![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why is rubber used for car tyres? |
Rubber is hard and elastic |
|
|
Fibres are used to weave cloth into clothes. True or false? |
True |
|
|
Plastics keep their shape when moulded into objects like washing-up bowls. True or false? |
True |
|
|
What do we mean by melting point? |
The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. |
|
|
What does tensile strength mean? |
The force needed to break a material when it is being stretched. |
|
|
What does compressive strength? |
The force needed to break a material when it is being stretched. |
|
|
What does stiffness mean? |
The force needed to bend a material |
|
|
What does hardness mean? |
How well a material stands up to wear |
|
|
What is density? |
The mass of a given volume of the material. It compares how heavy something is for its size. |
|
|
What are the units of density? |
-Mass per unit volume -g/cm³ or kg/cm³ |
|
|
Ropes are made by winding fibres together. What would we have to do to increase the strength? |
The more that are wound, the greater the strength. |
|
|
What is an outlier? |
A result which is significantly different to the other results. |
|
|
What is another term used for "best estimate"? |
Average / Mean |
|
|
What are metals? |
Chemicals which are shiny, malleable and electrical conductors. |
|
|
What do ceramics include? |
Clay, glass and cement. They are hard and strong. |
|
|
What is crude oil? |
Crude oil (petroleum) is a mixture of thousands of hydrocarbons. |
|
|
What are hydrocarbons? |
Compounds of just carbon and hydrogen atoms. |
|
|
What are most hydrocarbons from crude oil are as? |
Fuels |
|
|
When fuels burn in oxygen, what products are made? |
Carbon dioxide and water |
|
|
What is the formula for alkanes? |
C(n)H(n+2) |
|
|
What is the formula for alkenes? |
C(n)H(2n) |
|
|
How is crude oil separated? |
Fractional distillation |
|
|
In fractional distillation how are the liquids grouped together? |
Liquids with similar boiling points are put together in fractions. |
|
|
The smaller the molecule chain length, the higher the boiling point. True or false? |
False - the boiling point would be lower |
|
|
The smaller the molecule chain length, the smaller the forces between molecules. True of false? |
True |
|
|
List the gases as you go down the fractional distilllation column. |
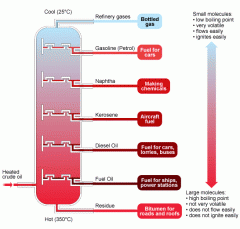
|
|
|
Temperatures decrease as you go down the fractional distillation column. True or false? |
False - temperatures increase as you go down the column |
|
|
In crude oil, where are the attractive forces? |
Between molecules holding them together |
|
|
What happens to the force between the molecules as the hydrocarbon chain length increases? |
The force between these molecules increases |
|
|
Why do larger molecules have higher boiling points? |
They need more energy to break them out of a liquid to form a gas. |
|
|
What is a polymer? |
A large molecule made by joining many smaller molecules called monomers. |
|
|
How are polymers made? |
Polymerisation |
|
|
What happens in Polymerisation? |
Some small molecules can join together to make very long molecules called polymers. |
|
|
Ethene is a monomer used to make what? |
Polyethene |
|
|
Explain why during the distillation of crude oil, small hydrocarbon molecules rise to the top of the tower. |
-Different hydrocarbons have different boiling points, they condense at different levels up the tower. -Hydrocarbons with high boiling points condense first, low down the tower. -Hydrocarbons with low boiling points can get all the way to the top before they condense. -Some hydrocarbons have very low boiling points and so they are gases. They don't condense but are collected as 'fuel gases'. |
|
|
When in molecules are forces the strongest? |
When the molecules are close together |
|
|
The stronger the force... |
-The more energy id needed to separate the molecules. -The higher the melthing point. |
|
|
Low Density Polyethene (LDPE) has long molecules with branches. What do these branches do? |
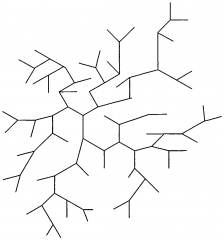
The branches keep the molecule chains apart, so the forces between different molecules are weak. |
|
|
Items like plastic carrier bags are made from LDPE. Name some properties of a carrier bag. |
-Weak -Flexible -Soft -Low melting point |
|
|
High Density Polyethene (HDPE) has long chains but no branches, so the molecules are aligned close to each other. What does this suggest about its properties. (E.g. water pipes) |
-Much stronger -Hard -Stiff -Used to make long-lasting products |
|
|
How can polymer chains be altered? |
By replacing hydrogen atoms with other atoms or groups of atoms. |
|
|
HDPE has a high degree of crystallinity. What does this mean? |

-The material has a higher density than LDPE -The forces of attraction between polymer molecules are strong -The material is stronger, and has a higher melting point, than LDPE |
|
|
What does making the molecule chain longer do? |
Makes it stronger |
|
|
What can you say about the forces needed to separate longer chain molecules? |
More force is needed to separated |
|
|
What can you say about the melting point of longer chain molecules? |
Higher melting points than short chains |
|
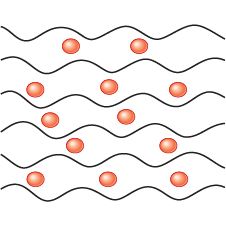
What are Plasticisers used for? |
To make a polymer softer |
|
|
What are Plasticisers? |
They are small molecules inserted into polymer chains to keep them apart, weakening the forces between them. |
|
|
What are thermoplastics? |
They soften when heated and can be moulded into shape. |
|
|
Thermosetting plastics do not soften when heated, as they contain cross-links. What do these cross-links do? |
They lock the molecules together so they cannot melt, therefore making the material tougher and less flexible. |
|
|
How can crystallinity be increased? |
By removing branches on the main polymer chain and making the chains as flat as possible. This is so that the molecule chains can line up neatly. |
|
|
What is the range in sizes of nanoparticles? |
Nanoparticles range in size from about 100 nm down to about 1 nm. |
|
|
What are nanoparticles? |
Materials containing up to 1000 atoms |
|
|
What can you say about the surface area to volume ratio of nanoparticles? |
Nanoparticles have a very large surface area compared with their volume. |
|
|
Why are nanoparticles useful? |
They are often able to react very quickly. This makes them useful as catalysts to speed up reactions. |
|
|
How many nanometres (nm) in a millimetre? |
A nm is 1 millionth of a mm |
|
|
Why are nanoparticles having a large surface area effective catalysts? |
Increasing surface area provides more sites for reactions to take place. |
|
|
Why are titanium dioxide nanoparticles used in sunblock creams? |
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles are so small they do not reflect visible light, so cannot be seen. They are used in sunblock creams to block harmful ultraviolet light without appearing white on the skin (transparent). |
|
|
Nanoscience may lead to the development of new products. Name examples. |
Nanoscience may lead to the development of: -New catalysts -New computers -Stronger and lighter building materials |
|
|
What are composites? |
The combined materials when nanoparticles mix with other materials like metals, ceramics and plastics. |
|
|
What is nanotechnology? |
The science of making and using nanoparticles. |
|
|
Name one concern about nanoparticles in the air? |
They could be breathed in and cause lung or brain damage. |

