![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Embryological sinus venosus gives rise to
|
Sinus venarum cavarum\sinus of the vena cava (part of atrium)
|
|
|
|
Embryological common atrium gives rise to
|
Atrium - the part separated from sinus venarum cavarum\sinus of the vena cava by the crista terminalis\terminal crest
|
|
|
|
Embryological ventricle gives rise to
|
Ventricle - the inflow part
|
|
|
|
Embryological bulbus cordis gives rise to
|
a. Trabeculated part of right ventricle, conus cordis, truncus arteriosus (the outflow part)
b. Separated from the inflow part (primitive ventricle) by supraventricular crest |
|
|
|
Truncus arteriosus gives rise to
|
Aorta + Truncus pulmonalis
|
|
|
|
Sinus venarum cavarum\Sinus of vena cava
|
The portion of the cavity of the right atrium that receives the blood from the venae cavae. It is separated from the rest of the atrium by the crista terminalis.
|
|
|
|
Crista terminalis
|
A vertical crest on the interior wall of the right atrium
Lies to the right of the sinus of the vena cava, and separates this from the remainder of the right atrium |
|
|
|
Common atrium
|
A single abnormal atrium in a 3-chambered heart in which an interatrial septum is absent
|
|
|
|
Sinus venosus
|
A cavity at the caudal end of the embryonic cardiac tube in which the veins from the intra- and extraembryonic circulatory arcs unite
In the course of development it forms the portion of the right atrium knows in adult anatomy as the sinus of the vena cava |
|
|
|
Bulbus cordis
|
A transitory dilation in the embryonic heart where the arterial trunk joins the ventral roots of the aortic arches
|
|
|
|
Truncus arteriosus
a. what b. derivative, how |
a. The common arterial trunk, the opening out of both ventricles in early fetal life
b. Later destined to be divided into aorta and pulmonary artery by development of the spiral septum |
|
|
|
Spiral (bulbar) septum\Aorticopulmonary septum
a. what b. distal part - derived from, does c. proximal part - derived from, does d. aided by which cell type |
a. A septum dividing the embryonic bulbus cordis into pulmonary and aortic outflow tracts from the developing heart
b. The distal spiral septum is derived from the right and left truncal endocardial cushions and so separates the pulmonary and aortic orifices c. The proximal spiral septum is derived from conal ridges (endocardial cushions), it is the portion of the septum that is incorporated into the membranous part of the interventricular septum d. Neural crest |
|
|
|
Atrioventricular canal cushions\Endocardial cushions
|
A pair of mounds (hauger) of embryonic CT covered by endothelium
They bulge into the embryonic AT canal They are located one dorsally and one ventrally They grow together and fuse with each other and with the lower edige of the septum primum, thus dividing the originally single canal into right and left AV orifices |
|
|
|
Septum primum
|
A crescenteric septum in the embryonic heart
Develops on the dorsocephalic wall of the originally single atrium and initiates its partitioning into right and left chambers The tips of the septum grows toward and fuse with the atrioventricular canal cushions |
|
|
|
Infundibulum\Conus arteriosus
|
The left or anterosuperior, smooth-walled portion of the cavity of the right ventricle
Begins at the supraventricular crest and terminates in the pulmonary trunk |
|
|
|
Crista supraventricularis
|
The internal muscular ridge that separates the conus arteriosus from the remaining part of the cavity of the right ventricle
|
|
|
|
Borders of the heart
|
1. Margo dexter\Right border \ Margo acutus
2. Margo sinister\Left border \ Margo obtusus |
|
|
|
Incisura apicis cordis\Notch of cardiac apex
|
A slight notch near the apex of the heart where the anterior interventricular sulcus reaches the diaphragmatic surface
|
|
|
|
Surfaces of the heart
|
1. Facies sternocostalis\Sternocostal surface
2. Facies diaphragmatica\Diaphgragmatic surface 3. Facies pulmonalis dextra\sinistra \ Right\Left pulmonary surfaces |
|
|
|
Components or systems of the heart
|
1. Working myocardium
2. Excitomotor apparatus (EA)\conducting m. 3. Fibrous skeleton of the heart |
|
|
|
Endocardium - layers & composition
What special structures do they form? |
1. Endothelial
2. Subendothelial (collagenous fibres) 3. Fibromuscular (collagenous, elastic CT, smooth muscle cells, thicker in atria) 4. Subendocardial (loose CT, contain branches of the conducting system (Purkinje fibers\Subendocardial rami of AV bundles) Endocardium forms heart valves |
|
|
|
Composition and attachment of heart valves
|
Duplication of endocardium with internal fibrous lamina (collagenous + elastic fibers) and endothelium superficially)
Attached to fibrous anuli\fibrous rings (no blood or lymph supply) |
|
|
|
Myocardium - the layers in the ventricles
|
1. Spiral (vortex (L. whirlpool))
2. Circular 3. Longitudinal |
|
|
|
How many times thicker is the myocardium in the left ventricle than in the right?
