![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When the heart has to compensate for increased after load, the result is ___ of the ventricular walls because the heart has to work harder to pump the blood. |
Hypertrophy |
|
|
Acquired valvular heart disease may be due to |
Age, rheumatic heart disease, or endocarditis |
|
|
Regurgitation travels in the ___ direction of the normal flow while stenosis travels in the ___ direction as the normal flow |
Opposite, same |
|
|
We refer to normal flow as ___ flow. It is smooth and it's highest velocity is within the center of the flow. |
Laminar |
|
|
True or false. If the area decreases, the cardiac output increases, so the velocity must decrease in an attempt to maintain the cardiac output. |
False. If area decreases, CO decreases, so velocity must increase to maintain CO |
|
|
We use the Bernoulli equation to describe the relationship between pressure and velocity. The simplified Bernoulli equation = |
4(V)2 |
|
|
True or false. The incidence of valvular heart disease has decreased due to advanced technology and antibiotics. |
True |
|
|
In the chamber that is ___ to the stenotic valve, the blood backs up, drives the pressure up, and creates a pressure overload pattern. |
Proximal |
|
|
True or false. In order to acquire a quick maximum pressure gradient, one can utilize the modified Bernoulli's equation. |
True |
|
|
True or false. Planimetry of the doppler waveform will provide the maximum pressure gradient, mean pressure gradient, and peak velocity across a cardiac valve. |
True |
|
|
A regurgitant valve creates a volume overload pattern because it is dumping extra blood into the ____ |
Proximal chamber |
|
|
Regurgitation increases |
Preload |
|
|
Stenosis increases |
Afterload |
|
|
Congenital heart disease means |
One is born with it |
|
|
When a normal valve is open there is a low ___ |
Pressure gradient. The pressure on either side of the valve is effectively equal. |
|
|
Laminar flow is also known as |
Parabolic flow |
|
|
Normal valve has |
Laminar flow, normal pressure and chambers |
|
|
A stenotic valve leads to |

Pressure overload pattern with turbulent flow, increased pressure and hypertrophy |
|
|
A regurgitant valve leads to |

Volume overload pattern with turbulent flow, increased volume and dilation. |
|
|
With color flow doppler, flow traveling away from the transducer is |
Blue |
|
|
With color flow doppler, flow traveling toward the transducer is |
Red |
|
|
With spectral doppler flow traveling toward the transducer appears ___ the baseline |
Above |
|
|
With spectral doppler, flow traveling away from the transducer appears ___ the baseline |
Below |
|
|
Normal, laminar color flow |
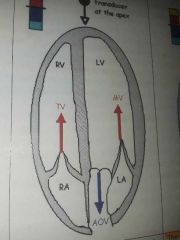
Travels in proper direction during proper phase of cardiac cycle. |
|
|
Stenotic, turbulent flow |
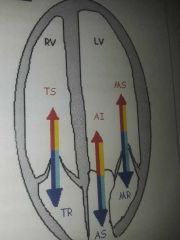
Travels in the same direction and time as normal flow |
|
|
Regurgitant, turbulent colorflow |
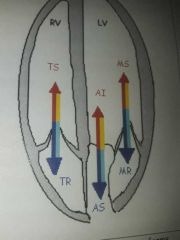
Travels in the opposite direction and phase of the cardiac cycle. |
|
|
Normal MV and TV doppler waveforms |
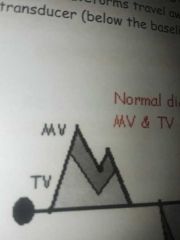
Travel toward the transducer (above baseline) |
|
|
Normal AOV and PV waveforms |
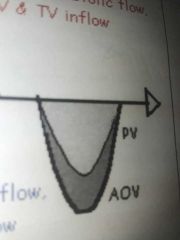
Travel away from transducer (below baseline) |
|
|
Stenotic waveforms |
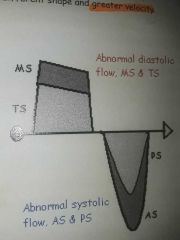
Travel in same direction as normal, but different shape and greater velocity. |
|
|
Regurgitant waveforms |
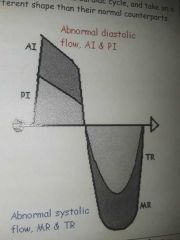
Travel in the opposite direction during opposite phase of the cardiac cycle and take on different shape than normal waveform. |
|
|
MR waveform usually has a higher velocity than___ |
TR because the LV is the high pressure side. |
|
|
A narrowing, thickening, fusion or blockage of a valve that produces obstruction to blood flow |
Valvular stenosis |
|
|
Stenosis can be caused by |
calcified valves or an obstruction |
|
|
Proximal to the stenotic valve |
Blood backs up, pressure increases, creates a pressure overload pattern (increased afterload),The heart must work harder to compensate for increased afterload causing hypertrophy. |
|
|
Aortic stenosis causes left ventricular |
Hypertrophy |
|
|
When the AV valves are stenotic the atria tend to |
Enlarge |
|
|
Mitral stenosis causes a pressure increase in the LA leading to left atrial |
Dilation |
|
|
At the level of the stenotic valve, the leaflets experience |
Doming during open phase and decreased valvular area within the valve orifice |
|
|
