![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the nucleus of an atom made of?
|
Protons and neutrons.
|
|
|
What is the relative charge of an electron?
|
-1
|
|
|
What is the relative charge of a proton?
|
+1
|
|
|
What is the relative charge of a neutron?
|
0
|
|
|
What is the relative mass on an electron?
|
0.0005
|
|
|
What is the relative mass of a proton?
|
1
|
|
|
What is the relative mass of a neutron?
|
1
|
|
|
What is an isotope?
|
Elements with the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
|
|
|
Groups are what?
|
Elements with the same amount of electrons in the outer shell.
|
|
|
How are groups arranged?
|
Vertically
|
|
|
What do periods increase in order of?
|
In order of how many shells the electrons occupy.
|
|
|
How are periods arranged?
|
Horizontally.
|
|
|
What did John Dalton do?
|
Developed the early theory of atoms.
|
|
|
Who confirmed John Dalton's theory?
|
JJ Thompson, Rutherford and Bohr.
|
|
|
Geiger and Mardsen's findings confirmed or disproved Dalton?
|
Disproved
|
|
|
What are atoms with 8 electrons in the outer shell?
|
Stable electronic Structure
|
|
|
How an atoms become stable?
|
By transferring electrons.
|
|
|
What does OIL RIG stand for?
|
Oxidation is loss
Reduction is gain |
|
|
Metals atoms lose/gain electrons to become stable?
|
Lose, and become a positive ion.
|
|
|
Non-metal atoms gain/lose electrons to become stable?
|
Gain to become negative ions.
|
|
|
What is the process of ionic bonding?
|
A metal atom becomes a positive atom by losing an electron and non-metal gains an electron to become a negative ion. These then attract each other.
|
|
|
How do we illustrate ionic bonding?
|
Dot and cross diagram
|
|
|
Draw a diagram for the ionic bonding of Magnesium and Oxygen.
|
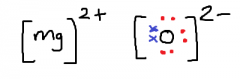
|
|
|
What is the structure of sodium chloride or magnesium oxide?
|
Giant ionic lattice with have strong electrostatic attraction.
|
|
|
When does sodium chloride conduct electricity?
|
In solution or molten
|
|
|
When does MgO conduct electricity?
|
When molten
|
|
|
Why does MgO have a higher boiling point than NaCl?
|
-Stronger electrostatic attraction
-Each Mg donates 2 electrons to each oxygen whereas Na only does 1 to chlorine -Mg has tiny radius so gets very close to the oxygen which makes bonds stronger |
|
|
What is covalent bonding?
|
Non-metals share electron pairs between atoms.
|
|
|
Draw a dot and cross diagram for Cl2
|
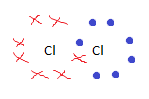
|
|
|
Why don't CO2 and H2O conduct electricity?
|
There's no free electrons.
|
|
|
The group number is the same as?
|
The number of electrons in the outer shell
|
|
|
In 1865, what did Newlands do?
|
Put 56 elements into groups and found that every 8th one behaved similarly.
|
|
|
In 1869, what did Mendeleev do?
|
Arranged elements into a table and noticed periodic changes in properties. He also noticed gaps and predicted more elements would be found.
|
|
|
In 1891 what did Mendeleev's table not contain?
|
The noble gasses.
|
|
|
What are the properties of group one metals?
|
-React vigorously with water
-Give off hydrogen -Reacts with water to form an alkali (the hydroxide of the metal) |
|
|
Put these in order of reactivity:
Sodium Lithium Potassium |
Most to least
1. Potassium 2. Sodium 3. Lithium (Reactivity increases down the group) |
|
|
What is the process called when an atom loses an electron?
|
Oxidation
|
|
|
How can we test if lithium, sodium or potassium are present in a compound?
|
The flame test
|
|
|
Explain the process of the flame test
|
-A flame test wire is moistened with dilute hydrochloric acid
-Then dipped into the solid chemical -Then put over a blue Bunsen flame -Colours of flames are recorded |
|
|
What colour will a flame burn if lithium is present?
