![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Heterotrophs
|
Obtain the chemical energy and carbon compounds they need from other organisms.
|
|
|
Primary Producers
|
An autotroph; a species that creates its own food trhough photosynthesis or from reduced inorganic compounds and that is a source of food for other species in its ecosystem.
|
|
|
Consumers
|
Organism that consumes food created by other organisms
|
|
|
Animals
|
A major lineage of eukaryotes. Typically have a complex, large, multicellular body, eat othe arganisms, and are mobile. Are a monophyletic group.
|
|
|
Body Plan
|
The basic architecture of an animal's body, including the number and arrangement of limbs, body segments, and major tissues. Early development is also studied.
|
|
|
Tissue
|
A group of similar cells that function as a unit, such as muscle tissue.
|
|
|
Parazoans
|
Literally "beside-animals"
Animals whose cells are not organized into distinct tissues (sponges) |
|
|
Eumetazoans
|
Literally "truly-among-animals"
Animals whose cells are organized into distinct tissues. (all except sponges) |
|
|
Diploblasts
|
Animals with 2 tissue layers in embryo: ectoderm + endoderm
|
|
|
Germ Layers
|
In animals, one of the 3 basic types of tissues of early embryonic development that give rise to all other tissues: endoderm, mesoderm, or ectoderm.
|
|
|
Asymmetrical
|
Having no planes of symmetry
|
|
|
Radial Symmetry
|

An animal body pattern in which there are at least 2 planes of symmetry. Typically, the body is cylindrical or disk shaped w/parts radiating from central hub.
|
|
|
Cephalization
|
Evolution of a head, or anterior region, where structures for feeding, sensing the environment, and processing info are concentrated
|
|
|
Coelom
|
An internal, usually fluid-filled, body cavity that forms within the mesoderm.
|
|
|
Acoelomates
|
Animals without body cavity (coelom)
|
|
|
Coelomates
|
Animals with body cavity (coelom)
|
|
|
Pseudocoelom
|
Literally "false-hollow"
The enclosed body cavity forms between the endoderm and mesoderm layers in embryo. |
|
|
Hydrostatic Skeleton
|
A system of body support involving fluid-filled compartments that can change in shape but cannot easily be compressed.
|
|
|
Bilateria
|
Group of orgs that are bilaterally symmetric animals with three embryonic tissue layers
|
|
|
Protostomes
|
A monophyletic group ofanimals that has a coelom, is bilaterally symmetric, shares a pattern of embryological development, including spiral cleavage, formation of the mouth earlier than the anus, and formation of the coelom by splitting of a block of mesoderm. Includes arthropods, mollusks, and annelids.
|
|
|
Deuterostomes
|
A major lineage of animals that share a pattern of embryological development, including radial cleavage, formation of the anus earlier than the mouth, and formation of the coelom by pinching off of layers of mesoderm from the gut. Includes echinoderms and chordates.
|
|
|
Cleavage
|
a rapid series of mitotic divisions that occurs in the absence of growth. Divides the egg cytoplasm. Often results in a hollow ball of cells.
|
|
|
Gastrulation
|
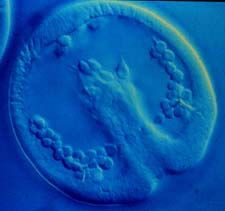
A series of cell movements that results in the formation of tissue layers
|
|
|
Sessile
|
Permanently attatched to substrate; not capable of moving to another location
|
|
|
Segmentation
|
A body plan involving division of the body into many similar segments that bear similar structures as other, nearby segments
|
|
|
Vertibrates
|
Phylum defined by presence of a skull
|
|
|
Invertibrates
|
Paraphyletic group defined as animals that are not invertibrates
|
|
|
Metamorphosis
|
Literally "between-forms"
A change in form during development. |
|
|
Filter Feeding
|
Capturing food by filtering out particles suspended in air or water
|
|
|
Foot
|
A muscular appendage of mollusks, used for movement and/or burrowing into sediment
|
|
|
Siphons
|
A tube-like appendage of many mollusks. Often used for feeding or propulsion.
|
|
|
Gill
|
Any organ in aquatic animals that exchanges gases and other dissolved substances between the bood and the surrounding water. Typically, a filamentous outgrowth of a body surface.
|
|
|
Deposite Eater
|
An organism that eats its way through substrate
|
|
|
Herbivory
|
Form of feeding that involves harvesting algae or plant tissue
|
|
|
Viviparous
|
Literally "live-bearing"
Give birth to live young |
|
|
Oviparous
|
Literally "egg-bearing"
Species that deposite fertilized eggs. |
|
|
Ovoviparous
|
Literally "egg-live-bearing"
Female retains eggs inside body during early development, but embryoes are nourished by yolk inside egg not nutrients transferred directly from mother. |
|
|
Pupa
|
Metamorphosing insect that is enclosed in a protective case.
|
|
|
Pupation
|
A developmental stage of many insects, in which the body metamorphoses from the larval form to the adult form while enclosed in a protective case.
|
|
|
Holometabolous Metamorphosis
|
Literally "whole-change"
A type of metamorphosis in which animal completely changes form. |
|
|
Hemimetabolous Metamorphosis
|
Literally "half-change"
Metamorphosis in which animal increases in size from one stage to the next but does not dramatically change body form. |