|
3x
|
|
|
|
Atrial myocardium
a. Number of layers b. Name of the internal layer |
a. 2 layers
b. The internal is the pectinate muscles (muscli pectinati) |
|
|
|
Pericardium - parts
|
1. Fibrous pericardium (Pericardium fibrosus)
a. Sternopericardial ligaments (Ll. sternopericardiaca) b. Pleuropericardial fold (Membrana bronchopericardiaca) 2. Serous pericardium (pericardium serosum) a. Parietal layer (lamina parietalis) of pericardium b. Visceral layer (lamina visceralis) of epicardium Subserosa (tela subserosa): loose CT, fat, vessels |
|
|
|
Cavitas pericardii
a. Spaces b. Liquor pericardii ? |
a. sinus obliquus, sinus transversus
b. 20 mL |
|
|
|
Puncture of pericardium is obtained via
|
Left parasternal 4th\5th intercostal space (watch for vasa thoracica int.)
|
|
|
|
Pleuroparicardial fold\membrana bronchopericardiaca
a. what b. effect c. formed by |
a. A tissue fold jutting (stikke frem i) into the right or left embryonic pericardioperitoneal canal
b. It separates the developing pericardium from the pleural cavity c. Formed by the growth of the common cardinal veins to the midline of the body |
|
|
|
Pericardioperitoneal canal\Pleural canal
a. what b. develops into |
a. The portion of the embryonic celom that joins the pericardial cavity to the peritoneal cavity
b. Develops into the pleural cavities |
|
|
|
Sinus obliquus\Oblique pericardial sinus
|
The recess in the pericardial cavity posterior to the base of the heart bounded laterally and superiorly by the pericardial reflections on the pulmonary veins and inferior vena cava, and posteriorly by the pericardium overlying the anterior aspect of the esophagus
|
|
|
|
Sinus transversus\Transverse pericardial sinus
|
a passage within the pericardial sac, between the aorta and pulmonary trunk cranioventrally, and the left atrium and SVC dorsally.
(Formed as a result of the flexure of the heart tube, partially approximating the great venous and arterial vessels) |
|
|
|
Clinical application of pericardial sinuses
|
Can be used used as entrance to open heart surgery and to pass ligatures in afterward
|
|
|
|
Mesocardium??
|
find answer
|
|
|
|
Neurovascular supply of pericardium
|
Phrenic nerve
Pericardiophrenic vessels |
|
|
|
2 Disposing factors for hypoxia of left ventricular subendocardial layers
|
1. The thicker muscular wall of the left ventricle cause increased risk of hypoxia
2. The worse blood supply of the subendocardial layers also cause increased risk of hypoxia |
|
|
|
Biochemical cardial tests
|
1. Troponins
2. CK MB 3. Myoglobin |
|
|
|
By-passing - used vessels
|
1. Venous grafts: great saphenous vein
2. Arterial grafts: radial artery (Allen's test) 3. Artery lifting (internal thoracic artery, left gastroomental artery) |
|
|
|
PTCA - abbreviation
|
Percutaneous transfemoral coronary angioplasty
|
|
|
|
Valves in right atrium with synonyms
|
1. Valve of IVC (Eustachian valve)
2. Valve of coronary sinus (Thebesian valve) |
|
|
|
Thebesian circulation
a. What b. Where c. Open into, synonyms (3) |
a. The system of smaller veins in the myocardium - called smallest cardiac veins\Thebesian veins.
b. Most numerous in right atrium, least in left ventricle c. Open into openings of smallest cardiac veins (Thebesian\Lannelongue foramina) in the wall of the right atrium (They drain the myocardium and pass through the endocardial layer to empty directly into the right atrium) |
|
|
|
Limbus (border, edge) fossa ovalis
a. synonym b. what |
a. Vieussens anulus
b. A muscular ring surrounding the fossa ovalis in the wall of the right atrium of the heart |
|
|
|
Foramen ovale
|
The oval opening at the free margin of the septum secundum.
