![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the 3 criteria that define intellectual disability
|
IQ under 70
Onset before age 18 Deficit in adaptive behaviour |
|
|
List barriers to taking history of, examining, and testing intellectually disabled patients
|
History by proxy (e.g. guardian) - lower accuracy
Longer appointments Initial non-cooperation with exams and tests Doctor's attitudes Patient's insecurity of own knowledge level |
|
|
What's the basic premise in treating intellectually disabled patients?
What may this require? |
That they receive the same quality of care as the general population
May require some adaptations to suit needs of patient |
|
|
Intellectual disability & consent: Children
Describe consent rights |
Children: Don’t possess decision-making capacity
(decision by parents/guardians) |
|
|
Intellectual disability & consent: "Mature minors"
Describe consent rights |
<18 but judged competent
(Can consent treatment) (Limitations on refusals in serious situations) |
|
|
Intellectual disability & consent: adults
Describe consent rights |
18+ with decision-making capacity
(entitled to consent) (can refuse treatment) |
|
|
Intellectual disability & consent: adults without competence
Describe consent rights |
(decision by substitute decision-maker)
|
|
|
List the 3 criteria for judging decision-making capacity
How many have to missing to deem person incompetent? |
o Understands nature and effect of decision
o Free and voluntary in making decision o Can communicate decision (any 1 missing = incompetent) |
|
|
Liver lobes:
4 anatomical and 2 functional Which functional lobe does caudate and quadrate belong to? |
Left functional lobe.
|
|
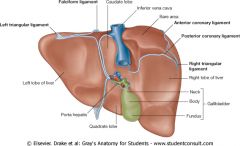
Name the ligaments and stuff
|
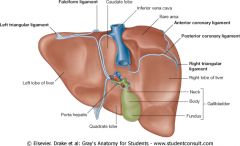
Top left, clockwise:
Left triangular ligament Falciform lig (same at bottom) Inferior vena cava Bare area Anterior coronary lig Posterior coronary lig Right triangular lig Gallbladder: -Head -Neck -Fundus Porta hepatis |
|
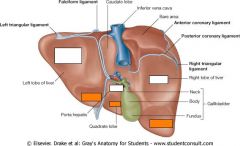
Name the liver impressions
|
(Left to right)
Top 3: Gastric, duodenal, and renal Bottom 3: All colic |
|
|
Name the 2 liver blood supplies
|
Hepatic artery proper
Hepatic portal vein |
|
|
Name liver innervation, and its inputs (sympathetic and parasym)
|
Coeliac plexus
Inputs from vagus (para) and coeliac ganglion (sym) |
|
|
Name liver lymphatic drainage
|
Coeliac drainage (via hepatic nodes)
|
|
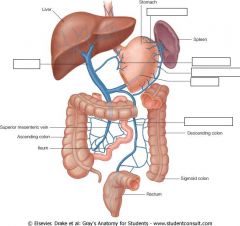
Name the veins of the hepatic portal system
|
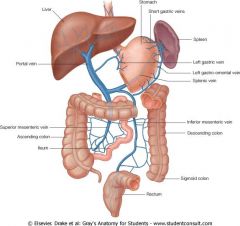
Left, clockwise:
Portal vein Short gastric v Right gastro-omental v Left gastro-omental v Splenic v Inferior mesenteric v |
|
Name the ducts of the biliary tree
|
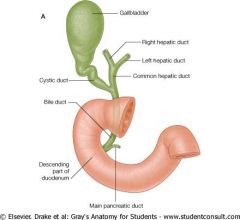
Bottom, clockwise
Main pancreatic duct Common bile d Cystic d Right hepatic d Left hepatic d Common hepatic d |
|
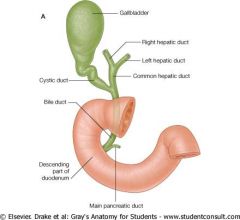
What do the common bile duct and common hepatic duct unite to form?
|
Hepatopancreatic ampulla
or Ampulla of Vater *Ampulla = dilated portion of a canal or duct |
|
|
What does the Hepatopancreatic Ampulla (of Vater) open into the duodenum via?
What's this eminence guarded by? |
The Major Duodenal Papilla.
