![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Structural units of the nervous system |
Neuron |
Specialized to conduct action potentials Lasts a lifetime Require energy: oxygen/glucose |
|
|
Branch-like extensions of the neuron cell that receive signals from surrounding area |
Dendrites |
Messages are almost always chemical in the form of neurotransmitter |
|
|
Tube-like extension of cell membrane that is specialized to conduct an electrical signal (action potential) towards its target cell |
Axon |
|
|
|
Whiteish lipid/protein substance that surrounds some axons like a sheath |
Myelinated |
|
|
|
In CNS myelin is produced by neuralgia cells called _____? |
Oligodenrocytes |
|
|
|
In the PNS myelin is produced by neuralgia cells called _____. |
Schwann cells |
Have gaps known as ‘nodes of ranvier’ that help creates myelin sheath |
|
|
Areas in the CNS with HIGH volume of UNmyelinated axons |
Gray matter |
|
|
|
Areas in the CNS with HIGH volume of myelinated axons |
White matter |
|
|
|
Swollen, cone-shaped area at the beginning of an axon (Near the cell body area) |
Axon Hillock |
|
|
|
Distal endings of an axon |
Axon Terminal |
AKA terminal Bouton |
|
|
Swollen, bulb-like ends of a piece of an axon terminal |
Synaptic end bulbs |
|
|
|
Body of nerve cell |
Soma |
|
|
|
One process off body cell Very common and long Myelinated Carry general sensory info (Hot cold pain) |
Uni-polar neurons |
|
|
|
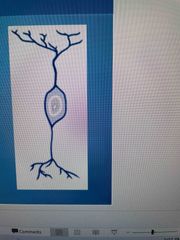
2 processes off body off cell Rare (only in special senses) Short, least common type NOT myelinated |
Bi-polar neurons |
|
|
|
Multiple processes Most common of the 3 types Vary in length ( long myelinated) Short ( not myelinated) Motor neurons |
Multipolar neurons |
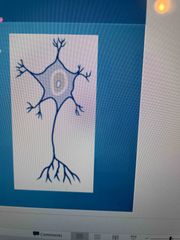
Control muscles and glands |
|
|
Detect stimuli such as light, heat, pressure & chemicals Transmit information to CNS Almost all ____ are unipolar |
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons |
|
|
|
Send signals away from CNS to muscles, glands & other organs Almost all are multipolar |
Motor (Efferent) Neurons |
|
|
|
Found between motor & sensory Shuttle signals through different pathways in brain Decisions based on what info the receive Most of our neurons are this |
Interneurons |
|

