![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
-Moves from Low concentration to high concentration. -Energy required (atp) required |
Active transport |
|
|
-Moves from high concentration to low concentration -no energy required |
Passive transport |
|
|
Equal movement back and forth across the membrane |
Equilibrium |
|
|
Movement of dissolved partials in a substance from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration (spreading out) |
Concentration gradient |
|
|
Three types of passive transport |
Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
Common molecules that move across the membrane by diffusion are _________ _________and _________. |
Carbon dioxide Oxygen |
|
|
Larger molecules like _____ _____ and ______ need help across. They diffuse using a ______ _____ to facilitate their movement. |
Amino acids Glucose Channel protein |
|
|
A special type of diffusion that involves the movement of water only. |
Osmosis |
|
|
A special type of diffusion that uses protein. (Lock and key) |
Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
To calculate the percent of change. |
#of water molecules on the outside ____________________________ # of molecules outside total
Answer* 100 to get % of change |
|
|
Combination of the solute and the solvent |
Solution |
|
|
The substance being dissolved |
Solute |
|
|
The substance doing the dissolving |
Solvent |
|
|
A physical process by which the solute is pulled into smaller pieces by the solvent. |
Dissolving |
|
|
The tendency of water to move across a membrane based on the number of solutes on each side. |
Osmotic pressure |
|
|
What type of solution is this? -the cell will shrink -higher concentration of soul it's outside the cell |
Hypertonic solution |
|
|
What type of solution is this? -the cell will swell and possible burst -lower concentration of solutes outside the cell |
Hypotonic |
|
|
What type of solution is this? -equal amounts of solute inside and outside the cell -equilibrium |
Isotonic solution |
|
|
What does the prefix Endo mean? |
Inside |
|
|
What does the prefix Exo mean? |
Outside |
|
|
What does the prefix Pino mean? |
Drinking |
|
|
What does the prefix Phago mean? |
Eating |
|
|
What does the suffix Cytosis mean? |
Cell |
|
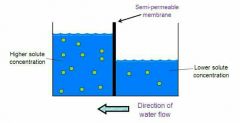
What type of diffusion is this? |
Osmosis |
|
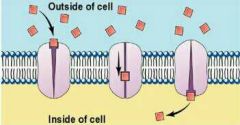
What type of diffusion is this? |
Facilitated diffusion |
|
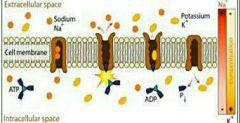
What type of diffusion is this? |
Ion channels |
|
|
Special transport proteins that can open and close. |
Ion channels |
|
|
The process in which cells surround and engulf substances that are too big to enter the cell. The cell uses its own membrane to engulf the substance into a vehicle and bring it in. |
Endocytosis |
|
|
The process in which the cell forms a vehicle around the unwanted particles and expels them out the cell. |
Exocytosis |
|
|
A specialised protein that pumps 3 sodium ions out of the cell for every 2 potassium ions. Against the gradient (low to high) |
Sodium potassium pump |
|
|
Osmosis (passive/active) energy required? _____ |
Passive No |
|
|
Endocytosis (passive/active) energy required? _____ |
Active Yes |
|
|
Ion channels (passive/active) energy required? _____ |
Passive No |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion (passive/active) energy required? _____ |
Passive No |
|
|
Exocytosis (passive/active) energy required? _____ |
Active Yes |
|
|
Sodium potassium pump (passive/active) energy required? _____ |
Active Yes |
|
|
What are three function of the cell membrane? |
1) regulates what enters and leaves 2) provides protection and support 3) communicate with other cells |
|
|
What is the cell membrane made up of? |
Lipid bilayer |
|
|
Lipid with a phosphate group attached. A polar group attached to the phosphate. |
Phospholipid |
|
|
Attracted to water |
Polar Hydrophilic |
|
|
Repelled by water |
Nonpolar Hydrophobic |
|
|
What surrounds each side of the cell membrane? |
Water based fluids |
|
|
What are the three main proteins in the plasma membrane important for cell function? |
1) transport proteins 2) marker proteins 3) receptor proteins |
|
|
What type of lipid in the cell membrane makes it more rigid? |
Cholesterol |
|
|
Proteins that go all the way through the bilayer |
Integral |
|
|
Proteins on only one side of the bilayer |
Peripheral |
|
|
What part of the membrane attracts water? |
Phosphate head |
|
|
What part of the membrane helps maintain flexibility? |
Cholesterol |
|
|
What part of the membrane is involved in cell recognition? |
Peripheral protein Carbohydrate chains |
|
|
Repels water in the cell membrane |
Fatty acid tails |
|
|
Helps transport large molecules across the membrane. |
Integral protein |
|
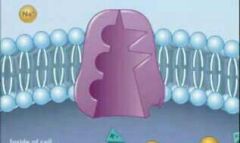
What type of diffusion is this? |
Sodium potassium pump |
|
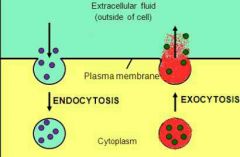
|
Difference in endocytosis and exocytosis. |
|
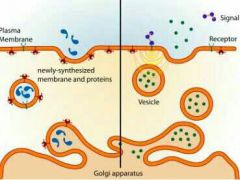
What type of diffusion is this? |
Exocytosis |
|
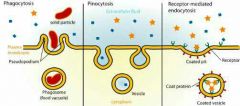
What type if diffusion is this ? |
Endocytosis |

