![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Cell Wall |
A rigid structure on the outside of a certain cells, usually plants and bacteria cells. |
|

Hydrophilic |
"water-loving"; pertaining to polar or charged molecules (or parts of molecules) that are soluble in water. |
|
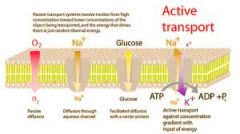
Active Transport |
Movement of molecules across a membrane requiring energy to be expanded by the cell. |
|
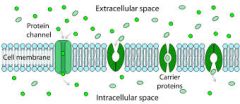
Protein Channel |
Proteins in the cell membrane whose role it is to allow specific molecules to pass through them. |
|

Plasmolysis |
As a plant cell shrivels its plasma membrane pulls away from the wall. |
|

Passive Transport |
Transport of molecules across a cell membrane by diffusion (no energy required). |
|
Concentration Gradient |
Difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another. |
|

Hydrophobic |
"water-fearing"; pertaining to nonpolar molecules (or parts of molecules) that do not dissolve in water. |
|

Diffusion |
The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. |
|
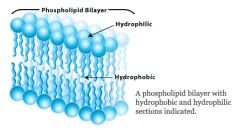
Lipid Bilayer |
The basic structure of a cell membrane, composed of two layers of Phospholipids. |
|
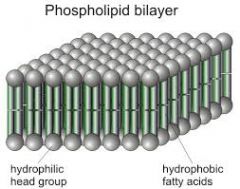
The inside of the phospholipid bilayer |
Which part of the cell membrane is hydrophobic. |
|
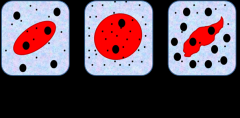
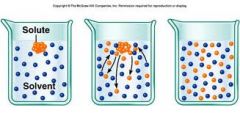
Hypotonic (Picture in the middle) |
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes than another solution. |
|
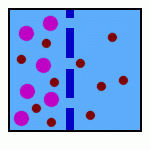
Selective Permeability |
A property of cell membranes that allows some to cross more than others. |
|
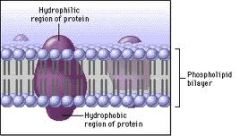
Phospholipids and Protein |
What 2 things in a cell membrane chemically composed of? |
|
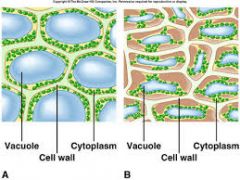
Turgor Pressure |
Pressure that is exerted on the inside of the cell walls and that is caused by the movement of water into the cell. |
|
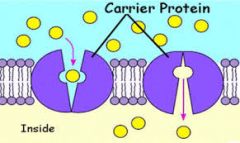
Protein Pumps |
Transport proteins that require energy to do work, as in sodium and potassium pumps in neurons. |
|
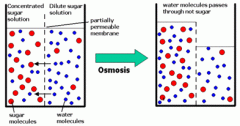
Omosis |
The diffusion of water through a selective permeable membrane. |
|
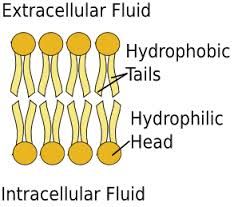
The outside of the phospholipid bilayer |
Which part of the cell membrane is hydrophilic? |
|
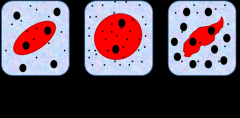
Isotonic (1picture from the left) |
When the concentration of two solutions is the same. |
|
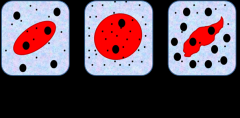
Hypertonic (3 picture from the left) |
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution. |

