![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
141 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define: HVAC
And who said this? |
AC is control of humidity by increasing/decreasing moisture content.
Heating or cooling controls temp Ventilation purifies air by filtering and controlling the motion of the air -Willis H. Carrier (inventor of Modern AC) |
|
|
Define: Psychrometrics
+different types of temperature readin |
Properties of Water Vapor in Air
-Dry Bulb Temp -Wet Bulb Temp -Dew Point Temp |
|
|
Which will read lower on the psychrometric scale:
Dry Bulb or Dew Point |
Dew Point
|
|
|
What is a Ton
How many BTUs is it? |
How much energy it takes to melt one ton of ice
Unit of Energy typically used in cooling systems 12,000 BTUs |
|
|
What are 7 levels of regulation for HVAC
|
-International Codes
-Wisconsin Commercial Building Code -Local AHJ "Authority Having Jurisdiction" -FGI -National Electric Code -NFPA 90A -ASME |
|
|
What is the important HVAC resource and what do they provide
|
ASHRAE (Ash-ray) "American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and AC Engineers"
-Standards -Guidelines -Publications |
|
|
Types of HVAC Design
|
-Basis of Design (BOD)
-Schematic Design (SD) -Design Development (DD) -Construction Documents (CD) -Submittals |
|
|
HVAC Design Criteria (7 pts)
"What do you want to regulate?" |
-Conditions: Temp and Humidity
-Loads: Heating/Cooling -Ventilation: Outdoor and Exhaust Air -More Ventilation: Mvt and Velocity -Air Purity: Filtration, Odor Control -Building Pressure: Positive v. Negative -Acoustics: Noise Levels |
|
|
HVAC Design Constraints (6 pts)
|
-Users: Do's/Don'ts, preferences
-Costs: first + annual operating and maintenance -Schedule: Durations and deadlines -Physical: of the building and of the systems -Regulatory: codes, standards, local authorities -Resources: Fuel, electricity, water |
|
|
What are some additional HVAC Design Constraints (4pt)
|
redundancy, security, sustainability, flexibility
|
|
|
Types of HVAC Systems (6pt)
|
Heating
Air Conditioning Ventilation Humidification De-Humidification Refrigeration |
|
|
Components of heating system
|
Boilers
Furnaces Space Heaters Hydronics Unitary Geothermal |
|
|
What is a wall fin
|
HW (hot water) Convector with no fan
heats using natural convection |
|
|
What does RTU stand for
|
Roof Top Unit
|
|
|
Cooling Components
|
Chillers
Cooling towers Evaporative coolers Hydronic Unitary Room Thermal Storage |
|
|
Three types of air to be ventilated
|
Outdoor Air
-natural -forced -leakage Room Air -mixing (classroom) -displacement (operating room) Exhaust Air |
|
|
Components of ventilation
|
Air inlets/outlets
-grilles, registers, diffusers, louvers Terminal units -VAV (very common in commercial), induction, chilled beam, fan-powered Fans -roof-mounted, inline, prop, utility, other Ductwork -pressure class, seal class, materials |
|
|
Ventilation Applications
|
Room Air: mixing (overhead), displacement (underfloor)
Exhaust Air: kitchen hood, fume hood, toilet room, industrial |
|
|
Why Humidification
|
For human comfort and health
(improve thermal, nasal, skin) Suppress static electricity Protect hygroscopic materials Required for various industrial processes (paper, textiles, foods, powders, electronics) |
|
|
Humidification Methods
(Cooling Effect) |
Adiabatic
-air washers/evaporative coolers -wetted media -water atomizing More common |
|
|
Humidification Methods
(Heating Effect) |
Isothermal
-vapor generators -steam humidifiers Less common |
|
|
Why De-humidification
|
Prevent moisture damage
Prevent mold growth Improve comfort Preserve building contents Reduce energy usage Prevent condensation |
|
|
Refrigeration
|
Used to preserve food/drink
Vapor-compression cycle most common Components similar to cooling |
|
|
HVAC Construction Process
|
Project qualifications
Cost estimating Design participation (sometimes) Coordination Pre-Construction Fabrication Installation Commissioning/Verification |
|
|
Name 4 Building Codes
|
International Building Code
Wisconsin Commercial Buildings-Administrative Code National Fire Protection Association National Electrical Code |
|
|
Which Code supplements which
|
WI Commercial Buildings-Administrative Code supplements IBC
|
|
|
What was building principle in 2,000 BC
|
"eye for an eye"
|
|
|
When was first evidence of building inspections and who observed it
|
341 BC
Socrates |
|
|
What former US politicians encouraged building regulations to ensure health and safety
|
G. Washington and T. Jefferson
|
|
|
How many regional groups were part the first building regulations in the US and when?
