
Gain |
Precision to which a control system maintains homeostasis. Large gain is more capable of correcting a disturbance in homeostasis. Pulmonary and cardiovascular systems are large gain systems |
|
|
The components of a negative feedback loop |
Sensor Control center Effector |
|
|
A series of interconnected connected components that maintain a chemical or physical parameter of the body near a constant value |
Biological control system |
|
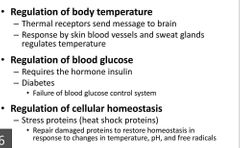
Examples of? |
Homeostatic control |
|
|
How can exercise disrupt homeostatic control |
Causes changes in ph,o2,co2, and temperature in cells |
|
|
Adaptation |
Change in the structure and function of a cell or an organ system that results in an improved ability to maintain homeostasis during stressful conditions |
|
|
The improved function of an existing homeostatic system |
Acclimation |
|
|
How does the body adapt to exercise |
Through cellular changes Cell signaling mechanisms The ability of cells to detect change in their internal environment and correctly respond |
|
|
Intracrine signaling |
Chemical messenger produced inside the cell triggers a signaling pathway within the same cell leading to a specific response |
|
|
Juxtacrine signaling |
Communication of cell to cell contact through small junctions that connect the two cell membranes |
|
|
Autocrine signaling |
Cell produces and releases a chemical messenger into the extracellular fluid that acts upon the cell producing the signal |