Guarded by Sphinter of Oddi. |
|
|
List the 6 functions of the liver
|
Metabolism
(fats, proteins, carbs) Storage (glycogen, iron, fat-soluble vitamins [e.g. vit A], copper) Production (plasma proteins [e.g. clotting factors], plasma lipoproteins, bile) Detox (drugs, blood-bourne toxins, metabolic waste products) RBC turnover & recycling component parts (similar to spleen) Haematopoisis (in fetus only, relinquished to bone marrow) |
|
|
Abdominal surface anatomy:
Which plane is at T9? |
Xiphisternal plane
|
|
|
Abdominal surface anatomy:
Which plane is at L1? |
Transpyloric plane
|
|
|
Abdominal surface anatomy:
Which plane is at L2-3? |
Subcostal plane
|
|
|
Abdominal surface anatomy:
Which plane is at L4? |
Supracristal plane
|
|
|
Abdominal surface anatomy:
Which plane is at L5? |
Transtubercular plane
|
|
|
Name and abdominal divisions
A B A C D C E F E |
A: Hypochrondriac
B: Epigastric C: Lateral/Lumbar D: Umbilical E: Iliac/Inguinal F: Hypogastric |
|
|
Liver circulation:
Specify for Hepatic arterioles |
Interlobar arteries
Interlobular arteries Hepatic arterioles |
|
|
Liver circulation:
Specify for Portal venules |
Interlobar veins
Conducting veins Interlobular veins Portal venules |
|
|
Liver circulation:
Specify for Interlobular bile ducts |
Bile canaliculi
Bile ductules (canals of Hering) Interlobular bile ducts R&L hepatic ducts Common hepatic duct |
|
|
Liver circulation:
Specify for Sinusoids |
Sinusoids
Central vein Sublobular Collecting Hepatic veins Inferior Vena Cava |
|
|
Hepatic acinus = functional unit of liver parenchyma (primary tissue)
Describe its 3 zones |
Zone 1:
Exposed to blood; well perfused with O2, incoming nutrients, toxins (Resists hypoxic damage) (Susceptible to drugs/toxins) Zone 2: Middle zone Zone 3: Near central vein Blood de-O2 and low nutrient (Susceptible to hypoxic damage) Higher conc of toxin/drug-metabolising enzymes (Susc to metabolic intermediates) |
|
|
GIT development:
Blood vessels travel in dorsal mesentery Fore/mid/hindgut division based on arterial supply - specify. |
Foregut: Coeliac Artery
Midgut: Superior Mesenteric Artery Hindgut: Inferior Mesenteric Artery |
|
|
Define viral hepatitis.
|
A systemic infection characterised particularly by: Inflammation and necrosis of liver.
|
|
|
List the 6 modes of viral transmission, giving examples.
|
Respiratory (Influenza)
Faecal-Oral (Polio) Sexual (HIV) Blood-borne (via insects, or direct transmission) (Hep B and C) Direct contact (Herpes) Zoonotic (animal disease transmitted to humans) (rabies) |
|
|
Hepatitis viral serology:
What is HBsAg? What does it mean? |
Hep B surface antigen
Presence = active infection (person infectious) |
|
|
Hepatitis viral serology:
What is HBV-DNA? What does it mean? |
Viral DNA
Presence = active infection (person infectious) |
|
|
Hepatitis viral serology:
What is Anti-HBs? What does it mean? |
Antibody against HBV surface antigen
Presence = vaccination, or actual infection (person infectious) appears late Does NOT appear in chronic carriers |
|
|
Hepatitis viral serology:
What is Anti-HBc? What does it mean? |
Antibody against HBV core antigen
Presence = only in actual infection Appears at onset of acute Hep B Persists for life |
|
|
Hepatitis viral serology:
What is Anti-HCV? What does it mean? |
Antibody against HCV
|
|
|
Hepatitis viral serology:
What is HAV-IgM? What does it mean? |
Antibody against HAV
IgM suggests current/early, acute infection |
|

Interpret the serology results
|

|
|
|
Hepatitis viruses:
Define transmission modes |
A: Faecal-oral
B: Parenteral (blood/IV, sexual, perinatal) C: Parenteral (mostly blood/IV, esp. needles & transfusions) D: Parenteral (mostly blood) E: Faecal-oral (usually water-bourne) |
|
|
Hepatitis viruses:
Define incubation period |
A: 2-6wks
B: 4-26wks C: 2-26wks D: 4-7wks E: 2-wks |
|
|
Hepatitis viruses:
Define disease type + progression |
A: Acute
B: Acute; 5% become chronic C: Acute (usu asymptomatic/mild); 55-85% -> chronic D: Acute or chronic E: Acute |
|
|
Hepatitis viruses:
Carrier state? |
A: N
B: Y C: Y D: - E: N |
|
|
Hepatitis viruses:
Cirrhosis? |
A: N
B: Y C: Y D: HDV increases HBV-induced progressive liver disease E: N |
|
|
Hepatitis viruses:
Vaccine available? |
A: Y
B: Y C: N D: N E: N |
|
|
Hepatitis viruses:
Preventions/Interventions |
A: Sanitation, hygiene (limit food/water contamination), human-human contact precautions
B: Avoid IV drugs, screen transfused blood, safe sex C: Avoid IV drugs, screen transfused blood, safe sex D: Ditto HBV E: Sanitation, hygiene (esp. water) |
|
|
Define jaundice (icterus)
|
Yellowish discolouration of tissue (e.g. sclerae of eyes, and skin).