The persistent part of the septum primum acts as a valve during fetal life and normally postnatally becomes fused to the septum secundum to close it. |
|
|
|
Crista terminalis of right atrium
|
A vertical crest on the interior wall of the right atrium that lies to the right of the sinus of the vena cava (sinus venarum cavarum) and separates this from the remainder of the right atrium
|
|
|
|
Pectinate muscles
|
Prominent ridges of atrial myocardium located on the inner surface of much of the right atrium and both auricles
|
|
|
|
The floor of fossa ovalis is a remnant of
|
Septum primum
|
|
|
|
Atrioventricular triangle (trigonum nodi atrioventricularis)
a. what b. where c. synonym |
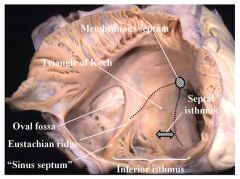
a. A roughly triangular area on the septal wall of the right atrium that mark the site of the AV node
b. Between the 1. septal cusp of the tricuspid valve, 2. coronary sinus orifice, in area of a. Sinus septum (a small folding forming the medial end of the IVC, it is developed from the dorsal wall of the embryonic sinus venosus) b. Eustachian ridge (small continuation of sinus septum) 3. tendon of Todaro (an inconsistent tendinous structure that extends from the right fibrous trigone of the heart toward the valve of IVC) c. Triangle of Koch |
|
|
|
Cusps of tricuspid valve
|
Anterior, posterior, septal
|
|
|
|
Papillary muscle
a. what b. how many |
a. One of the group of myocardial bundles which terminate in the chordae tendinae (that attach to the cusps of the AV valves.
b. Each ventricle has an anterior and a posterior papillary muscle, the right ventricle also has a septal papillary muscle (inconstant). |
|
|
|
False chordae tendinae (chordae tendinae falsae\spuriae)
a. what b. what do they do |
a. Tendinous cords that do not attach to the leaflets of the AV valves.
b. They connect papillary muscles to each other or to the ventricular wall (including the IVS), or merely pass between two points on the ventricular wall (including the septum). |
|
|
|
Trabeculae carnae of right and left ventricles
a. what b. synonym |
a. Muscular bundles on the lining walls of part of the ventricles of the heart
b. Rathke bundles |
|
|
|
Supraventricular crest
|
The internal muscular ridge that separates the conus arteriosus from the remaining part of the cavity of the right ventricle
|
|
|
|
Conus arteriosus
a. synonyms (2) b. what c. <-, -> |
a. Smooth parth (pars glabra) of right ventricle\Infundibulum
b. The left or anterosuperior, smooth-walled portion of the cavity of the right ventricle. c. <- Supraventricular crest, -> pulmonary trunk |
|
|
|
Pulmonary valve
a. Semilunar cusps\valvulae b. Nodules of semilunar Cusps (Arantius nodule) c. Lunula of semilunar cusps of aortic\pulmonary valves |
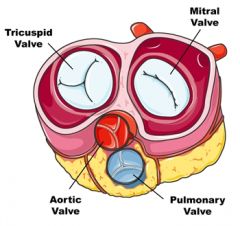
a. Anterior, left, right
b. A nodule at the center of the free border of each semilunar valve (both at pulmonary artery and aorta) c. The free border of a cusp of the semilunar valves on each side of the nodules of the semilunar cusps |
|
|
|
Cusps of mitral valve
|
Anterior & posterior
|
|
|
|
Commissural cusps (Cuspides commissurales)
|
Two small cusps (leaflet) that form the two outer of the three scallops (kamskjell) constituting the posterior cusp of the mitral valve
|
|
|
|
Commissures of the semilunar cusps of the pulmonary valve
|
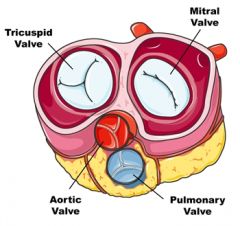
a. Incisures lying at the fibrous ring between the different cusps
