![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How are compounds formed?
|
When two or more atoms join together
|
|
|
How do the atoms of elements join together? |
By sharing or transferring electrons |
|
|
Why is this done? |
To achieve stable electronic structures |
|
|
Which atoms already have a stable electronic structure? |
Noble gases |
|
|
What is it called when atoms of non-metallic elements join together by sharing electrons? |
Covalent bonding |
|
|
What is produced when metallic and non metallic elements react? |
Ionic compounds |
|
|
The metal atoms lose electrons to form what type of ion? |
Positive |
|
|
The atoms of a non-metals gain electrons which results in? |
Negative ions |
|
|
How do ions attract each other? |
Oppositely charged |
|
|
What is this called? |
Ionic bonding |
|
|
What do elements in Group 1 of the periodic table have? |
Atoms with 1 electron in their outer shell |
|
|
How many electrons do Group 7 atoms have in their outer shell? |
7 |
|
|
How do we write the compound of sodium chloride and why? |
NaCl Because they have the same amount of sodium ions as they do chloride ions |
|
|
Describe the detail of an ionic lattice.
|
Positive and negative ions are joined together, forming a giant ionic lattice. Each one is held to the other by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
|
|
|
Explain properties of an ionic lattice.
|
The ions being held together increases the boiling and melting point because it takes more energy to break the bonds. They are solid because the particles are packed tightly together.
|
|
|
Giant Ionic Lattice: Sodium and Chlorine
|
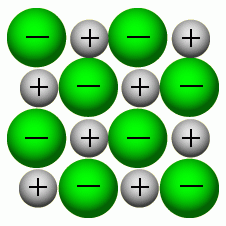
|
|
|
State a definition for a covalent bond.
|
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
|
|
|
Name element that has a giant covalent structure.
|
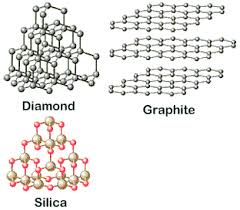
|
|
|
Explain the formation for a covalent bond.
|
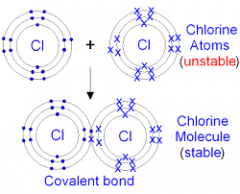
When two non-metal atoms share a pair of electrons:
|
|
|
Dot and cross diagram for methane:
|
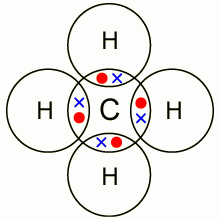
|
|
|
Explain the bonding for a giant covalent structure.
|
They contain many atoms (non-metal) joined by covalent bonds, carbon atoms hold the bonds together strongly.
|
|
|
List some elements that have giant metallic structure.
|
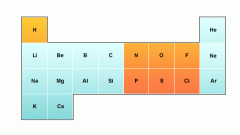
|
|
|
Describe the bonding in metals.
|
Metals form giant structures, electrons in the outer shells of the metal atoms are free to move. The metallic bond is the force of attraction between these free electrons and metal ions.
|
|
|
State properties of ionic compounds.
|
High melting and boiling points, solid and R.T.Conduct electricity when liquid.
|
|
|
Explain why ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
|
Ionic bonds are very strong - a lot of energy is needed to break them. The carbon atoms hold the bond together.
|
|
|
Explain why ionic compounds conduct electricity when liquid.
|
Ionic compounds only conduct electricity if their ions are free to move, they are stable when the compound is solid, there is space for them to move when they become liquid.
|
|
|
Give examples of substances made of simple molecules.
|
Covalently bonded compounds: Hydrogen, ammonia, methane and water.
|
|
|
State physical properties of substances made of simple molecules.
|
Low melting and boiling points; weak intermolecular forces break down easily.Not conductive; Have no free electrons or overall charge.
|
|
|
List examples of structures with giant covalent structures.
|
Diamond, graphite, silica, fullerenes.
|
|
|
Recognise giant covalent structures.
|
Non-metal atoms, joined by adjacent atoms by covalent bonds.
|
|
|
State physical properties of graphite.
|
Very high melting points, conducts electricity, much softer then diamond, carbon atoms can slide over each other.
|
|
|
State physical properties of diamond.
|
Very high melting points, does not conduct electricity, structure: one carbon atom joined to 4 other carbon atoms, making it very hard.
|
|
|
Explain what a fullerene is.
|
A large, hollow ball of over 60 carbon atoms, they are very strong and have high melting points and boiling points. They're used as semiconductors in electrical circuits and reinforcement in tennis rackets.
|
|
|
State the physical properties of metals.
|
High melting and boiling points, heat and electrical conductor, dense and high tensile strength.
|
|
|
Explain how properties of a certain metal make them suited to their specific purpose.
|
Copper is an electrical conductor so it's suitable for electrical wiring.Aluminium is a heat conductor so suitable for frying pans.
|
|
|
Define an alloy.
|
A mixture of two elements, one of which is a metal. They are harder than the metal they contain, they contain atoms of different sizes; distorting the regular arrangements. They can't slide over each other this way.
|
|
|
Explain why metals can be bent into shape.
|
They consist of layers of atoms, these layers can slide over each other.
|
|
|
Explain how polymers are made.
|
Multiple monomers (double bond) are joined in a reaction (polymerisation) to create polymers (single bonds).
|
|
|
Give an example of a polymer that has different properties in different conditions.
|
High density polyethene (HDPE): Strong, softens at 120°C.Low density polyethene (LDPE): Softens at 85°C, more flexible and weaker than HDPE.