From deposition of bilirubin/bile pigment (either un- or conjugated) |
|
|
What is hyperbilirubinaemia?
How does it occur? |
Abnormally high amounts of bile pigment (bilirubin) in the blood
From either - increased production or - decreased removal |
|
|
Summarise heme metabolism
|
\\Reticuloendothelial cells\\
(in spleen, liver, bone marrow) - Break down old RBCs (main work) Heme -> [Heme oxygenase] -> Biliverdin -> [Biliverdin reductase] -> ---> \\Unconjugated Bilirubin\\ Water-insoluble (can't excrete via urine) Tightly bound to serum albumin Toxic! (Don't you know?) ---> \\Liver\\ 1. Uptake 2. Conjugation 3. Excretion (actively transported into bile) ---> \\Conjugated Bilirubin\\ Water-soluble (can piss out) Only loosely albumin-bound Relatively non-toxic ---> \\Bile\\ Bile -> Duodenum (conjug bili passes along small intestine) Conjug bili -> [via bacteria beta-glu.] -> unconjug bili Unconj bili -> [via normal gut bacteria] -> Urobilinogen (colourless, soluble) ---> //Stool// 80-90% passed here Urobilinogen -> Stercobiligen -> Stercobilin (colours stool) ---> //Bloodstream reabsorption// 10-20% AKA Enterohepatic circulation (ie. back to liver) ---> //Urine secretion// ~5% Via kidneys Urobilinogen -> Urobilin (colors urine) |
|
|
Prehapatic jaundice:
Explain mechanism. |
Excess bilirubin production (e.g. due to haemolysis - RBC breakdown) OVERWHELMS liver capacity of conjugate/excrete it
i.e. Increased unconj bili in blood Unconj and conj bili both increased. *Nothing wrong with liver |
|
|
Prehapatic jaundice:
Explain complications. |
Urine not dark (bili not excreted via urine)
Stool not pale/clay-coloured Urobilinogen levels INCREASED in urine and stools (Liver can increase conj bili output, but can't keep up totally) May be spleen enlargement (palpable) |
|
|
Hapatic jaundice:
Explain mechanism and complications. |
Impaired liver function/Hepatocellular damage
(virus, toxins, enzyme defects) 1. Defective uptake of unconj bili = unconj bili in blood = Urine not dark = May have pale clay-coloured stool (if decreased stercobilin in stool) 2. Defective conj of bili = Raised unconj bili in blood = Urine not dark = May have pale clay-coloured stool (if decreased stercobilin in stool) ***3. Defective excretion of conj bili (AKA intrahepatic cholestasis) = Raised *conj bili* in blood = Dark urine (presence of conj bili) = Pale clay-coloured stool (conj bili can't get to GIT properly) |
|
|
Hapatic jaundice:
Explain multiple stages by viral hepatitis |
Viral hepatitis can
Damage cells (decrease conj of bili) Cause tissue swelling = impair conj bili outflow (dark urine) |
|
|
Post-hepatic Jaundice:
Explain mechanism and complications |
Blockage of bile after liver
(gall stones or pancreatic head cancer) Increased conj bili in blood Dark urine (presence of conj bili) Pale/clay-coloured stool (conj bili can't get to GIT properly) Pain from gall-stones (aggrav. by fatty food consumption - needs bile for digestion) |
|
|
Cell injury and death:
Contrast Necrosis and Apoptosis |
Uncontrolled VS genetically programmed
Involves energy deprivation VS requires energy Inflammation VS ~no inflammation Group of cells affected VS single/few cells Reversible -> irrev VS Irreversible once started Cell swells/lyses due to water influx VS Cell shrinkS as cytoskeleton disassembled Random destruction of organelles and nuclear material VS Orderly packaging of organelles/nuclear fragments |