b. 1. Anterior commissure - right & left semilunar cusps 2. Right commissure - dorsal & right semilunar cusps 3. Left comissure - dorsal & left semilunar cusps |
|
|
|
a. Cusps\valvulae of aortic valve
b. Other featuers (4) |
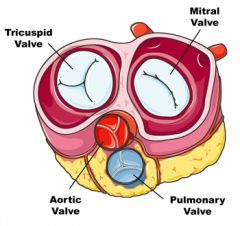
a. Right, left, posterior
b. Arantius nodules\nodules of semilunar cusps, lunulae, commissurae, aortic sinus (Valsalva sinus) |
|
|
|
Aortic sinus (Valsalva sinus)
|
The space between the superior aspect of each cusp of the aortic valve and the dilated portion of the wall of the ascending aorta, immediately above each cusp
|
|
|
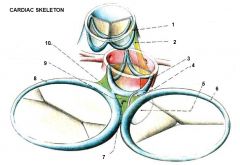
|
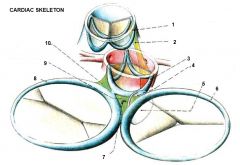
1. Anulus trunci pulmonalis
2. (Tendo infundibuli (fibrous connection between right side of anulus trunci pulmonalis & anulus aorticus) 3. Anulus aorticus 4. AV septum 5. Membranous part of IVS 6. Anulus fibrosus dexter 7. Todaro tendon (tendon of valve of IVC of Todaro)(tendo valvulae IVC Todaroi) 8. Anulus fibrosus sinister 9. Trigonum fibrosum dexter 10. Triognum fibrosum sinister |
|
|
|
Fibrous skeleton of heart
a. what b. forms |
a. A complex framework of dense collagen
b. 1. form four fibrous rings (annuli fibrosi) which surround the ostia of the valves 2. A right and left fibrous trigone (formed by connecting the rings) 3. The membranous portion of the interatrial and interventricular septa |
|
|
|
Fibrous skeleton of heart\cardiac skeleton - functions
|
1. Contribute reinforcement of the valvular ostia while providing attachment for the leaftlets and cusps of the valves
2. Providing origin and insertion for the myocardium 3. Electric "insulator", only provide passage for the AV bundle of conductive tissue through the right fibrous trigone and membranous IVS |
|
|
|
Right fibrous trigone of heart\Trigonum fibrosum dextrum
|
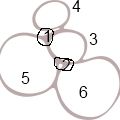
The part of the fibrous skeleton of the heart located between the aortic fibrous ring and rings surrounding the right and left AV ostia
(1 Left fibrous trigone 2. Right fibrous trigone 3. Anulus fibrosus aorticus 4. Anulus fibrosus trunci pulmonalis 5. Anulus fibrosus sinister 6. Anulus fibrosus dexter) |
|
|
|
Left fibrous trigone of heart\Trigonum fibrosum dextrum
|
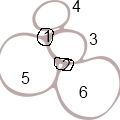
The part of the fibrous skeleton of the heart located in the interval between the left side of the AV ring and the aortic ring
(1 Left fibrous trigone 2. Right fibrous trigone 3. Anulus fibrosus aorticus 4. Anulus fibrosus trunci pulmonalis 5. Anulus fibrosus sinister 6. Anulus fibrosus dexter) |
|
|
|
Draw the cardiac skeleton - include
1. Annuli fibrosi dexter & sinister 2. Anulus fibrosus aorticus, anulus trunci pulmonalis 3. Trigonum fibrosum dexter & sinister |
1 Left fibrous trigone
2. Right fibrous trigone 3. Anulus fibrosus aorticus 4. Anulus fibrosus trunci pulmonalis 5. Anulus fibrosus sinister 6. Anulus fibrosus dexter |
|
|
|
Draw the cardiac skeleton - include
1. Annuli fibrosi dexter & sinister 2. Anulus fibrosus aorticus, anulus trunci pulmonalis 3. Trigonum fibrosum dexter & sinister |
1 Left fibrous trigone
2. Right fibrous trigone 3. Anulus fibrosus trunci pulmonalis 4. Anulus fibrosus aorticus 5. Anulus fibrosus sinister 6. Anulus fibrosus dexter |
|
|
|
Coronary veins - systems
|
1. Emptying into coronary sinus
2. Anterior cardiac veins\Anterior veins of right ventricle (venae ventriculi dextri anteriores) 3. Smallest cardiac veins (Thebesian circulation)(Venae cordis minimae) |
|
|
|
Valves in coronary veins?
