![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
bone as a tissue
|
connective tissue with a matrix hardened by minerals (calcium phosphate)
individual bones consist of bone tissue, marrow, blood, cartilage and periosteum continually remodels itself |
|
|
functions of the skeletal system
|
support, protection, movement, electrolyte balances, acid-base balance and blood formation
|
|
|
shapes of bones
classifications of bone by gross anatomy |
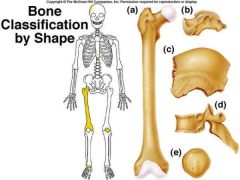
a) long - ulna, radius, femur, phalanges
b) short - carpals, tarsals c) flat - scapula, sternum, skull d) irregular - vertebra e) sesamoid - patella _) wormian |
|
|
long bones
|
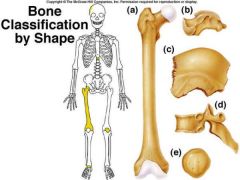
identify A
levers acted upon by muscles In general consists of a shaft with heads at either end. Composed predominantly of compact bone. Ex: femur and phalanges |
|
|
short bones
|
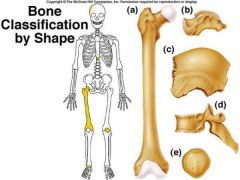
identify B
glide across one another in multiple directions Cube shaped. Contain more spongy bone than compact bone. Ex: tarsals and carpals |
|
|
flat bones
|
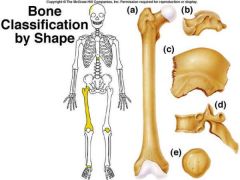
identify C
protect soft organs Thin, with two layers of compact bone with a layer of spongy bone in between them. Many are curved. Ex: bones of the skull |
|
|
irregular bones
|
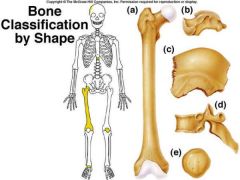
identify D
Bones that do not fall into one of the preceding categories. Ex: vertebrae |
|
|
sesamoid bones
|
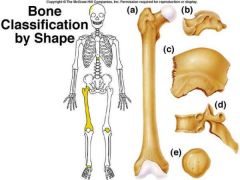
identify E
Special types of short bones formed in tendons. Ex: patella |
|
|
wormian (sutural) bones
|
Tiny bones between cranial bones.
|
|
|
classifications of bone by texture
|
compact bone and spongy bone
|
|
|
compact bone
|
smooth and homogeneous
|
|
|
spongy bone
|
composed of small trabeculae (bars) of bone and lots of open space
|
|
|
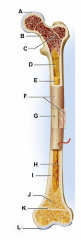
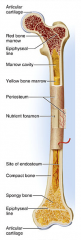
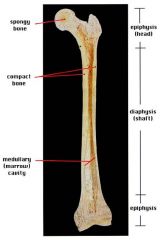
diaphysis
|
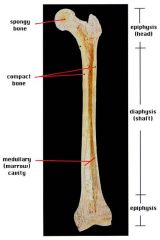
shaft
