![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define cell respiration
|
The controlled release of energy, in the form of ATP, from organic compounds in cells
ATP: Molecule that directly fuels the majority of biological reactions |
|
|
State that, in cellular respiration, glucose in the cytoplasm is broken down by glycolysis into pyruvate, with a small yield of ATP (nucleic acid)
|
Location: Cytoplasm
Process: Glycolysis Substrate: Glucose Products: 2 Pyruvates and small amount of ATP Glycolysis does not use oxygen Glycolysis is the break down of one glucose molecule into 2 pyruvate molecules with some ATP This process also results in the reduction of two hydrogen acceptors (NAD+) to form 2 molecules of NADH + H+ |
|
|
Explain that, during anaerobic cell respiration (also called fermentation), pyruvate can be converted in the cytoplasm into lactate, or ethanol and carbon dioxide, with no further yield of ATP
|
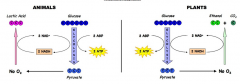
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of a ready supply of oxygen (e.g. during intense physical activity)
In order to generate small amounts of energy provided by glycolysis, pyruvate (end substance) must be converted into another substance before more glucose can be used This is because the conversion of pyruvate replenishes the levels of the hydrogen acceptor needed for glycolysis to occur The conversion of pyruvate occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and the products are: • Lactate in animal cells • Ethanol and carbon dioxide in plants, fungi (e.g. yeast) and bacteria |
|
|
Explain that, during aerobic cell respiration, pyruvate can be broken down in the mitochondrion into carbon dioxide and water with a large yield of ATP
|
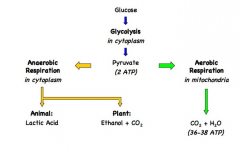
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen and takes place in the mitochondrion
Pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide and water and a large amount of ATP is formed (34 - 36 molecules) Although this process begins with glycolysis (to break down glucose into pyruvate), glycolysis does not require oxygen and is an anaerobic process |

