![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the functions of cell membrane? |
• Defines the boundary of cells and cellular organelles; • Separates the cellular environment from the extracellular environment; • Separates aqueous regions of different composition within cells; • Controls the movement of molecules between different environments; • Regulates signal transduction between cells and within cells. |
|
|
outline the Fluid mosaic model of cell membranes |
Pattern of different molecules (lipids & proteins) put together in a cell membrane forms a mosaic, and these molecules are constantly moving in two dimensions, in a fluid fashion. The movement of the mosaic of molecules makes it impossible to form a completely impenetrable barrier. |
|
|
What is the general structure of phopsholipids? |
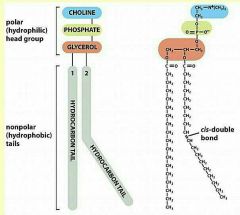
# hydrophilic (polar) head {> consists of choline, phosphate, glycerol}; # 2 hydrophobic (non-polar) tails. |
|
|
What are the phosphoglycerides (glycerophospholipids)? |
# glycerol-based phospholipids, # main component of the cell membranes. |
|
|
Which structures are the same in different phosphoglycerides? |
# in the hydrophilic cap: > phosphate > glycerol # hydrophobic (non-polar) tail - fatty acid |
|
|
What are the 3 types of phosphoglycerides? |
1) phosphatidyl-ethanolamine 2) phosphatidyl-serine 3) phosphatidyl-choline # ethanolamine, serine, choline - amino acids |
|
|
where can Sphingomyelin be found? |
- in the membranous myelin sheath surrounding axons of neurons. - and in general, in some other animal cell membranes. __________ # Sphingomyelin is a sphingolipid. |
|
|
What is the role of lipids in membrane structure and function? |
"A primary role of lipids in cellular function is in the formation of the permeability barrier of cells and subcellular organelles in the form of a lipid bilayer." (Dowhan and Bogdanov, 2002) |
|
|
What is the general structure of a cell membrane? |
Cell membrane is composed of:
a phospholipid bilayer, > with the hydrophilic phosphate “head” groups facing the aqueous environment on either side, > and the hydrophobic “tails” in middle.
The cell membrane is primarily made up of three things: 1. Phospholipids 2. Sterol 3. Proteins |
|
|
What are the functions of sterols? |
Sterols are essential in all eukaryotic cell membranes.
# reduce membrane fluidity and permeability, # increase membrane rigidity and strength.
> chholesterol - mammalian sterol |
|
|
Useful resources about cell membranes |
http://bio1510.biology.gatech.edu/module-3-molecules-membranes-and-metabolism/02-membranes/
https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/cells/cell-membrane-overview/a/fluid-mosaic-model-cell-membranes-article https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Membrane_Proteins |
|
|
α-helical transmembrane proteins |
# the more common of the 2 types of transmembrane proteins. # can be found in the inner membrane of bacterial cells or the plasma membrane of eukaryotes. Examples: Glycophorin A, Bacteriorhodopsin. |
|
|
β-barrel transmembrane proteins |
# the less common type of transmembrane proteins; # present in the... > outer membranes of Gram -ve bacteria, > cell wall of Gram +ve bacteria, > outer membrane of mitochondria and chloroplasts. |
|
|
What are the common features of transmembrane proteins? |
# they span across the entire membrane. # They may cross the membrane only once or several times, weaving in and out. # The two kinds of transmembrane proteins are alpha-helical and beta-barrels. |
|
|
How fattiness of acids affects membrane fluidity? |
Fatty acids form the tails of phospholipids that make up cell membrane.
Saturated fatty acids - tightly packed & less permeable. # chains of carbon atoms with single bonds between them => they are more straight => it's easier to pack tightly.
Unsaturated fatty acids - less tightly packed & more permeable. # chains of carbon atoms with some double bonds between them => double bonds cause some sharp twists, so the tails are less straight => it is more complex to pack tightly. |