cylinder of compact bone marrow cavity (medullary cavity) lined with endosteum (osteogenic cells and reticular connective tissue) |
|
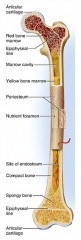
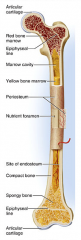
periosteum
|
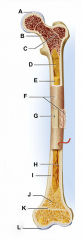
identify F
covers the shaft outer fibrous layer of collagen inner osteogenic layer of bone forming cells fibrous membrane covering |
|
|
perforating (Volkmann's) canals
|
Run into compact bone and marrow cavity from the
periosteum, at the right angles of the shaft. Complete the communication pathway between the bone interior and its external surface. |
|
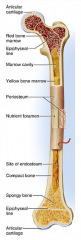
medullary cavity
|
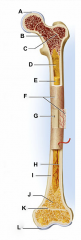
identify D
central cavity of the shaft |
|
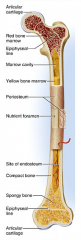
yellow marrow
|
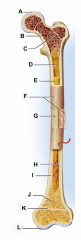
identify E
located in the medullary cavity adipose tissue |
|
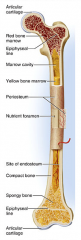
red marrow
|
identify B
located in the medullary cavity Where red blood cells are formed. In adult, occupies spaces b/w trabeculae of spongy bone, to the interior of the epiphyses. |
|
endosteum
|
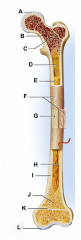
identify H
Lines inside of the shaft, trabeculae of spongy bone, and canals of compact bone. Contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts. |
|
|
epiphysis
|
enlarged ends of the bone
spongy bone covered by compact bone enlarged to strengthen joint and attach ligaments The end of long bone. Thin layer of compact bone with a layer of spongy bone in between. |
|
articular cartilage
|
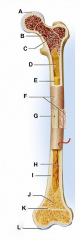
identify A and L
Covers epiphyseal surface in place of the periosteum. covers the joint surface |
|
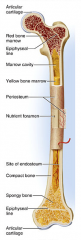
epiphyseal plate
|
precursor to C and K
growth plate Thin area of hyaline cartilage that provides for longitudinal growth of the bone during youth. |
|
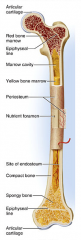
epiphyseal lines
|
identify C and K
Remnants of the epiphyseal plate, after the bone has stopped growing. |
|
|
osteon (haversian system)
|
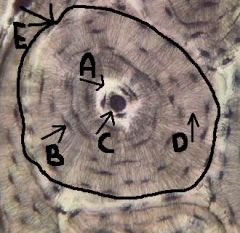