The increased pressure in the chamber proximal to the stenosis causes |
Doming of the tethered leaflets while open |
|
|
This valve is notorious for doming |
Mitral valve |
|
|
If the valves area decreases the cardiac output decreases so the velocity must ___ to maintain the CO |
Increase |
|
|
Distal to the stenotic valve the flow is turbulent and the pressure |
Decreases |
|
|
The more severe the stenosis |
The smaller the area, the greater the velocity, & more turbulent the blood flow |
|
|
Turbulent bloodflow displays a ___ pattern |
Mosaic |
|
|
Increased pressure proximal to stenosis and decreased pressure distal to stenosis causes an increased |
Pressure gradient |
|
|
The Max pressure gradient is acquired via ___ doppler |
CW |
|
|
Doppler echo doesn't measure pressure directly. Instead it measures ___ |
Velocity |
|
|
___ equation is used to describe the relationship between pressure and velocity (pressure gradients) |
Bernoulli |
|
|
Bernoulli equation |
P1-P2=PG=4(V)2 or simplified: PG=4(V)2 P1: pressure proximal to valve P2: pressure distal to valve V: peak velocity of flow between 2 chambers (use CW to aquire) |
|
|
Absolute peak velocity |
Overall peak velocity of same valve from various views. Use for valvular calculations. Can be done with steerable CW doppler or PEDOF |
|
|
The best correlation between the echo lab and the cath lab is the ___ |
Mean PG, not the Max PG |
|
|
If there is stenosis you should always ___ the waveform |
Trace. (Planimetry) to get the mean PG, max PG, and peak velocity |
|
|
Valvular Regurgitation (insufficiency) is the result of |
A valve that doesn't close properly. Portion of the blood travels backward from the distal chamber, through the valve while it's closed. |
|
|
Initially, a regurgitant valve creates |
Volume overload pattern (increased preload) because it's dumping extra blood into the proximal chamber. This leads to dilated chambers. |
|
|
Dilation can be good because it allows the chamber to accommodate for increased volume without causing |
An increase in pressure |
|
|
The pressure the heart must pump against |
Afterload |
|
|
Stenosis initially causes |
Pressure overload (increased afterload) |
|
|
MR |
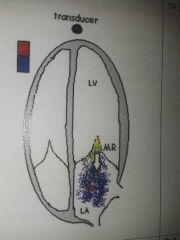
|
|
|
TR |
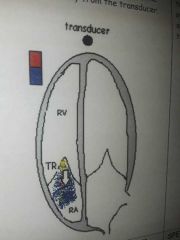
|
|
|
MR and TR spectral doppler |
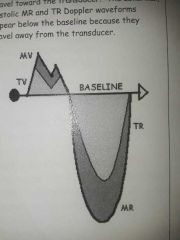
Normal MV and TV (diastolic) MR and TR (systolic) |
|
|
AI |
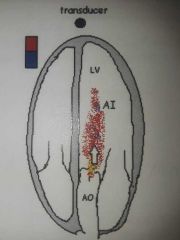
|
|
|
PI |
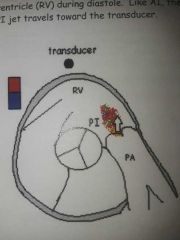
|
|
|
AI and PI spectral doppler |
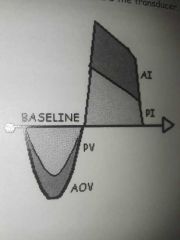
Normal systolic AOV and PV and abnormal diastolic AI and PI |
|
|
Diastolic function parameters depend on our ability to evaluate |
Pressure/volume relationships of LV filling |
|
|
Mitral valve flow provides critical information about diastolic function including |
E to A ratio, E wave deceleration time, A wave duration |
|
|
Tissue doppler imaging of mitral annular motion measures the velocity of myocardial movement as it passes through sample gate |
True |
|
|
The pulmonic A wave normally equals |
2.7mm |
|
|
Several steps are required during the diastolic function calculations to include |
Mitral valve flow, pulmonary venous flow, isovolumic relaxation time. |
|
|
When a LVOT obstruction is present, a typical finding is |
A dagger shape doppler waveform |
|
|
While acquiring diastolic function parameters, it is advised that the sweep speed be decreased from 50 mm/sec to 25 mm/sec |
False. Increased to 100 mm/sec |
|
|
The mitral A wave duration should be greater than or equal to the |
Pulmonary vein a wave duration |
|
|
An indication of increased left ventricular end diastolic pressure and decreased diastolic compliance is a pulmonary venous a wave reversal that is greater than 35 cm/sec |
True |
|
|
An indication of increased left ventricular end diastolic pressure is a pulmonary venous "a" wave duration that is less the mitral A wave duration |
False |
|
|
The isovolumic relaxation time can be found |
Between the aortic valve closing click and mitral valve opening click |
|
|
How to obtain Aortic valve area using the continuity equation |
LVOTd: PLAX 2D early-systole right before opening of cusps. VTI of LVOT: 5c or 3c, color, PW doppler, trace waveform. VTI of AOV: 5c or 3c, CW through AOV, trace waveform. |
|
|
VTI is measured in units of |
Distance |
|
|
Continuity equation |
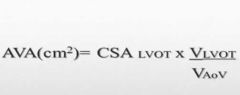
|
|
|
Continuity equation simplified |
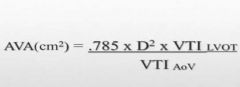
|
|
|
CSA |
To find the CSA of the LVOT use d^2×.785 |