|
No
|
|
|
|
Coronary lymph drainage
|
3 plexuses
2 trunks a. left to right lymphatic duct b. right to thoracic duct |
|
|
|
Right coronary artery
a. <- b. branches, % of AV and SA branches |
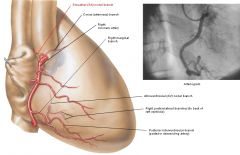
a. <- right aortic sinus (Valsalva sinus)
b. 1. conus cordis (conus arteriosus) b. -> Vieussen's circle (arterial circle formed by right and left conus arteriosus branches at the start of the pulmonary trunk) 2. Atrial bb a.Sinuatrial node branch - 65% 3. Right marginal branch (r. marginalis dexter (RMD)) 4. Posterior interventricular branch (r. interventricularis posterior (RIP)) 6. AV nodal branch (80%) 7. Right posterolateral branch (r. posterolateralis dexter (RPLD) (to back of left ventricle) |
|
|
|
Left coronary artery
a. <- b. branches |
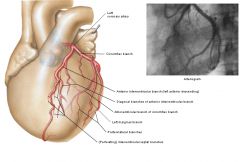
a. <- right aortic\valsalva sinus, (continues 2-3cm before branching)
b. 1. anterior interventricular branch (r. interverntricularis anterior (RIA) a. Conus arteriosus branch (r. coni arteriosi) -> Vieussen's circle b. Diagonal branch (r. diagonalis (RD) 2. Cricumflex branch (r. circumflexus (RC)) a. Atrial branches b. Left marginal branch (r. marginalis sinister (RMS)) c. Left posterolateral branch (r. posterolateralis sinister (RPLS)) d. Intermediate branch (r. intermedius (RIM)) (from bifurcation of LCA) |
|
|
|
Auscultation points\Testut points
|
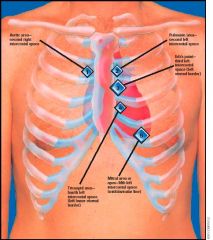
1. Mitral valve -> left medioclavicular line in 5th intercostal space
2. Tricuspid valve -> left parasternal line in 4th intercostal 3. Aortic valve -> right parasternal line in 2nd intercostal space 4. Pulmonary valve -> left parasternal line in 2nd intercostal space 5. Erb's point (for murmurs) -> left parasternal line in 3rd intercostal space |
|
|
|
SA nodal branch
a. path when arising from RCA, % b. path when arising from LCA, % |
a. SA nodal branch <- ascending atrial branch <- anterior stem of RCA (65%)
b. SA nodal branch <- circumflex branch <- LCA (35%)(run around the base of SVC to reach the SA node) |
|
|
|
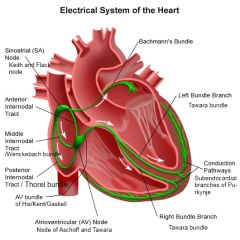
Sinuatrial node
a. Synonyms b. Location |
a. Flack\Keith\Keith-Flack node
b. Under the epicardium at the upper end of sulcus terminalis |
|
|
|
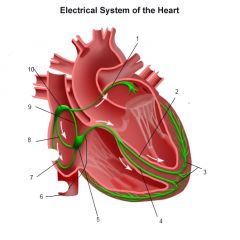
Bachmann bundle
|
Division of the theoretical anterior internodal tract that continues into the left atrium, thus providing a specialized path for interatrial conduction
(the anatomic reality of this structure has been disputed) |
|
|
|
Wenckebach bundle
|
Middle internodal tract
|
|
|
|
Thorel bundle
|
Posterior internodal tract
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kent bundle
a. what, where b. cause c. treated by |
Accessory pathway between atria a. and ventricle (left: type A pre-excitation, right: type B pre-excitation)
b. Presence cause WPW syndrome c. Treated by catheter ablation |
|
|
|
AV block
|
1. 1st degree, > 0.2s
2. 2nd degree, a. Type 1 Mobitz\Wenckebach - progressive b. Type 2 Mobitz\Hay - regular loss of AV conduction 3. 3rd degree - total |
|
|
|
AV bundle (His, Gaskell, Keith)
a. What b. Path |
a. The bundle of modified cardiomyocytes that begins at the AV node as the trunk of the AV bundle and passes through the right AV fibrous ring to the membranous part of the IVS where the trunk divides into two branches, the right bundle (crus dextrum) of the AV bundle and the left (Tawara bundles)
The two crura ramify in the subendocardium of their respective ventricles |
|
|
|
Purkinje fibers\Subendocardial branches of AV bundles
|
Interlacing fibers formed of modified cardiomyocytes. They are the terminal ramifications of the conducting system of the heart found beneath the endocardium of the ventricles
|
|
|
|
Purkinje cardiomyocytes - characteristics
|
1. Larger
2. Lighter cytoplasm, with central granulations 3. Transverse striated peripheral portion |
|
|
|
Septomarginal trabecula
a. what b. synonym |
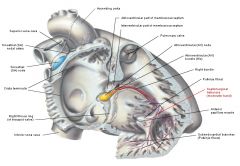
a. One of the trabeculae carneae (muscular bands\ridges) in the right ventricle that carries part of the right branch of the AV bundle from the septum to the anterior papillary muscle