|
3 regional groups
early 1900s |
|
|
When was IBC first published and how often is it updated
|
1997
every 3 yrs |
|
|
When was Adaption of Americans with Disabilities Act first published and when was it required to abide by
|
1990
1992 |
|
|
When did the ADA become part of the IBC
|
2010
|
|
|
How many pages are in the IBC
How many are in the WI Commercial Buildings-Admin. Code? |
722 pages
253 pages |
|
|
Who can help you with interpreting code?
|
Code Consultants and Local Code officials
|
|
|
What are the duties of the Plan Commission
|
-State has building commission
-make/adopt a master plan for physical development of the municipality -recommend location/architectural design of public buildings and projects -final approval on land divisions |
|
|
What are the duties of the Common Council
|
-adopts City budget and passes laws, policies, and regulations that govern the City
-->conduct legislative business -Plan Commission makes reports/recommendations to Common Council -Council approves "Does it fit in bylaws?" |
|
|
Types of Permitting
|
-Building Plan Approval Application
-Electrical -HVAC data sheet -Plumbing data sheet -General Plumbing Plan Approval Application -Compliance Statement -Disproportionality Form -Erosion Control |
|
|
What additional approval must you get to begin construction?
|
Work permit from fire department
-fire extinguisher, welding, etc |
|
|
What are turnaround times for council vs building permit vs erosion control
|
council - 8 weeks
building permit - 6 weeks erosion control - 4 weeks |
|
|
What is the point of specifications?
|
identify how to build
|
|
|
Which comes first: Specs or Plans?
|
Specs
|
|
|
What is most common spec type and who does it encompass?
|
AIA A201
between owners, architects, and contractors |
|
|
What specs are used on State jobs in WI
How is it made? |
Sate of WI General Conditions
Take AIA, turn into GCs Every State differs |
|
|
How many divisions of specs were there before 2004 and how many are there now?
|
were 14
now almost 50 |
|
|
What is the most important part of specs?
|
Precedence
|
|
|
What does the Precedence encompass?
|
-Amendments over specs
-Specs over drawings -State dimensions over scaled dimensions -Large-scale detail drawing over small '' -Schedules over other data on plan |
|
|
What are two questions to ask about plans?
|
What codes and standards govern your building?
What does the set of documents do for you? |
|
|
Where are architectural plans found?
Where are structural plans found? |
-Same page as sheet index
-In general notes |
|
|
What systems encompass plumbing?