|
Red
|
|
|
What colour will a flame burn if sodium is present?
|
Yellow
|
|
|
What colour will a flame burn if potassium is present?
|
Lilac
|
|
|
At room temp, what is chlorine?
|
A green gas
|
|
|
What is bromine at room temp?
|
Orange liquid
|
|
|
What is iodine at room temp?
|
Grey solid
|
|
|
Why are atoms with less shells more reactive?
|
The nearer the outside shell is to the nucleus, the more pull there is and thus it's easier to pull in an electron. This means it's more reactive.
|
|
|
What is a halogen?
|
A group 7 element
|
|
|
What happens when halogens react with alkali metals?
|
A metal halide is formed.
|
|
|
Name a metal halide
|
Potassium iodide
|
|
|
What happens if a halide is bubbled through solutions of metal halides?
|
Either there'll be no reaction, or there'll be a displacement reaction.
|
|
|
What is a displacement reaction?
|
A type of oxidation-reduction reaction when an element or ion moves out of one compound and into another - that is, one element is replaced by another in a compound.
|
|
|
Give an example of a displacement reaction?
|
Cl + KBr --> KCl + Br
Chlorine displaces the bromine to form bromine solution. This makes an orange solution. |
|
|
What colour is the product of a bromine + potassium iodide reaction?
|
It's just iodine solution, so red-brown
|
|
|
What colour are copper compounds?
|
Blue
|
|
|
What colour are Iron(II) compounds?
|
Pale green
|
|
|
What colour are Iron(III) compounds?
|
Orange/brown
|
|
|
What are transition elements often used as?
|
Catalysts
|
|
|
Which catalyst is used in the Haber process?
|
Iron
|
|
|
What catalyst is used in the manufacture of margarine?
|
Nickel
|
|
|
What happens when a metal carbonate is heated?
|
It undergoes thermal decomposition
|
|
|
What is a catalyst?
|
A chemical that speeds up a reaction but is not changed or used up by the reaction.
|
|
|
How do we identify the presence of metal ions in a solution?
|
Add sodium hydroxide solution
|
|
|
What colour does Cu2+ turn when you add sodium hydroxide solution?
|
Blue solid
|
|
|
What colour does Fe2+ turn when you add sodium hydroxide solution?
|
Grey/green solid
|
|
|
What colour does Fe3+ turn when you add sodium hydroxide solution?
|
Orange/brown gelatinous solid
|
|
|
Cu2+, Fe2+ and Fe3+ are all ...?
|
Metal hydroxide precipitates
|
|
|
Name a physical property of copper
|
High thermal conductivity- making it good for saucepans.
|
|
|
Name a chemical property of gold
|
Resistance to attack by oxygen
|
|
|
Name some physical properties of metals
|
Lustrous, malleable, ductile
|
|
|
Why is aluminium good for making car frames?
|
It has low density
|
|
|
Name three conductive metals
|
Copper, silver and gold
|
|
|
What is a metallic bond?
|
Strong electrostatic force between close-packed positive metal ions and a sea of de-localised electrons.
|
|
|
What are superconductors?
|
Materials that conduct with little or no resistance as there's no magnetic fields inside it. Mercury is one at -268.8 degrees.
|
|
|
What are the potential benefits of superconductors?
|
-Loss free power transmission
-Superfast electric circuits -Powerful electromagnets |
|
|
Why is the use of superconductors low?
|
Because they require extreme temperatures
|
|
|
What are so pollutants found in river water?
|
-Nitrates from fertilisers
-Pesticides from crop spraying -Lead from old water pipes |
|
|
What are the three stages of water purification?
|
Sedimentation: chemicals added make solid particles and bacteria settle out
Filtration: layer of sand or gravel filters out remaining fine particles, some types also filter microbes Chlorination: chlorine added to kill microbes |
|
|
What colour is barium sulphate?
|
white
|
|
|
What colour is silver bromide?
|
cream
|
|
|
What colour is silver iodide?
|
yellow
|
|
|
What colour is silver chloride?
|
white
|

