![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Matter |
Anything that takes up space and has mass |
|
|
Facts |
H = Only one proton, no neutron
93 naturally occurring elements, ~20 utilized by organisms In the periodic table- valence e- increase from left to right |
|
|
Protons usually match # of neurons |
Atoms usually electrically neutral |
|
|
Atomic # & wt |
Differ by atomic # (#of protons)
H-1 C-6 O-8 Atomic wt = mass of P+N |
|
|
Isotope |
Different # of N 👉 different wt
Labeled by wt carbon-12, carbon- 13 |
|
|
Bohr model atomic structure |
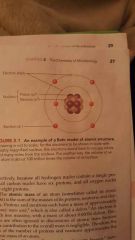
|
|
|
(+) or (-) valence shell |
Depends on whether it's easier to give up or take e- to fill the valence shell O has 6 valence e-, 2 spots to fill, 👉 -2 Ca has 2 valence e-, 2 to giveup, 👉 +2 |
|
|
Chemical bond |
Bonded atoms by sharing or transferring e- |
|
|
Molecule |
Chemical bond of 2 or more same element |
|
|
Compound |
Molecule of 2 or more elements |
|
|
Electronegativity |
Attraction to another atom for its e- to fill a valence shell |
|
|
Why is C the backbone in bio molecules? |
It has 4 valence e- and a large potential for covalent bonds |
|
|
Organic compound |
Compound that contain C or H ProA and carbs |