|
-water supply
-water distribution -wastewater drainage -reclaimed water systems -storm water use |
|
|
Types of plumbing utilities
|
-sanitary
-storm -water -gas |
|
|
Types of sanitary systems
|
-sewer
-building drain -drains -vents -greasy waste |
|
|
What are Water Supply Systems
|
-Private water main, water service, and water distribution system
-conveyed to points of usage -fixtures, appliances, water-using equipment, etc |
|
|
Types of Water Supply Systems
|
-Domestic (drinking, showering, flushing)
-Non-potable (fire protection, HVAC systems, etc) -Process (food-making, beer-making) |
|
|
Types of Storm Systems
|
-roof drains
-overflow drains -clearwater drains |
|
|
Types of Gas
|
-fuel (water heater, furnace, HVAC, emergency generators)
-medical gas (nitrous oxide, nitrogen, oxygen, vacuum, etc) |
|
|
Examples of Equipment
|
water heaters
water softeners booster pumps RO systems |
|
|
Examples of Fixtures
|
lavatories
urinals showers janitors sinks electric water cooler |
|
|
Examples of Assemblies
|
reduced pressure detector
reduced pressure zone |
|
|
When was first sprinkler system installed
|
1874
Henry Parmalee's Piano Factory |
|
|
When were sprinklers being installed in commercial buildings
|
1940s
|
|
|
What sections in codes and standards relate to sprinkler systems?
|
NFPA 13, 14, 20
IBC Chapter 9 |
|
|
Temps for red/blue bulb sprinkler heads
|
red = 155 F
blue = 200 F |
|
|
6 Sprinkler head types
|
-upright, pendent & sidewall sprinklers
-standard coverage & extended coverage -dry barrel -residential -storage -special |
|
|
What are two system risers and zone controls
plus standard pipe size |
-backflow preventers
-OS&Y and butterfly valves -Pipe size 6", maybe 4" |
|
|
Types of fire sprinkler systems
|
wet pipe
dry pipe pre-action deluge anti-freeze |
|
|
Types of Fire pumps
|
-electric and diesel
-transfer switch and emergency power -jockey pumps |
|
|
What are some alternative agent systems of fire protection
|
-wet/dry chemical
-foam (for flammable liquid) -clean agent (displaces oxygen) |
|
|
Who has jurisdiction of plumbing
(what does jurisdiction mean in this case?) |
-Inspection
-typically the municipality where work is to be done -if no municipality Inspection Unit, independent contractor is hired |
|
|
Who reviews the plumbing plans and according to what codes?
|
-Sate or Agent Municipality
-SPS table 382 |
|
|
Who has jurisdiction on Fire Protection
And what do they do? |
Fire Sprinkler Contractor
-design -install -inspect -test -maintain automatic fire sprinkler system |
|
|
Who reviews the fire protection plans
|
Architect & Engineers
Fire department State Review Agencies Building owner's insurance plan reviewers |
|
|
Fire protection prefabrication
Original vs. Today |
Original = 10'-0" pipe with "made-on" fittings
Today = "cut to fit" pipe "cut one end" pipe "random" pipe |
|
|
Fire protection/Plumbing Installation
|
quality control
inspections & testing building occupancy owner turnover items -as-builts, O&M's, training |
|
|
What are the phases of procurement
|
1. Successful job bid or proposal
2. Buyout/sign up subs and suppliers 3. Submittals 4. Lead Time 5. Delivery |
|
|
What is something to keep in mind in the "buyout/sign up subs and suppliers" phases of procurement
|
Get rid of gaps, uncover overlap
|
|
|
Describe the submittal process
|
a. process by subcontractor/supplier to GC
b. processed by GB to architect - 5 days c. reviewed by architect - 10 working days d. processed from architect to GC (approved) e. processed by GC to subcontractor/supplier f. material released for fabrication g. mock ups - are multiple items required? |
|
|
What are some questions regarding delivery
|
To jobsite or temp location?
Is project phased? Is there room on site to store it? Cost savings if one drop shipment? Does it need to be in a temperature controlled environment or kept dry? |
|
|
What items cross trades in the procurement process?
|
Window shades
Door frames Door hardware Access Control Owner Equipment |
|
|
What are some questions regarding shipping?
|
What's included in the contract?
