![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Organism composed of many similar cells, each capable of living and reproducing on its own. |
Colonial Organism |
|
|
|
Organism composed of interdependent cells that vary in their structure and function. |
Multicellular Organism |
|
|
|
Evolution of an organelle from bacteria that entered a host cell and lived inside it. |
Primary Endosymbiosis |
All chloroplasts evolved by this process. |
|
|
Eukaryote that is not a plant, fungus or animal. |
Protist |
|
|
|
Evolution of an organelle from a protist that itself contains organelles that arose by primary endosymbiosis. |
Secondary Endosymbiosis |
|
|
|
In freshwater protists, an organelle that collects and expels excess water. |
Contractile Vacuole |
|
|
|
Flagellated protozoan with multiple mitochondria; may be heterotrophic or have chloroplasts descended from green algae. |
Euglenoid |
Structure contains an eyespot to detect light and saltier interior than surroundings. |
|
|
Protist belonging to an entirely or mostly heterotrophic lineage with no cell wall and one or more flagella. unique structure includes feeding groove and pellicle body. |
Flagellated Protozoan/Excavata |
Includes anaerobic flagellates, trypanosomes and euglenoids. |
|
|
Layer of proteins that gives shape to many unwalled, single-celled protists. |
Pellicle |
|
|
|
Parasitic flagellated Protozoan protist with a single mitochondrian and a flagellum that runs along the back of the cell. |
Trypanosomes |
Some cause sleeping sickness |
|
|
Heterotrophic single-celled protists with a porous calcium carbonate shell and long cytoplasmic extensions. |
Foraminifera |
From the super group Rhizarian. |
|
|
Community of tiny drifting or swimming organisms. |
Plankton |
|
|
|
Heterotrophic single-celled protists with a porous shell of silica and long cytoplasmic extensions. Part of the Rhizarian supergroup of protists. |
Radiolaria |
May be part of plankton. |
|
|
Light emitted by a living organism. |
Bioluminescence |
|
|
|
Single-celled, heterotrophic protist with many cilia. Part of the alveolate supergroup. |
Ciliate |
Contain macro and micronucleus and contractile vacuoles in their structure. |
|
|
Single-celled aquatic protist that moves with a whirling motion; may be heterotrophic or photosynthetic. |
Dinoflagellate |
Part of alveolate supergroup. Some species are bioluminescent. Some can create red tides in great numbers. |
|
|
Parasitic protist that reproduces in cells of its host. Part of the Alveolate protist supergroup. |
Apicomplexan |
Ex: Plasmodium (protist that causes malaria) |
|
|
Muticelled marine protist with a brown accessory pigment (fucoxanthin) in its chloroplasts. |
Brown Algae |
Part of Stramenopile supergroup |
|
|
Single-celled photosynthetic protist with a brown accessory pigment in its chloroplasts and a two part silica shell. |
Diatom |
Part of stramenopile supergroup. Store their food in the form of lipids. |
|
|
Heterotrophic protist that grows as a mesh of nutrient-absorbing filaments. some are parasites of plants or animals. Decompose dead animals and plants in fresh water. |
Water Mold |
Stramenopile |
|
|
Of land plants and some algae, a life cycle that includes haploid and diploid multi-celled bodies. |

Alternation of Generations |
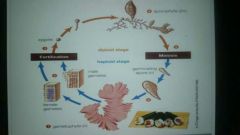
|
|
|
Gamete-producing haploid body that forms in the life cycle of land plants and some muticelled algae. |
Gametophyte |
|
|
|
Single-celled, colonial, or multicelled photosynthetic protist that has chloroplasts containing chlorophylls a and b. |
Green Alga |
Part of archaeplastida supergroup. |
|
|
Photosynthetic protist; typically multicelled, with chloroplasts containing red accessory pigments (phycobilins). |
Red alga |
Archaeplastida. What is used to make nori (gametophyte) |
|
|
Spore-forming diploid body that forms in the life cycle of land plants and some multicelled algae. |
Sporophyte |
|
|
|
Single celled protist that extends psuedopods to move and to capture prey. |
Amoeba |
Member of the amoebozoan supergroup. |
|
|
Super group. Shape-shifting heterotrophic protist with no pellicle or cell wall; an amoeba or slime mold. |
Amoebozoan |
|
|
|
Amoeba-like protist that feeds as a single predatory cell; joins with others to form a muticellular, spore-bearing structure under unfavorable conditions. |
Cellular Slime Mold |
Member of Amoebozoan supergroup. |
|
|
Protist that feeds as a multinucleated mass; forms a spore bearing structure when environmental conditions become unfavorable. Contains brightly colored pigments. |
Plasmodial Slime Mold |
Member of the Amoebozoan supergroup. |
|
|
Heterotrophic fresh water protist with a flagellum and a food capturing collar. May be solitary or colonial. |
Choanoflagellate |
Closely related to animals. supergroup of protist. |
|
|
List the general characteristics of protista. |
Very diverse, mostly unicellular, some colonial, some multicellular. |
Can be autotrophs, mixotrophs or heterotrophs. Can be fungus-like animal-like or plant-like. |
|
|
An organism that can photosynthesize and depend on other organisms as a source off food/energy. |
Heterotroph |
|
|
|
Flagellated protozoan with modified mitochondria. Many are human pathogens. |
Anaerobic Flagellates |
Example: Giardia intestinalis |
|
|
Supergroup of protists. They are single-celled marine protists with sieve-like shells (porous). Capture food with cytoplasmic extensions. |
Rhizarians |
Foraminiferans and Radiolarians |
|
|
Diverse protist supergroup. Major component of phytoplankton, small sacs beneath the plasma membrane. Mostly aquatic and free living. |
Alveolates |
Includes ciliates, dinoflagellates, and apicomplexans. |
|
|
Protist supergroup consisting of autotrophs and heterotrophs. Can be unicellular or multicellular. Defined mainly by genetic similarities than by physical traits. |
Stramenopiles |
Include diatoms, brown algae/kelp and water molds. |
|
|
Protist supergroup. Can be unicellular, multicellular and colonial. Closely related to land plants. Contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis and cullulose in cell walls. |
Archaeplastida |
Includes red algae and green algae. |
|
|
Fall under Amoebozoan supergroup. "Social amoebas" found on the floor of temperate forests. |
Slime Molds |
|
|
|
List the supergroups of protist and their members. |
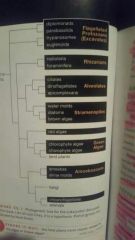
|
|