b. moderator band |
|
|
|
Sympathetic cardiac innervation
a. nerves |
1. Superior, middle and inferior cervical cardiac nerves (from sympathetic trunk ganglia with same name, inf = stellate)
2. Thoracic cardiac nerves (T2-T5) (All are cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves) (also carry afferent fibers : T1-T5) |
|
|
|
Sympathetic cardiac innervation - effect
|
Positive
1. Dromotropic (speed of conduction, esp. in AV node) 2. Bathmotropic (modification of threshold of excitation) 3. Inotropic (contractility) 4. Chronotropic (rate) effects |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic innervation of heart - nerves
|
Branches from vagus nerve
1. Sup. (base of skull) & inf. (root of neck) cervical cardiac branches 2. Thoracic cardiac branches (have reflex afferent fibers as well) |
|
|
|
Anterior cardiac veins
|
2-3 small cardiac veins in the anterior wall of the right ventricle that open directly into the right atrium independently of the coronary sinus
|
|
|
|
Anterior cardiac veins
|
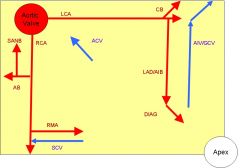
2-3 small cardiac veins in the anterior wall of the right ventricle that open directly into the right atrium independently of the coronary sinus
|
|
|
|
Valve of Vieussens
|
A prominent valve in the great cardiac vein where it turns around the obtuse margin to become the coronary sinus
|
|
|
|
Cardiac veins draining into coronary sinus
Accompanying artery |
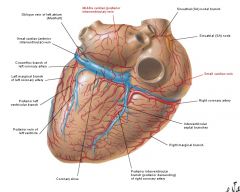
1. Great cardiac vein (circumflex branch of LCA, anterior interventricular branch of LCA)
2. Middle cardiac vein (posterior interventricular branch of RCA) 3. Small cardiac vein (RCA in coronary sulcus) (right marginal vein drains into it) |
|
|
|
Cardiac veins draining into coronary sinus
Accompanying artery |
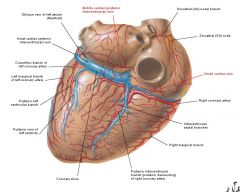
1. Great cardiac vein (circumflex branch of LCA, anterior interventricular branch of LCA)
2. Middle cardiac vein (posterior interventricular branch of RCA) 3. Small cardiac vein (RCA in coronary sulcus) |
|
|
|
Trusts - Duties of Trustee
The trustee had a duty to make sure the beneficiary wasn't drinking SPOILED CABS. |
The trustee is the legal owner of trust property, who holds it for the benefit of the beneficiaries. Legal title to, and responsibility for, the management of the trust res resides in the trustee. The beneficiaries are the beneficial owners of the trust assets, but cannot ordinarily affect or alter the dispositive or administrative provisions of the trust.
A trustee cannot be a minor, mentally incompetent person, a nondomiciliary alien, a felon, or someone who does not possess the requisite ability because of substance abuse, dishonesty, or improvidence. The court may also refuse to allow someone who does not read and write English to serve as the trustee. A corporation can serve as a trustee also. Any interested party may seek removal or suspension of a trustee for insolvency or threatened insolvency or unsuitability. Any other power to remove trustees must be granted in the trust instrument. A trustee who has accepted the position cannot resign as of right; his resignation must be accepted by the court. The duties are SPOILED CAB. |
refrain from SELF-DEALING (duty of loyalty)
PROTECT the corpus of the trust by preserving principal and diversifying the trust portfolio. refrain from usurping OPPORTUNITIES available to trust (duty of loyalty) INFORM settlor and beneficiaries of transactions involving more than 25% of trust assets and wait for objections prior to executing the transaction LITIGATE on behalf of the trust when necessary EXERCISE degree of care, skill and prudence which would be exercised by a reasonably prudent person in managing his/her own property avoid DELEGATION of duties involving judgment, discretion or power of appointment (proper administration) COMPLY with terms & duties under trust detailed ACCOUNTING, including earmarking and refrain from BORROWING funds from the trust (duty of loyalty) SEGREGATING trust assets separately from personal assets |

