![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Neurons are derived from what embryological precursor?
|
Neuroectoderm
|
|
|
Type of glial cell found in the PNS
|
Schwann Cells
|
|
|
Types of glial cells found in the CNS (4)
|
-Astrocytes
-Oligodentrocytes -Microglia -Ependymal Cells |
|
|
Which type of glial cell is not derived from neuroectoderm? What is it derived from?
|
Microglia - derived from Mesoderm
|
|
|
The receiver component of the neuron is called what?
|
Dendrite
|
|
|
The metabolic center which contains the nucleus and organelles of the neuron, also a receiving component of the neuron
|
Cell body
|
|
|
The area of the cell that transduces the signal to be sent to other cells is called what?
|
Axon
|
|
|
A neuron can only have one ________ but may have multiple ____________.
|
one axon; multiple dentrites (if has many dendrites called "multipolar")
|
|
|
The secretory portion of the axon where signal transmission to another cell occurs
|
axon terminal
|
|
|
Information coming into the cell body is called ____________; information going out from the cell body is called ______________.
|
Afferent - into cell body
Efferent - away from cell body |
|
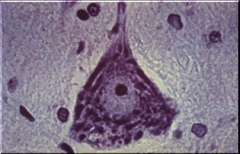
Organelle depicted here that is present in high amounts in neurons
|
Rough ER or Nissl substance - reflects the large amount of protein synthesis that occurs in neurons
|
|
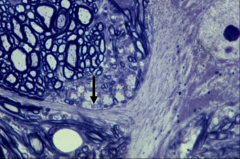
The unmyelinated initial segment where the axon connects to the cell body shown is called what? What occurs here?
|
-Axon hillock
-where the action potential is generated |
|
|
T/F Axons are capable of protein synthesis
|
False
-protein synthesis occurs in dendrites and cell body only |
|
|
The layer of insulation on the axon that allows for more rapid impulse conduction
|
Myelin sheath
|
|
|
The process by which proteins, lipids, mitochondria and synaptic vesicles move to and from the axoplasm is called what?
|
Axonal transport
|
|
|
Movement toward the cell body from the axon terminal is called _________; movement from the cell body to the axon terminal is called ____________.
|
-retrograde transport
-anterograde transport |
|
|
What is protein tau?
|
A microtubule associated protein thought to maintain the integrity of microtubules which are important for axonal transport
|
|
|
A type of intermediate filament found in nerve cells; also important for axonal transport, along with microtubules
|
Neurofilaments
|
|
|
The degeneration of neurofilaments has been implicated in what disease?
|
Alzheimer's
(microtubule and neurofilament degeneration associated with many neuropathologies) |
|
|
Slow anterograde transport is used for the movement of _________.
|
soluble proteins
|
|
|
Proteins destined to become membrane proteins or neurotransmitters are transported via ______________.
|
Fast anterograde transport
|
|
|
Retrograde transport occurs similarly to which anterograde transport system?
|
Fast anterograde transport
|
|
|
What kind of diseases require treatment with antimitotics that can affect microtubules? What side effect does this cause?
|
-Hodgkin's and Non-Hodgkin's cancers
-Paresthesias (affects anterograde transport) |
|
|
What important things are transported back to the cell body via retrograde transport? How can this be detrimental to the cell?
|
-Trophic/growth factors
-Can transmit viruses |
|
|
The presynaptic terminal or axon terminal is also called what?
|
synaptic bouton
|
|
|
A neuron can have many or few ___________, and this determines how much the cell is "listening" to
|
dendrites
|
|
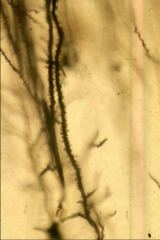
The non-smooth edges of the dendrite shown depict what?
|
Dendritic spines
|
|
|
Dendritic spines are correlated with what processes?
|
Learning and neuroplasticity
|
|
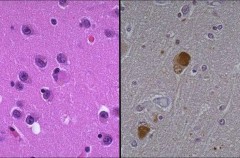
Shown are aggregates of cytoskeleton called what?
|
Lewy bodies
|
|
|
Lewy body disease is the second most common cause of what?
|
Dementia
-also they are found in the substantia nigra in Parkinson's |
|
|
What is a tauopathy?
|
A neurodegenerative disease associated with formation of aggregates of protein Tau
|
|
|
What disease is a tauopathy? What two features are associated with it?
|
-Alzheimer's disease
-amyloid plaques (tau protein aggregates outside the neuron) and neurofibrillary tangles (tau protein aggregates within the neuron) |
|
|
What kinds of deficits are associated with abnormal dendritic spines?
|
Mental retardation (Down's Syndrome)
|
|
|
T/F Glial cells do not generate action potentials
|
True - do not form synapses and are electrically unexcitable
|
|
|
T/F Glial cells, like neurons, have axons and dendrites
|
False - only one type of cytoplasmic process
|
|
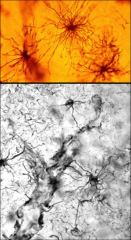
The "medusa-like" glial cells depicted here are called what?
|
astrocytes
|
|
|
Two major functions of astrocytes
|
-maintain ionic homeostasis
-form a barrier between CNS and Non-CNS tissue (wall it off, often found near vessels) |
|
|
The downside of the tendency of astrocytes to protect the CNS from Non-CNS tissue is what?
|
Glial scar formation and tumor formation (astrocytomas, glioblastoma multiforme)
|
|
|
Glial cells in the CNS responsible for myelin formation
|
Oligodentrocytes
|
|
|
The _______ determines whether myelin is made and how much.
|
Axon (cross-talk with developing oligodentrocyte)
|
|
|
Junctions where segments of myelin sheath stop and start again are called what?
|
Nodes of Ranvier
|
|
|
Nodes of Ranvier are important for what?
|
Rapid signal transduction
|
|
|
What disease involves the interruption of the myelin sheath?
|
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
|
|
|
Compare oligodentrocytes with Schwann cells in their ability to myelinate neurons
|
-Oligodendrocytes - one can myelinate many internodes
-SCs - one can only myelinate one internodal segment on one axon |
|
|
Which (oligodentrocytes or SCs) also surround unmyelinated neurons?
|
SCs
|
|
|
Which has connective tissue - PNS or CNS?
|
PNS
|
|
|
Autoimmune disease in which autoimmune complexes attack myelin sheath causing interruptions in the sheath and conduction block?
|
MS
|
|
|
What are MS plaques?
|
Demyelinated areas that light up white when tissue is stained for myelin
|
|
|
_______ matter contains mostly myelinated axons.
|
White
Grey - mostly cell bodies |
|
|
Microglia play a role in what?
|
Mediating immune and inflammatory processes in the CNS
|
|
|
These cells line the ventricular system and help circulate CSF via cilia action
|
Ependymal cells
|
|
|
Tumors that can form from these cells and spread via the CSF are called what?
|
Ependymomas
|

