![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
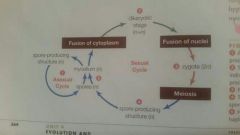
Describe the stages of the life cycle of fungi. |

|
|
|
|
Fungus with flagellated spores (zoospores) |
Chytrid |
|
|
|
Fungi that produce spores in club-shaped structures (basidiospores) during sexual reproduction. |
Club Fungi (basidiomycetes) |
Produce club-shaped fruiting bodies/basidia (basidium) |
|
|
Having two genetically distinct nuclei. |
Dikaryotic |
|
|
|
Unicellular or multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph that digests food outside the body, then absorbs the resulting breakdown products. Has chitin-containing cell walls. |
Fungus |
|
|
|
Fungus that partners with plant roots; fungal hyphae grow inside the cell walls of root cells. |
Glomeromycete |
|
|
|
Component of a fungal mycelium; a filament made made up of cells arranged end to end. |
Hypha |
|
|
|
Fungus that grows as a mass of asexually reproducing hyphae. |
Mold |
|
|
|
Mass of thredlike filaments (hyphae) that make up the body of a multicelled fungus. |
Mycelium |
|
|
|
Fungi that form spores (ascospore) in a sac-shaped structure during sexual reproduction. |
Sac Fungi (ascomycetes) |
|
|
|
Fungus that lives as a single cell. |
Yeast |
|
|
|
Fungi that live in damp places and form a thick-walled zygospore during sexual reproduction. |
Zygote Fungi (zygomycetes) |
|
|
|
Describe Life cycle of a zygote fungus |

|

|
|
|
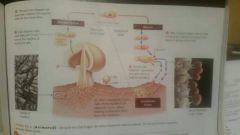
Describe the life cycle of club fungus |
|
|
|
|
Composite organism consisting of a fungus and green algae or cyanobacteria. |
Lichen |
|
|
|
Mutually beneficial partnership between a fungus and a plant root. |
Mycorrhiza |
|
|
|
Multicelled heterotroph with unwalled cells. Most ingest food and are motile during at least part of the life cycle. |
Animal |
|
|
|
Having paired structures so the right and the left halves are mirror images. |
Bilateral Symmetry |
|
|
|
Evolutionary trend toward having a concentration of nerve and sensory cells at the head end. |
Cephalization |
|
|
|
Body cavity lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. |
Coelom |
|

