![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cell cycle
|
interphase and mitosis
|
|
|
stages of interphase
|

G1 G2 S
|
|
|
S phase
|
Cell replicates genetic material
|
|
|
G1 stage
|
cell prepares for reproduction and makes sure there's enough of everything needed to reproduce
|
|
|
G2 stage
|
Checkpoint and make sure everything is going as needed
|
|
|
CDK
|
cyclin-dependent kinase; repairs damaged cells
|
|
|
mitosis prophase
|

Nucleolus disappears chromosomes turn to chromatin centrioles begin to move towards poles spindle fibers began to spin out and connect to kinetochore
|
|
|
mitosis metaphase
|

meta-middle
|
|
|
cyclin
|
increases as the cell ages under normal conditions. It is what causes the R1 to get passed and go into mitosis
|
|
|
mitosis anaphase
|
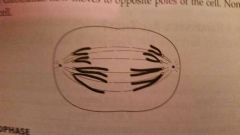
sister chromatids separate at centromere goes to poles microtubules that pulled apart chromatids shorten nonkinetichore microtubules elongated the cell
|
|
|
mitosis telophase
|

nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes nucleoli reappear
|
|
|
mitosis cytokinesis
|

splits along cleavage furrow (or cell plate in plants) to form 2 daughter cells
|
|
|
diploid cells
|
2n both sets of chromosomes (if question is asked DOUBLE THE HAPLOID NUMBER)
|
|
|
haploid cells
|
n 1 set of chromosomes (half the diploid number)
|
|
|
homologues
|

|