identify E
central canal and all the concentric lamellae |
|
|
central canal
|
identify C
runs parallel to long axis of the bone, carries blood-, nerves- and lymph vessels |
|
|
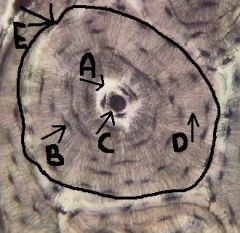
osteocytes
|
mature bone cells, spider-like appearance; located within the lacunae (B)
|
|
|
lacunae
|
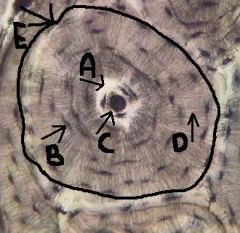
identify B
chambers which houses osteocytes |
|
|
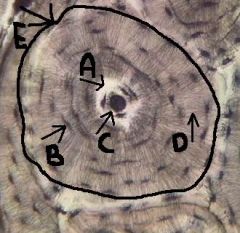
lamella
|
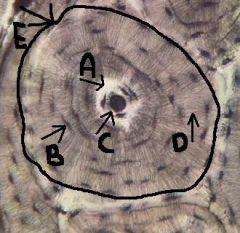
concentric circles, surrounding canal, houses lacuna and osteocytes
(think tree rings) |
|
|
canaliculi
|
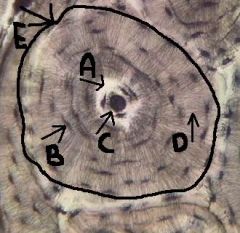
identify D
tiny canals radiating outward from the central canal to the lacunae of the first lamella and then from lamella to lamella, connects to nutrient supply |
|
|
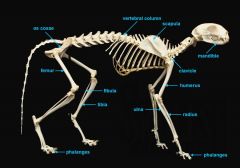
endoskeleton characteristics
|
An internal supporting skeleton
Derived from the mesoderm. Enclosed in other tissues Composed of mineralized tissues such as bone and cartilage |
|
|
exoskeleton characteristics
|
A rigid external covering
Composed of chitin, calcium carbonate, bone, cartilage, and/or dentine Ecdysis (molting) |
|
|
endoskeleton functions
|
Support & protection as internal framework
Provides system of levers with which skeletal muscles work to move the body Bones store lipids & minerals (calcium) Site for hematopoiesis (blood cell formation) |
|
|
exoskeleton functions
|
Protection
Excretion Sensory Support Defend from pests and predators Act as a barrier against desiccation Provide an attachment framework for muscles |
|
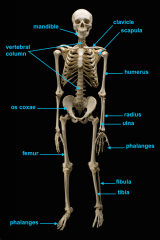
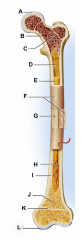
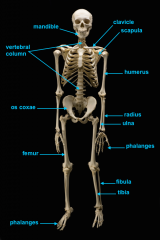
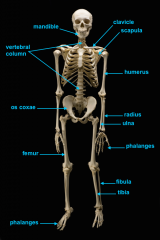
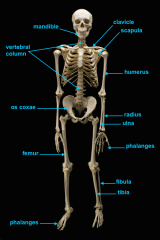
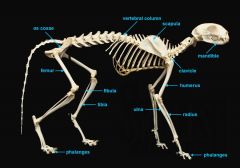
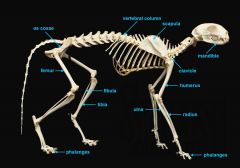
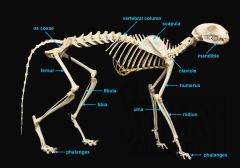
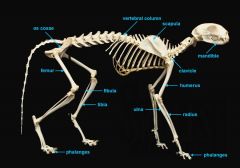
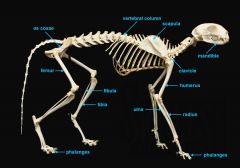
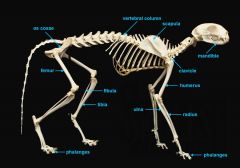
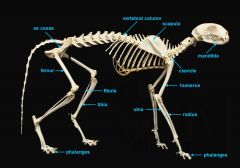
