![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
A virus that infects bacteria |
Bacteriophage |
|
|
|
An enveloped RNA virus that replicates within human white blood cells. Causes the disease known as AIDS. |
HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus) |
|
|
|
RNA virus that uses reverse transcriptase to produce viral DNA in a host cell. |
Retrovirus |
|
|
|
Noncellular, infectious particle of protein and nucleic acid; replicates only in a host cell. |
Virus |
|
|
|
Bacteriophage replication path in which viral DNA becomes integrated into the host's chromosome and is passed to the host's descendants. |
Lysogenic Pathway |
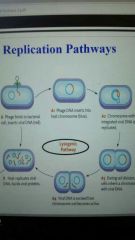
|
|
|
Bacteriophage replication pathway in which a virus immediately replicates in its host and kills it. |
Lytic Pathway |
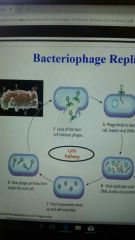
|
|
|
Describe the Characteristics and structures of a virus. |

|
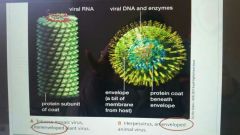
|
|
|
Describe how HIV replicates. |

|
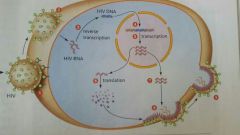
|
|
|
Method of asexual reproduction that divides one bacterial or archaeal cell into two identical descendant cells |
Binary Fission |
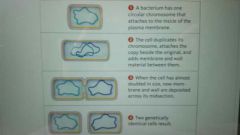
|
|
|
Organism that uses carbon dioxide as it's carbon source and obtains energy by oxidizing inorganic molecules. |
Chemoautotroph |
Only bacteria and archaea obtain energy in this way. |
|
|
Organism that obtains energy and carbon by breaking down organic compounds. |
Chemoheterotroph |
This includes bacteria, archaea, fungi, animals, and nonphotosynthetic protists |
|
|
Mechanism of horizontal gene transfer in which one prokaryote passes a plasmid to another. |
Conjugation |

|
|
|
Transfer of genetic material between existing individuals. |
Horizontal Gene Transfer |
|
|
|
Organism that obtains carbon from carbon dioxide and energy from light. |
Photoautotroph |
Includes bacteria, archaea, photosynthetic protists, and plants. |
|
|
Organism that obtains it's carbon from organic compounds and it's energy from light. |
Photoheterotroph |
Includes bacteria and archaea. |
|
|
Mechanism of horizontal gene transfer in which bacteria or archaea take up DNA from their environment and integrate it into their genome. Introduction of foreign DNA. |
Transformation |
Example: streptococcus pneumonia |
|
|
Mechanism of horizontal gene transfer by which DNA is transferred from one prokaryotic host cell to its next host by a virus. |
Transduction |
|
|
|
Photosynthetic, oxygen producing bacteria. Believed that chloroplasts in eukaryotes evolved from this bacteria. |
Cyanobacteria |
Partner with fungi to form lichens. |
|
|
Organism that breaks down organic compounds in wastes and remains into their inorganic subunits that plants can take up and use. |
Decomposers |
|
|
|
Resistant resting stage of some soil bacteria. Contains the cell's DNA and a bit of cytoplasm in a protective coat. Formed when conditions are unfavorable. Usually gram + |
Endospore |

Examples |
|
|
Bacteria with thick cell walls of peptidoglycan that are colored purple when prepared for microscopy by gram staining. |
Gram-positive Bacteria |
|
|
|
Incorporation of nitrogen gas into ammonia |
Nitrogen Fixation |
|
|
|
Most diverse bacterial lineage. All gram negative. Share one RNA sequence. |
Proteobacteria |
Ex: E. Coli, Agrobacterium sp., Rhizobium sp. |
|
|
The largest known bacterium. Proteobacteria containing an enormous vacuole that holds sulfur and nitrate. |
Thiomargarita Nambiensis |
|
|
|
Bacteria that resemble a stretched out spring. |
Spirochetes |
some pathogenic forms are responsible for syphilis, and Lyme disease. |
|
|
Normally harmless or beneficial microorganisms that typically live in or on a body. Protect us against infections and provide us with vitamins. |
Normal Flora |
Examples: E. Coli (Vit.K) and lactobacillus sp. (Vit. B) |
|
|
Polymers of sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides. Makes up a cell wall of bacteria. |
Peptidoglycan |
|
|
|
Substances that bacteria release into their environment which may be toxic to other organisms. Directly harm Human cells. |
Exotoxins |
Ex: botulinum toxin (botulism) |
|
|
Components of the outer membrane which may be poisonous to other organisms it inhabits. |
Endotoxins |
|
|
|
A disease that was previously unknown or has recently begun spreading to a new region. |
Emerging Disease |
|
|
|
Disease-causing agent |
Pathogen |
|
|
|
Animal that carries a pathogen from one host to the next. |
Vector |
|
|
|
Multiple strains of virus infect a host simultaneously and swap genes. |
Viral Recombination |
Example: H1N1 "swine flu" |
|
|
A small, circular, single stranded RNA that can infect plants. Not capable of encoding proteins but interferes with normal gene expression. Replicates with assistance of a plant's RNA polymerase. |
Viroid |
|
|
|
Organism adapted to life in a highly salty environment. Most are photoheterotrophs that capture light energy with red pigment. |
Extreme Halophile |
|
|
|
Organism adapted to life in a very high temperature environment. Chemoautotrophs that reduce sulfur to obtain energy. |
Extreme Thermophile |
|
|
|
Organism that produces methane gas (CH4) as a metabolic by-product. Cannot live in the presence of oxygen. |
Methanogen |
Found in the stomach of cattle and some in the mouths of humans. |
|
|
One of two lineages of prokaryotic cells. Cell walls (when present) contain peptidoglycan. |
Bacteria |
|
|
|
Group of single celled organisms that lack a nucleus but are more closely related to eukaryotes than to bacteria. |
Archaea |
|
|
|
Producer. An organism that makes its own food using energy from the environment and carbon from inorganic molecules such as CO2 |
Autotroph |
|
|
|
Of many prokaryotes, small ring of nonchromosomal DNA. |
Plasmid |
|
|
|
The most diverse and well known group of prokaryotes. |
Bacteria (bacterium sing.) |
|
|
|
Informal name for a single celled organism without a nucleus; a bacterium or archaean. |
Prokaryote |
|

