![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Prokaryotic cells |
Bacteria cell Single celled organism |
|
|
|
Eukaryotic cell |
Complex cell Animal and plant |
|
|
|
Animal cell sub cellular structure |
Nucleus- genetic material controls activity of cell Cytoplasm- chemical reactions, contains enzymes for chemical reactions Cell membrane- holds cell together & controls what goes in and out Mitochondria- aerobic reactions take place & transfers energy that the cells need to work Ribosomes- proteins are made in cell |
|
|
|
Plant cell sub cellular structure |
All animal cell parts and . . . Cell wall- made form cellulose, supporta & strengthens cell Vacuole- contains cell sap, weak solution of sugar and salts Chloroplast- photosynthesis occurs, food for plant. Contain chlorophyll which absorbs light for photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Bacteria cells |
Contains DNA in plasmid No nucleus but single circular strand of DNA that floats freely in cytoplasm No mitochondria or chloroplast |
|
|
|
Magnification= |
Image size divided real size |
|
|
|
Light microscopes |
Use light and lenses Can see Individual cells and sub cellular structures, like nuclei |
|
|
|
Electron microscope |
Electrons Higher mag ( bigger) and resolution ( distinguish between two points, sharper image) |
|
|
|
Differentiation |
Cells become specialised for their jobs As they change they develop different sub cellular structures and turn into different cells so they can do specific functions In mature animals the cells that differentiate are mainly used for repairing and replacing Undifferentiated cells are stem cells |
|
|
|
Sperm cells are specialised for... |
REPRODUCTION- male DNA to female DNA Long tail and streamline head help swim to egg Lots of mitochondria to provide energy Enzymes in head to get through egg cell membrane |

|
|
|
Nerve cells are specialised... |
RAPID SIGNALLING- carry electrical signals from 1 part of body to another Long to cover more distance branched connections at ends to connect with other nerve cells to form network through body |

|
|
|
Muscle cells are specialised for ... |
CONTRACTION- contract quickly Long so more space to contact Lots of mitochondria for energy of contraction |

|
|
|
Root hair cells are specialised for ... |
ABSORBING WATER AND MINERALS- on surface of plant root which grow to long hairs which stick out into soil Big surface area to absorb water and mineral ions from soil |
|
|
|
phloem and xylem cells are specialised for... |
TRANSPORTING SUBSTANCES- tubes which transport water and food around plant Long and joined either end to form tubes Xylem hollow in middle and phloem have few sub cellular structures so stuff can flow through them |
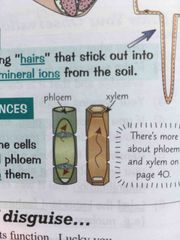
|
|
|
Chromosomes |
Contain genetic information Coiled up lengths of DNA molecules Chromosomes carry large no’ of genes
|
|
|
|
In body cells the chromosomes... |
Have two copies 23 paid of chromosomes |
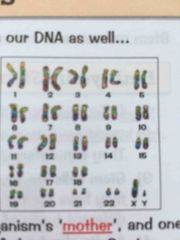
|
|
|
What is the cell cycle |
Makes new cells for growth, development and repair Body cells in sub cellular organisms divide to produce new cells Results In two identical copies of original cell with same number of chromosomes |
|
|
|
Where are stem cells found |
Bone marrow |
|
|
|
How can stem cells cure diseases |
Stem cells transferred from bone marrow from healthy person can replace faulty blood cells in patient Insulin producing cells for diabetes Nerve cells for paralysed spinal injuries |
|
|
|
How could stem cells be used for cloning |
In therapeutic cloning an embryo could be made to have the same genetic info as the patient. This means he stem cell would also have same genes so would be rejected by patient body. |
|
|
|
What is a risk of using stem cells in medicine |
If contaminated with virus in lab his could be passed onto the patient and make them sicker |
|
|
|
Why are some people against stem cell research |
Feel human embryos shouldn’t be used for experiments when is a potential human life Scientists should find and develop other sources of stem cells so people can be helped without using embryos In some counties stem cell research is banned. UK is allowed with strict guidelines |
|
|
|
Why are some people for stem cell research |
Curing existing patient ma who are suffering if more important than right of embryos Embryos used in research from fertility clinics and are unwanted- if not used for research they are destroyed |
|
|
|
How do stem cells produce identical plants |
In plants stem cells are found in meristems (where growth is) Through plants life stem cells in meristem can differentiate into any cell These stem cells can be used to clone whole plants quickly and cheaply Grow plants of rare species (no extinction) Grow crops of identical plants with desired features for farmers e.g disease resistance |
|
|
|
What is diffusion |
The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration |
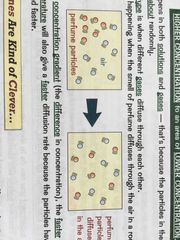
|
|
|
What is Osmosis |
The movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of high water conc to an area of lower water conc |
|
|
|
Hhh |
Jhjj |
|
|
|
What is active transport |
When substances have to absorb something against a concentration gradient |
|
|
|
Give an example of active transport in humans |
Taking in glucose from gut and from kidney tubules Lower concentration of nutrients in gut than in blood active transport allows for glucose to still be taken into the blood stream. |
|
|
|
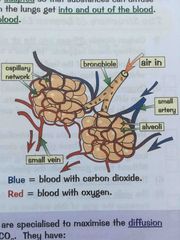
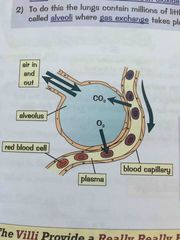
Explain gas exchange in the lungs |
The lungs transfer oxygen to blood and get rid of waste CO2 So lungs can do this they have millions of air sacs called alveoli where gas exchange he takes place |
|
|
|
How are alveoli specialised to max diffusion of O2 and CO2 |
Enormous surface area Moist lining for dissolving gases Very thin wall one cell thick Good blood supply through capillary
|
|
|
|
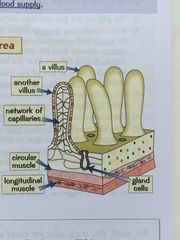
How are villi specialised to absorb nutrients |
Small intestine covered in tiny little projections called villi Increase surface area so digested food can be absorbed much more quickly into blood Single layer of surface cells Good blood supply to assist absorption |
|
|
|
How is the leafs structure specialised so gases can diffuse in and out easily |
CO2 diffuses into air spaces within the lead which then diffuses into the cell where photosynthesis happens Underneath the leaf is an EXCHANGE SURFACE covered in stomata (little holes) which CO2 diffuses through Oxygen (produced in photosynthesis) and water vapour diffuse out of stomata Guard cells control size of stomata and open and close them Flattened surface of leaf increases exchange surface Water vapour evaporates from cells inside leaf. Escapes by diffusion because a lot inside and less in air outside. |
|
|
|
How are fishes gills specialised for gas exchange |
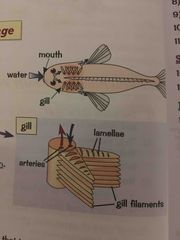
Water enter through fish mouth and pass through gills, oxygen from water diffuses into blood in gills and CO2 from blood to water Gill filaments give big surface area for gas exchange Gill filaments covered in lamellae increase surface area, lots of blood capillaries to speed diffusion, thin layer of cells less space for gas to travel Conc of O in water always higher than in blood |
|