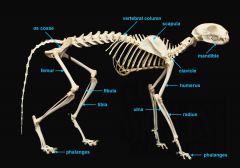
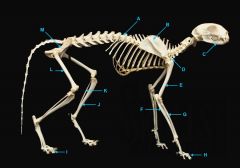
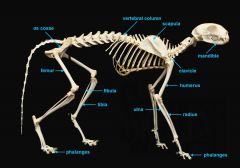
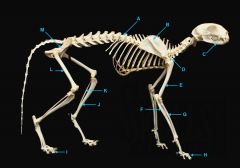
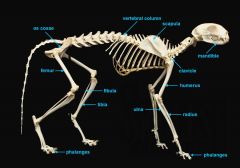
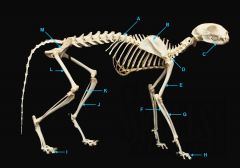
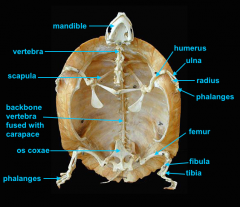
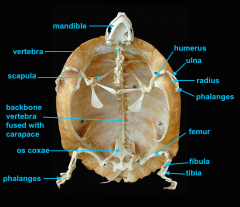
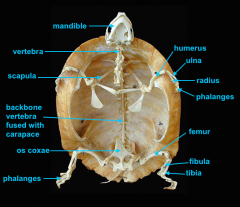
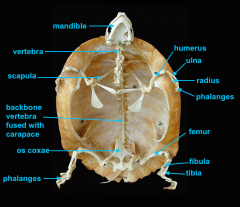
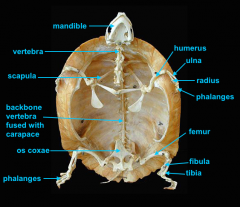
mandible (lower jaw)
|
identify A
|
|
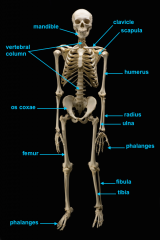
vertebral column
|
identify M
|
|
|
pectoral girdle
|
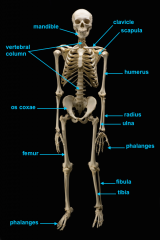
consists of the clavicle and scapula
|
|
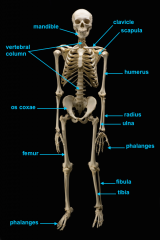
clavicle
|
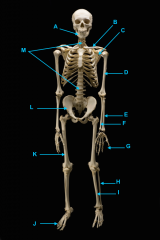
identify B
|
|
scapula
|
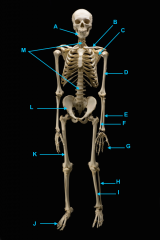
identify C
|
|
|
upper appendages
|
humerus
ulna radius phalanges |
|
humerus
|
identify D
|
|
ulna
|
identify F
longer, inner bone |
|
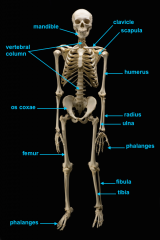
radius
|
identify E
shorter, on the thumb side |
|
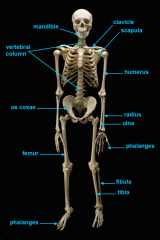
phalanges
|
identify G
|
|
|
lower appendages
|
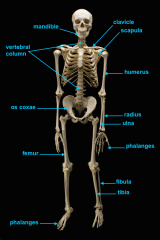
os coxae
femur fibula tibia phalanges |
|
os coxae (hip bone)
|
identify L
|
|
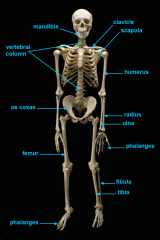
femur
|
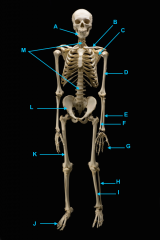
identify K
|
|
fibula
|
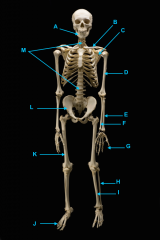
identify H
small bone |
|
tibia
|
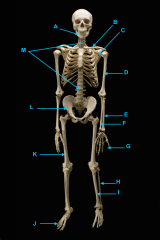
identify I
large bone |
|
phalanges
|
identify J
|
|
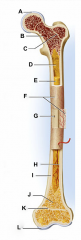
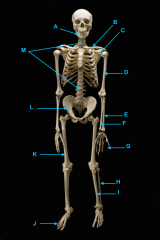
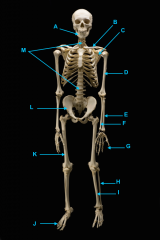
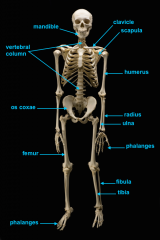
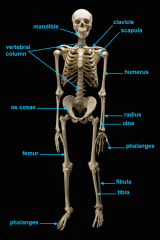
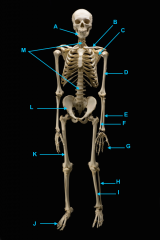
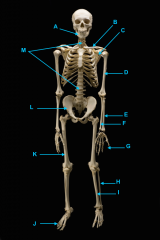
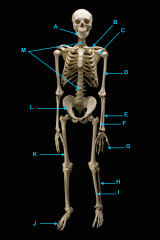
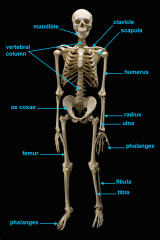
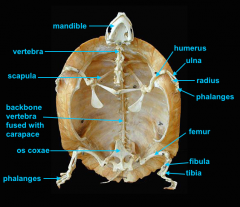
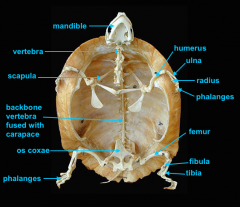
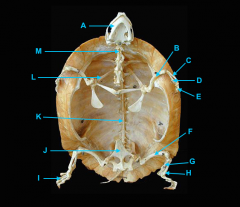
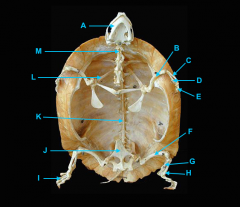
