![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types |
During embryonic development, fertilized egg makes different cell types Cells are organized into tissues organs organ systems and organism Gene expression orchestrates the developmental programs of animals |
|
|
Differentiation |
Process by which cells become specialized in structure and function ie: special cells to form liver. Turn certain ends on/off for this to occur |
|
|
Morphogenesis |
Physical process that gives an organism its shape |
|
|
Materials in the egg set up a program of ___That is carried out as cells divide |
Gene regulation |
|
|
Cytoplasmic determinants |
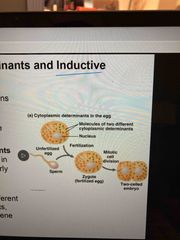
Maternal substances in the egg that influence early development Cytoplasm contains RNA, proteins, and other substances When zygote divides, uneven distribution of cytoplasmic determinants which leads to different gene expression |
|
|
Another source of developmental info in embryonic development... |
Environmental info and signals from other cells (Induction) |
|
|
Induction |
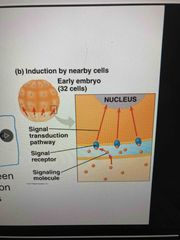
Signal molecules from embryonic cells cause changes in nearby target cells (cell signaling) These interactions induce differentiation of specialized cell type |
|
|
Determination |

Commits a cell to becoming a particular type Precedes differentiation Precursor cell-determined cell-differentiated cell (molecular change) ie: MyoD and myoblast |
|
|
Marked by the production of tissue-specific proteins |
Cell differentiation Differentiation is specific structure and function |
|
|
Example of cell differentiation |
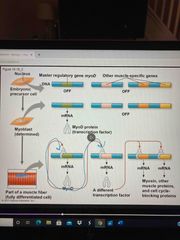
Myoblast cells are determined to form muscle cells and produce large amounts of muscle-specific proteins —> MyoD (master regulator gene) encodes a transcription factor that commits cell to becoming skeletal muscle—> Some target genes for MyoD encode additional muscle specific transcription factors |
|
|
Pattern formation |
Development of spatial organization of tissues and organs Begins with establishment of major axes in animals |
|
|
Positional information |
Molecular cues control pattern formation Tells cell it’s location relative to the body axes and to neighbor cells |
|
|
Life cycle of drosophila(pattern formation) |
Cytoplasmic determinants in unfertilized egg determine the axes before fertilization After fertilization, embryo develops into segmented larva w three stages Then forms pupa, metamorphosis into an adult |
|
|
Homeotic genes |
Control pattern formation in the late embryo, larva, and adult stages Nobel prize for finding this in Lewis, nusslein-volhard, and wieschaus |
|
|
Maternal effect genes |
Encode auto plastic determinants that initially establish the axes of the drosophila Also called egg-polarity genes ie: biocides gene |
|
|
Egg polarity genes |
Also called maternal effect genes Control orientation of the egg and consequently the fly |
|
|
Bicoid gene |
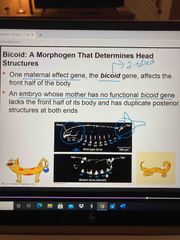
Maternal effect gene that affects front half of body An embryo who’s mother has no bicoid gene functioning lacks the front half of its body and has duplicate posterior ends |
|
|
Morphogens |
Substances that establish an embryos axes and other features of its form Morphogen gradient hypothesis |
|
|
Morohogen gradient hypothesis |
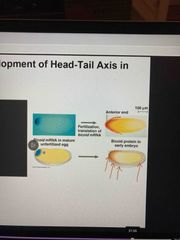
There are gradients of morphogens Experiments showed that bicoid is distributed in an anterior to posterior gradient in the early embryo |
|
|
Bicoid research was groundbreaking for 3 reasons... |
1. Identified specific protein required for early steps in pattern formation 2. Increased understanding of mothers role in embryo development 3. Demonstrated a gradient of molecules determine polarity and position in embryo |
|
|
Evolutionary developmental biology |
Evo-devo Study of genes and how they shape the development of the body Molecular development |

