![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
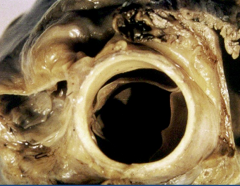
Normal Aortic Valve |
|
|
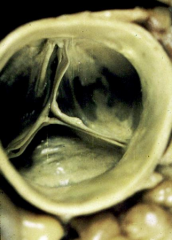
Normal Aortic Valve |
|
|
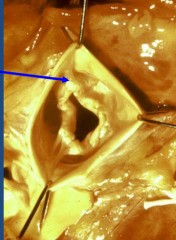
Aortic Stenosis from Chronic Rheumatic fever |
|
|
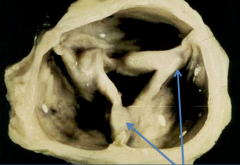
Aortic Stenosis from Chronic Rheumatic fever
*notice the fused leaflets |
|
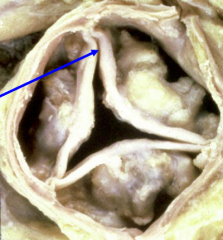
|
Senile/Degenerative/Calcific Aortic Stenosis
*notice the calcium nodules and that the leaflets are NOT fused |
|
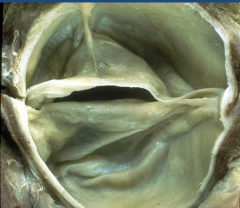
|
Non-stenotic Bicuspid Aortic Valve |
|
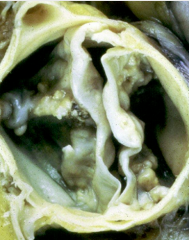
|
Stenotic Bicuspid Aortic Valve
*usually begins calicifying at age 50 |
|
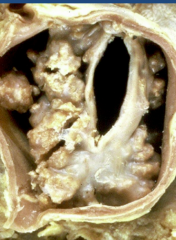
|
A VERY stenotic Bicuspid Aortic Valve
*probably experience symptoms of angina or syncope by this stage
EEEPP! |
|
|
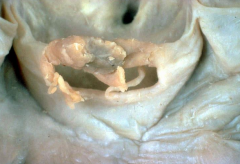
Bacterial Endocarditis that causes acute aortic insufficiency/regurgitation due to leaflet destruction |
|
|
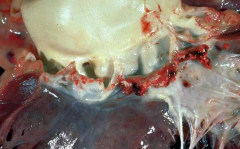
Bacterial Endocarditis that causes acute aortic insufficiency/regurgitation due to leaflet destruction |
|
|
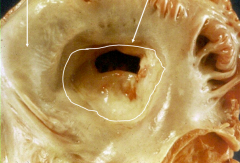
Mitral Stenosis from chronic rheumatic endocarditis
*outline shows normal diameter of opening during diastole |
|
|

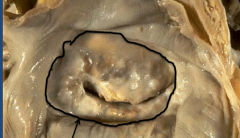
"Fish Mouth Valve" (*blub, blub*) - severe Mitral stenosis due to chronic rheumatic fever
|
|
|
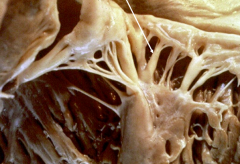
Thickened and Fused Chordae Tendinae in Mitral Stenosis from Chronic Rheumatic Fever |
|
|
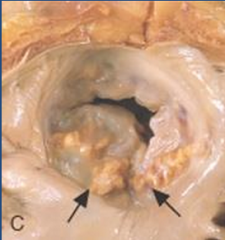
Mitral Valve Anulus Calcification causing mitral regurgitation |
|
|
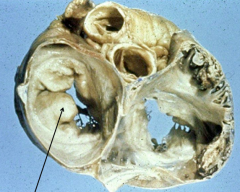
Mitral Valve Prolapse causing Mitral regurgitation |
|
|
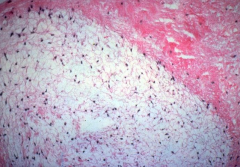
Myxomatous Degeneration in mitral valve prolapse causing mitral regurgitation
*Loose blue material is degenerated connective tissue |
|
|
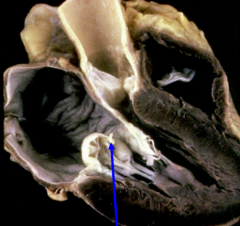
Chordae tendinae rupture secondary to mitral valve prolapse |
|
|
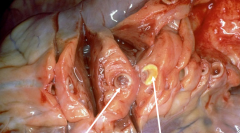
Left = Recent thrombus (pharamcologically reversible Right = well-developed plaque (can't be reversed w/ drugs) |
|
|
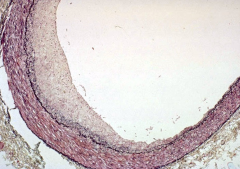
Intima hyperplasia in early atherosclerosis |
|
|
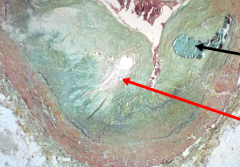
Complicated Plaque . Black = calcification . Red = lipid core |
|
|
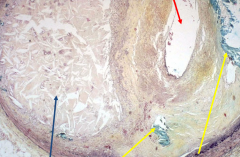
Severely occluded artery w/ atherosclerosis . Black = Necrotic core w/ cholesterol crystals . Yellow = calcification . Red = remaining lumen |
|
|
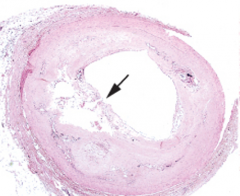
Ruptured plaque in a coronary artery (may lead to MI) |
|
|
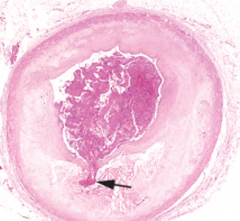
Thrombus formation in a coronary artery proceeding plaque rupture |

