![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy |
Study of structure and relationships among structures |
|
|
Physiology |
The function of body parts |
|
|
Basic life processes |
Movement, reproduction, differentiation, metabolism, growth, and responsiveness |
|
|
Histology |
Study of tissues |
|
|
Metabolism |
Break down of large complex molecules (catabolism), build up of complex molecules (anabolism) |
|
|
Responsiveness |
Ability to detect and respond to changes in internal and external environment |
|
|
Movement |
Motion of the whole body |
|
|
Growth |
Increase in size |
|
|
Differentiation |
When unspecified cells becomes specialized cells |
|
|
Reproduction |
Formation of new cells through cell division |
|
|
Prone |
Anatomical position lying face down |
|
|
Supine |
Anatomical position lying face up |
|
|
Dorsal/ posterior cavity |
Cranial and vertebral cavity |
|
|
Ventral cavity |
Thoracic cavity & abdominopelvic cavity (peritoneum cavity) |
|
|
Serous membrane |
Covers viscera and lines walls of thoracic abdomen |
|
|
Parietal layer |
Thin epithelium that lines walls of body cavities |
|
|
Visceral layer |
Thin epithelium that covers and adheres to viscera w/in body cavities |
|
|
Homeostasis |
A condition of balance in the body's internal environment |
|
|
Disorder |
Sign is measurable, objective Ex: fever, swelling |
|
|
Disease |
Symptom is subjective, differs w/ patient Ex: pain nausea |
|
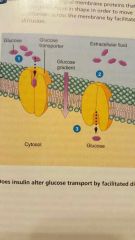
|
Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion |
|
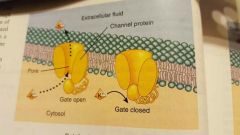
|
Channel mediated facilitated diffusion |
|
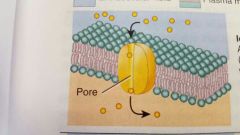
|
Ion channel Allows specific ions to move through membrane |
|
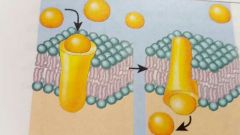
|
Carrier (transfor) Transport specific substance across membrane by changing shape |
|
|
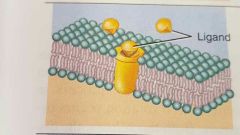
Receptor Recognize specific ligand and alter cells function in some way |
|
|
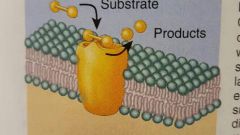
Enzyme (integral & peripheral) Catalyzes reaction inside or outside cell |
|
|
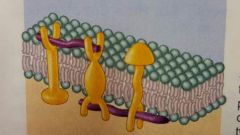
Linker (integral & peripheral) Anchors filaments inside and outside the plasma membrane for structure and shape |
|
|
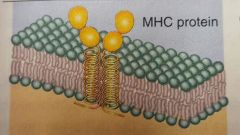
Cell identity marker (glycoprotein) Distinguishes cells |
|
|
Cytosol (intracellular fluid) |
In cytoplasm a Reactions occur |
|
|
Centrosome |
Cell division Move chromosomes |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Builds proteins Forms peptide bonds |
|
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
Has ribosomes Modifies and transports proteins |
|
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
Produces fatty acids and steroids Inactivates and detoxifies harmful substances |
|
|
Golgi complex |
To sort, modify, packages, and transports proteins |
|
|
Lysosomes (yellow) |
Digesting for cells Acidic ph |
|
|
Peroxides (grey) |
Oxidizing and removing free radicals |
|
|
Mitochondrion |
Produces ATP cellular respiration |
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center Entire structure |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Produce subunits of ribosomes |
|
|
Nuclear envelope |
Contains all DNA Layer |
|
|
Chromatin |
DNA fibers |
|
|
Integumentary |
Skin, hair, nails Protects body, regulates body temp, provides insulation |
|
|
Skeletal |
Bones, joints, cartilages Supports and protects body, aids body movement |
|
|
Muscular |
Skeletal muscle, tissue, tendon Participates in body movement, maintains posture and produces heat |
|
|
Nervous |
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, eyes, ears Generates action potentials to regulate body activities |
|
|
Endocrine |
Pineal gland, thyroid gland, hypothalamus, ovaries, testes, etc Regulates body activities by releasing hormones |
|
|
Cardiovascular |
Blood, heart, blood vessels, vein, artery Carries oxygen and nutrients to cells, defends against disease, repairs damaged blood vessels |
|
|
Lymphatic |
Thymus, thoracic duct, spleen, lymph node, tonsil, etc Returns lipids through GI tract, protects against disease |
|
|
Respiratory |
Lungs, trachea, pharynx, larynx, bronchial tubes Transfers oxygen to blood, exhale carbon dioxide, produce sound |
|
|
Digestive |
Mouth, pharynx, stomach, esophagus, small and large intestine, anus, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and salivary gland Physical and chemical break down of food, absorbs nutrients and eliminates waste |
|
|
Urinary |
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra Produces stones, and eliminates urine, helps production of red blood cells |
|
|
Reproductive |
Testicles, ovaries, uterines, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, prostate, epididymides, seminal vesicles, ductus deferences, penis Produce gametes, transport and store gametes |
|

|
Early prophase |
|

|
Mid prophase |
|

|
Late prophase |
|

|
Metaphase |
|

|
Early anaphase |
|

|
Mid anaphase |
|

|
Late anaphase |
|

|
Telophase |
|
|
Glycocalyx |
Glycoprotein and glycolipids Allows cells to recognize each other |
|
|
Phagocytosis |
Cell engulfs large solid particles |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
Engulfs tubular fluid |
|
|
Osmotic pressure |
Pressure due to nondiffusable solutes |
|
|
Hydrostatic pressure |
Pressure exerted by fluid on a membrane/wall |
|
|
Adherents junction |
Connect adjacent cells |
|
|
Tight junctions |
Water proof |
|
|
Desmosomes |
Welding |
|
|
Hemidesmosomes |
Anchor cells |
|
|
Gap junctions |
Connexion Communicate between cells |
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
Pleural cavity Pericardial cavity Mediastinum |
|
|
Transcription |
1st step In nucleus mRNA |
|
|
Translation |
2nd step In cytoplasm, needs ribosomes tRNA |
|
|
Endocytosis |
Material moves into cell via viscle |
|
|
G1 |
Organelles and cytosolic components duplicate |
|
|
S |
Replication of DNA centrosomes |
|
|
G2 |
Replication of centrosomes is complete |

