![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Give an example of a fast reaction and slow reaction |
Slow: rusting Fast: burning and explosion |
|
|
The limiting reactant determines the .......... Amount of product that can be made |
Maximum |
|
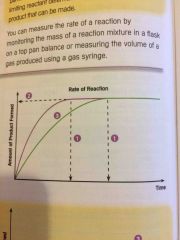
What does each number stand for? |

|
|

Fill in the gaps |
1.faster 2. Energy 3. Fast |
|
|
Increasing temperature effect the rate of reaction, why? |
Increase in kinetic energy- the particles move faster; the greater change of them colliding resulting in a faster reaction. Also, more energetic collisions lead to more successful collisions. |
|

Fill in the gaps |
1. Fewer successful collisions 2. Collide 3. Faster reaction |
|
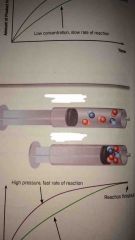
Which one is a high pressure reaction? |
The bottom one with the particles more close together |
|

Fill in the gaps |
1.less often 2. Fewer successful collisions |
|

Fill in the gaps |
1. Faster 2. Powdered solids 3. Reactants 4.greater 5. Increases 6.greater 7. Chance Of colliding 8. Explosion |
|

Fill in the gaps |
Used or changed itself at the end of the reaction |
|
|
To conclude name all the factors you've learnt that increase rate of reaction |
-temperature -pressure (gas) -surface area (solid) -concentration -catalyst |