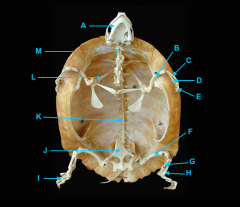
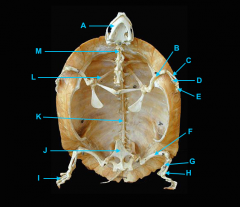
mandible
|
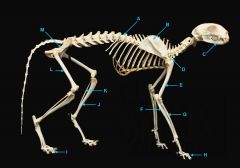
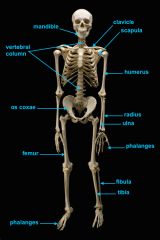
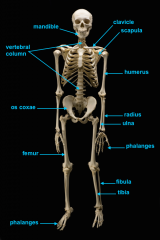
identify C
|
|
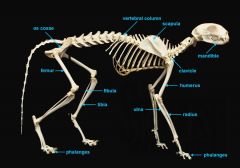
vertebral column
|
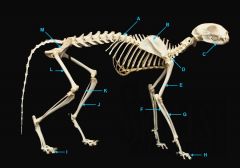
identify A
|
|
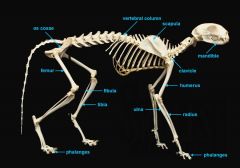
clavicle
|
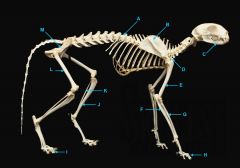
identify D
|
|
scapula
|
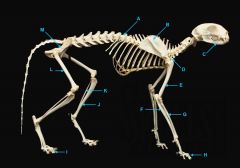
identify B
|
|
humerus
|
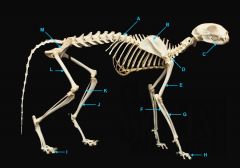
identify E
|
|
ulna
|
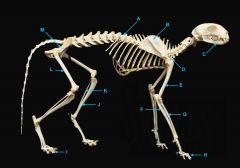
identify F
long bone |
|
radius
|
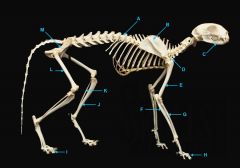
identify G
short bone |
|
phalnges
|
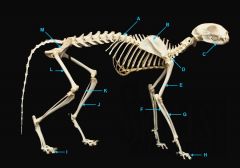
identify H
|
|
os coxae
|
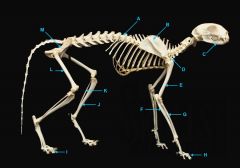
identify M
|
|
femur
|
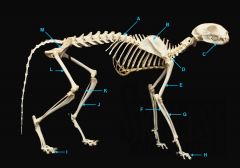
identify L
|
|
fibula
|
identify K
|
|
tibula
|
identify J
|
|
phanges
|
identify I
|
|
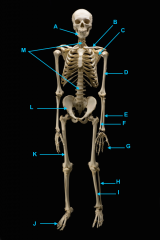
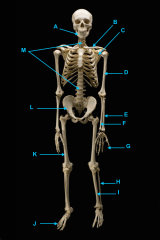
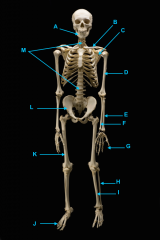
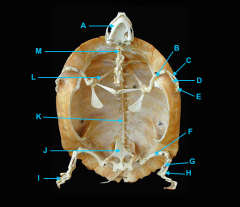
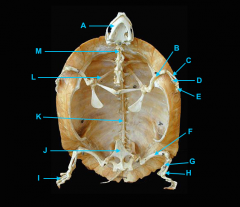
mandible
|
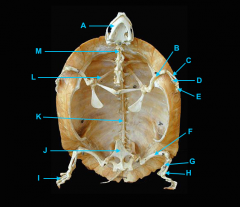
identify A
|
|
vertebral column
|
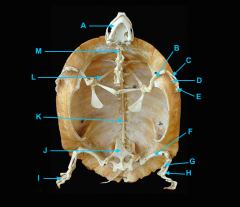
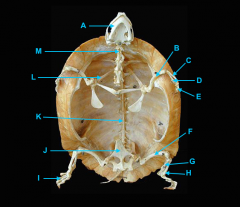
identify K - fused with plastron
identify M - cervical |
|

clavicle
|
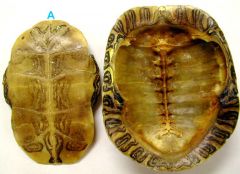
forms the plastron
|
|
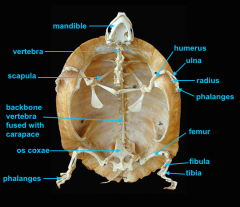
scapula
|
identify L
located inside the rib cage |
|
humerus
|
identify B
|
|
ulna
|
identify C
|
|
radius
|
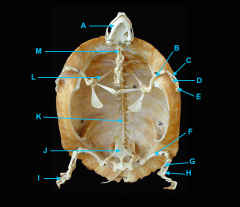
identify D
|
|
phalanges
|
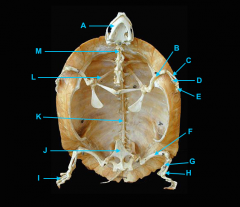
identify E
|
|
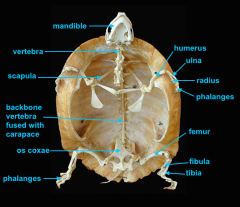
os coxae
|
identify J
|
|
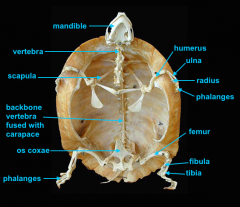
femur
|
identify F
|
|
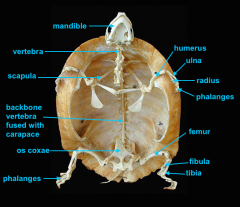
fibula
|
identify G
|
|
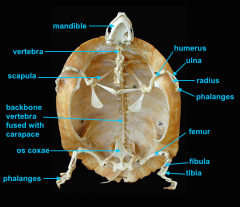
tibia
|
identify H
|
|
phalnages
|
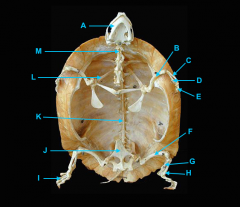
identify I
|

