![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Skeletal muscle tissue: Attaches to ____ and ____ Striated or Not Striated ? Voluntary or Involuntary? |
Attached to BONES and SKIN Striated Voluntary (conscious control) Powerful |
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle Tissue: Only in _____Striated or Not Striated ?Voluntary or Involuntary? |
Only in the heart Striated Involuntary |
|
|
|
Smooth Muscle Tissue: In the walls of ________Striated or Not Striated ?Voluntary or Involuntary? |
In the walls of hollow organs, e.g., stomach, urinary bladder, and airways. Not Striated Involuntary |
|
|
|
Excitability |
(Responsive or irritability): ability to recieve and respond to stimuli. |
|
|
|
Contractility |
Ability to shorten when stimulated |
|
|
|
Extensibility |
Ability to be stretched |
|
|
|
Elasticity |
Ability to recoil to resting length |
|
|
|
Muscle Functions |
1. Movement of bones or fluids 2. Maintaining posture and body position. 3. Stabilizing joints 4. Heat generation |
|
|
|
Each muscle is served by _____ |
Each muscle is served by one artery, one nerve, and one or more veins |
|
|
|
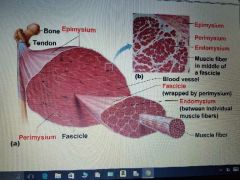
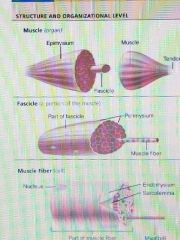
What are the Connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle ? |
Epimysium, Perimysuim, Endomysuim. |
There is three: P.E.E |
|
|
Epimysium |
Dense regular connective tissue surrounding entire muscle. |
|
|
|
Perimysuim |
Fibrous connective tissue surrounding fascicles (groups of muscle fibers) |
|
|
|
Endomysium |
Fine areolar connective tissue surrounding each muscle fiber. |
|
|
|
Know the Muscle parts. |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
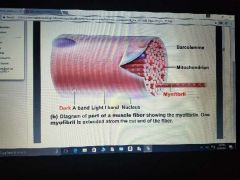
Myofibrils Three characteristics |
Densly packed, rodlike elements 80 % of cell volume Exhibits striations: perfectly aligned repeating series of a dark A bands and light I bands. |
|
|
|
Myofibril |
|
|
|
Sarcomere Three characteristics |
Smallest contractile unit (functional unit) of a muscle fiber. The region of a myofibril between two successive Z discs. Composed of thick and thin myofilaments made of contractile proteins. |
|
|
|
Thick filaments |
Run the entire length of an A band |
|
|
|
Thin filaments |
Run the length of the I band and partway into the A band. |
|
|
|
Z disc |
Coin-shaped sheet of proteins that anchors the thin filaments and connects myofibrils to one another. |
|
|
|
H zone |
Lighter midregion where filaments do not overlap. |
|
|
|
M line |
Line of protein myomesin that holds adjacent thick filaments together. |
|
|

|
Enlargements of one sarcomere |
|
|

|
Longitudinal section of filaments within one sarcomere of a myofibril |
|
|
|
Myosin tails contain |
2 interwoven, heavy polypeptide chains |
|
|
|
Myosin heads contain |
2 smaller, light polypeptide chains that act as cross bridges during contraction. Binding sites for actin of thin filaments Binding sites for ATP ATPase enzymes |
|
|
|
Insertion |
Attachment to movable bone |
|
|
|
Origin |
Attachment to immovable or less movable bone. |
|
|
|
Direct (fleshy) |
Epimysium fused to periosteum if th bone or perichondrium if cartilage. |
|
|
|
Indirect |
Connective tissue wrappings extend beyond muscle as ropelike tendon or sheetlike aponeurosis |
|
|
|
Sacolemma |
Muscle fiber plasma membrane |
|
|
|
Sacroplasm |
Muscle fiber cytoplasm |
|
|
|
Contains many glycosomes for glycogen storage as well as myoglobin for O2 storage. |
Muscle fiber |
|
|
|
Modified organelles |
Myofibril, Sacroplasmic recticulum |
|