Is it direct shipment? If overseas, comes in plane or boat? Customs? Who holds risk of delivery? Delivery limits on weight, size, what roads can be traveled? Will they delivery on time or 4-6 weeks from date? |
|
|
True of False:
The CG is liable for freight onboard jobsite before it's delivered |
False
|
|
|
Define BIM
|
Building Information Modeling
-the process of using 3D models to facilitate the construction process from design through turnover |
|
|
Where is BIM most effective
|
design/build or IPD environments
|
|
|
What is the Macleamy Curve
|
Graph that relates time vs effect/cost/effort
Used for cost estimating/estimating/schedule modeling |
|
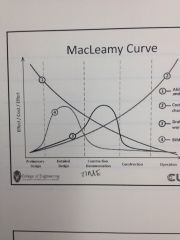
|
1. Ability to impact cost and performance
2. Cost of design changes 3. Drafting-centric workflow 4. BIM workflow |
|
|
What does BIM essentially do to the MacLeamy Curve?
|
Pulls the curve forward, saving cost
|
|
|
Why/What is BIM helpful for with regards to design?
|
Concept design
Technical design Closer collaboration Parametric design Immediate information sharing |
|
|
What is BIM helpful for with regards to Analysis
|
Structural integrity
Temperature Control Ventilation Lighting Circulation Acoustics Energy distribution and consumption Cost estimation |
|
|
What is BIM helpful for with regards to the construction team
|
MEP coordination
Quantity takeoff and cost estimating Construction Analysis and 4D planning Lift drawings Integration with cost and schedule control Prefab and modularization Verification and tracking of construction activies |
|
|
What is BIM helpful for with regards to the Owner
|
Increased building value
-energy design and analysis to improve building performance Shorten project schedule Obtain early/reliable cost estimates Assure building compliance Produce market ready facilities Optimize facility management and maintenance |
|
|
What is the primary use of BIM for owner?
|
Dumb down
Put it in facility management program |
|
|
How many types of BIM software are there?
What three are most common for contractors? |
hundreds
Revit, Navisworks, and Sketchup |
|
|
What is one nice thing about Revit
|
When you change one thing somewhere, it changes it everywhere for you
|
|
|
How long ago was it that you had to use light tables to coordinate between drawings?
|
10 years ago
|
|
|
Why prefab & modularization?
|
Schedule
Quality Safety |
|
|
What are some challenges in concrete beam reinforcing
|
-Complexity of items to be installed in cast beam
-Where/what rebar to pre-tie? -Embed conflicts -column dowel conflicts -what sequence |
|
|
What are some challenges for concrete shear wall coordination
|
-Validate plan for steel erection
-Tight spatial tolerances -Demanding schedule does not allow for any delay |
|
|
How did they solve the challenges of concrete shear wall coordination?
|
Model shear wall and area of congestion
Coordinate with steel fabrication model |
|
|
What do IBS and VDV stand for
|
Integrated Building Systems
Voice, Data, Video |
|
|
What are the three phases of getting electricity to a building
|
Power Generation
Power Transmission Building Distribution |
|
|
When should the electrical room be built and why?
|
Should be one of the first rooms built
Electrical contractor needs a start point Critical to success of the electrical slab |
|
|
What's one way to describe the MDF/IDF rooms
|
"nervous system of a building"
|
|
|
What is a key thing to remember about electrical contractors
|
They're one of the only trades to be on site from start to finish
|
|
|
How does the sequence of electrical installs go in construction?