|
|
|
Explain why Polyvinyl chloride is fit for it's purpose.
|
Used for wall coverings, electric cables and packaging. Is stiff and hard wearing so is reliable and strong enough for the job.
|
|
|
Define thermosetting and give an example.
|
Do not soften when heated and cannot be reshaped. Example: Vulcanised rubber.
|
|
|
Define thermosoftening and give an example.
|
Can be reheated while hot. Example: Polyethene.
|
|
|
Explain cross linking in thermosetting.
|
The links created between polymer chains create stronger bonds and prevent movement between the chains. If the chains can't be broken the molecule can't be melted.
|
|
|
Explain how intermolecular forces between the polymer molecules in thermosoftening affects their properties.
|
Polymers melt when their intermolecular forces are over come. Weak intermolecular forces pull the polymer molecules towards each other.
|
|
|
Define nanoscience.
|
A nanometre, 1 nm, is one billionth of a metre. They have a large surface area, so they are able to react very quickly. Making them useful as catalysts to speed up reactions.
|
|
|
List advantages and disadvantages of nanoscience.
|
Advantages:New catalysts, new computers, stronger and lighter building materialsDisadvantages:Loss of jobs in farming, costly process.
|
|
|
Define the rate of reaction.
|
The speed of a reaction, affected by temperature, concentration, pressure of reacting gases, surface area of reacting solids, and the use of catalysts.
|
|
|
List ways of finding rate.
|
1) Measure the rate at which a reactant is used up.2) Measure the rate at which a product is formed.
|
|
|
Explain how to calculate the rate of reaction.
|
Rate of reaction = Amount of reactants used/product formed time taken
|
|
|
Define collision theory.
|
Reactions that occur slowly, low rate of reaction. Occur quickly, high rate of reaction. Collision theory is the factors that effect this rate of reaction.
|
|
|
Explain how surface area effects the rate of reaction.
|
As the surface area increases, more particles are exposed to other reactants, there are more collisions and therefore more successful collision. Increasing the rate of reaction.
|
|
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
What effect increasing the concentration of reactants in solutions has on the rate of reaction.
|
Increasing the concentration means there are more particles so they are more likely to collide, meaning more successful collisions.
|
|
|
Describe what is meant my gas pressure.
|
Gas particles moving and bumping in to each other or the walls of their container. This causes the pressure, the more gas particles that hit the wall the more pressure that gets built up.
|
|
|
What effect does increasing the pressure of reacting gases have on the rate of reaction.
|
The increase in pressure means an increase in gas particles, the more they bump into each other, the more collision, the more successful collisions.
|
|
|
Define a catalyst.
|
A substance that speeds up the rate of reaction, there's only one catalyst for one reaction.
|
|
|
Give an example of an industrial process that uses a catalyst.
|
Manufacturing of margarine uses Nickel as a catalyst.
|
|
|
Why are catalyst using for industrial processes?
|
More can be made in a shorter time.Catalyst can be reused.Reaction can occur at lower temperatures.
|
|
|
State some advantages of catalysts.
|
Reactions can happen at lower temperatures.Speeds up reaction.Saves money.Catalyst doesn't run out.
|
|
|
State some disadvantages of catalysts.
|
Only one catalyst suits one reaction.Expensive to buy.Reactive substances must be kept clean.Need to be removed from the product afterwards.
|
|
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
Define exothermic reactions.
|
A reaction in which heat is released into the atmosphere.
|
|
|
Define endothermic reactions.
|
A reaction in which heat is taken in from the atmosphere.
|
|
|
State an example of an exothermic reaction.
|
CombustionOxidisation reactionsNeutralisation reactions
|
|
|
State an example of an endothermic reaction.
|
Electrolysis.Calcium carbonate in a blast furnace.Ethanoic acid and calcium carbonate.
|
|
|
Explain how energy change in a reaction can be monitored.
|
Recording the temperature at regular intervals. Measuring the mass of the reactants and products at the beginning and end of the reaction.
|
|
|
List properties of acids.
|
Have a pH between 1 and 6.The lower the pH the stronger the acid.
|
|
|
List properties of alkalis.
|
Have a pH between 8 and 14.The higher the pH the stronger the alkali.
|
|
|
Explain in terms of ions what acids are.
|
Acids produce hydrogen ions that are soluble in solution.
|
|
|
Explain in terms of ions what alkalis are.
|
Alkalis produce hydroxide ions that are also soluble in solution.
|
|
|
Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid react. What's the salt produced.
|
Sodium chloride. Sodium and acid. Leaving out the ions from the acid and alkali.
|
|
|
What's the ionic equation for neutralisation?
|
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
|
|
|
Define neutralisation.
|
A reaction in which acidity or alkalinity is removed. A neutralisation involving an acid and a base (or alkali) always produces salt and water.
|
|
|
State the general word equation when a base reacts with an acid.
|
acid+base→salt + water
|
|
|
State the general word equation when a metal reacts with an acid.
|
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
|
|
|
Record a method to make soluble salts.
|
* acid + metal oxide → salt + water* acid + metal hydroxide → salt + water
|
|
|
Record a method to make insoluble salts.
|
silver nitrate (soluble) + sodium chloride (soluble) → silver chloride (insoluble) + sodium nitrate (soluble)AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
|
|
|
What's a precipitation reaction?
|
Silver chloride forms a precipitate. The precipitate can be filtered, washed with water on the filter paper and then dried in an oven.
|

