![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Necessary steps of cell reproduction |
Copy, separate, divide cytoplasm |
|
|
Describe binary fission |
In the process of binary fission, an organism duplicates its genetic material, or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and then divides into two parts (cytokinesis), with each new organism receiving one copy of DNA. |
|
|
Explain the first step of Mitosis (early prophase) |
the cell starts to break down some structures and build others up, setting the stage for division of the chromosomes.
The chromosomes start to condense (making them easier to pull apart later on).The mitotic spindle begins to form. The spindle is a structure made of microtubules, strong fibers that are part of the cell’s “skeleton.” |
|
|
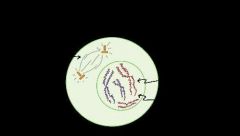
Explain the second step of mitosis (prometaphase) |
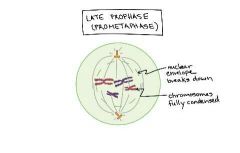
-The chromosomes finish condensing, so they are very compact. -The nuclear envelope breaks down, releasing the chromosomes. -The mitotic spindle grows more, and some of the microtubules start to “capture” chromosomes. -The chromosomes finish condensing, so they are very compact.-The nuclear envelope breaks down, releasing the chromosomes. -The mitotic spindle grows more, and some of the microtubules start to “capture” chromosomes. |
|
|
Explain the 3rd step of mitosis (metaphase) |
All the chromosomes align at the metaphase plate (not a physical structure, just a term for the plane where the chromosomes line up). At this stage, the two kinetochores of each chromosome should be attached to microtubules from opposite spindle poles. |
|
|
Explain the 4th step of mitosis (anaphase) |
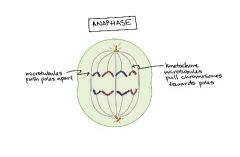
In anaphase, the sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell. |
|
|
Explain the 5th step of mitosis (telephase) |
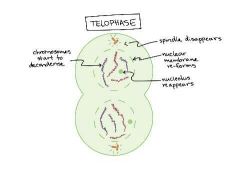
In telophase, the cell is nearly done dividing, and it starts to re-establish its normal structures as cytokinesis (division of the cell contents) takes place. |
|
|
What is chromatin? |
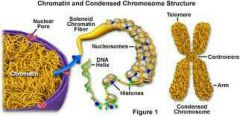
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. |
|
|
What is a chromatid? |
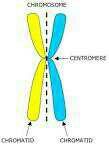
Each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. Each contains a double helix of DNA. |
|
|
What is a chromosome? |
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. |
|
|
What is a centromere? |
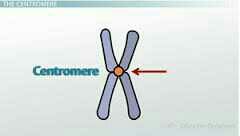
the point on a chromosome by which it is attached to a spindle fiber during cell division. |
|
|
What is a kinetochore? |
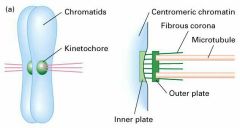
A protein structure that forms on a chromatid during cell division and allows it to attach to a spindle fiber on a chromosome |
|
|
What are cohesion proteins? |
Cohesin is a protein complex that regulates the separation of sister chromatids during cell division, either mitosis or meiosis. Cohesion holds newly replicated sisters in close proximity from S phase until the initiation of chromosome segregation in anaphase, |
|
|
What are condensin proteins? |
condensin organizes mitotic chromosomes into compact, discrete segregatable units. |