|
Safety
Temporary Power Rough in LIght Fixtures Power/HVAC equipment connections Finishes |
|
|
Four things to wear to ensure safety on the job
|
Hard hats
Glasses Gloves Hi-vis vest |
|
|
What is number 1 safety hazard
|
electrocution
|
|
|
What types of out of the ordinary temporary power might be needed on the construction site
|
dewatering pumps
tower cranes large power equipment temp heat power |
|
|
When and with whom are rough ins installed
|
-during the footing and foundation stages
-coordinated with plumber, forming, and concrete crews |
|
|
Where are three places rough ins might be embedded
|
-under or in slab on grade
-in post tension slab -in concrete walls |
|
|
Define:
Feeders |
-Bigger wire for the distribution backbone within the building
-More coordination due to bigger size conduits |
|
|
Define:
Branch |
-smaller wire for power and lighting circuits usually 40A and below
-ideally done before drywall and ceiling grid, but usually coordinated somewhere in between |
|
|
What are the uses for Total Station - Laser Survey Tool
|
-as built
-complicated ceiling layouts for lights -pinpoint layout for underground and slab work |
|
|
What are benefits of using Tablets
|
-better than smartphones
-cloud communication -quick reference for drawings in field -- paperless |
|
|
Roofing components have specific:____
|
-design
-manufacturers -means and methods of installation -maintenance needs |
|
|
What are functions of these roof components:
a. Structural b. Thermal c. Weather Protection d. Fire e. Wind f. building moisture |
a. roof deck
b. insulation c. membrane and flashing d. membrane and coverboard e. fasteners and adhesives f. vapor retarder/air barrier |
|
|
Types of roof systems for Low slope roofs
|
-membrane
-standing seam metal -specialty metal -spray urethane foam -coatings/liquids |
|
|
Which roof type is waterproof and which is watershed
|
Waterproof = low slope
Watershed = steep slope |
|
|
What are steepnesses of low/steep sloped roofs
|
low slope = 1/4":1'
steep slope = 3:12 |
|
|
Name two asphalt based membranes
|
Built Up Roof (BUR)
Modified Bitumen (Mod-Bit) |
|
|
Which roof membrane is two-ply
|
Mod-Bit
|
|
|
How much of the market does Single Ply roof membrane take up
|
70%
|
|
|
What materials are used for BUR systems
(how many layers) |
-typically four layers
-roofing felt -asphalt, modified asphalt, or coal tar -surfaced with bitumen, aggregate, liquid coating, or granular-surfaced cap sheet |
|
|
What is Bitumen?
|
asphalt modified by the addition of one or more polymers ie APP or SBS
|
|
|
How does Mod-Bit come?
|
as a roll for easy installment
-coated with granules -foil surfacing such as coper and aluminum are available |
|
|
Application methods for Mod-Bit
|
Torching (APP/SBS)
Mopping with asphalt (SBS) Cold adhesives (APP/SBS) Self adhesive "SA products (SBS) |
|
|
How long does Mod-Bit last?
|
25-30 years
(less expensive) |
|
|
Different ways to install Single Ply roofing
|
-Ballasted
-Fully adhered -Mechanically fastened |
|
|
What are the two major categories of Single Ply roofing
|
Thermoplastics
Thermosets |
|
|
What is another name for protected membrane assembly
|
IRMA - Inverted Roof Membrane Assembly
|
|
|
How is Protected Membrane Assembly installed
|
Membrane placed on the roof deck
Insulation and some type of ballast placed on top |
|
|
What type of roof includes green roofs?
|
Protected membrane assembly
|
|
|
What is a pro and a con to green roofs
|
Pro - visually attractive
Con - more expensive to install |
|
|
What is the minimum thickness of soil for green roof
|
4 inches
|
|
|
What are the four layers of protected roof assembly
|
1. Soil
2. Insulation 3. Drainage layer 4. Membrane |
|
|
What are two types of standing seam systems
|
Architectural
Structural |
|
|
Describe architectural standing seam systems
|
-requires deck support
-seams not water tight unless locked and rolled by machine with sealant enclosed -system is intended to shed water |
|
|
Describe structural standing seam systems
|
-self supporting when laid over purlins 5 ft on center
-needs a locked seam for structural strength |
|
|
How long do specialty metal roofings last
|
50-70 years
|
|
|
What roof system is growing in new construction
|
Spray polyurethane foam
|
|
|
Four coatings and liquids for roof systems
|
-acrylic
-urethane -plyurea -PMMA |
|
|
Materials used in steep roof systems
|
-asphalt shingles
-metal panel -clay tile -concrete tile -artificial tile -slate -wood shake |

