![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four organic compounds important to the body? |
1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Nucleic Acids 4. Proteins |
|
|
Give two reasons why carbon is so important to biochemistry in the body |
1. Carbon is electro-neutral, meaning it shares electrons instead of losing or gaining them 2. Because carbon is electro-neutral it shares 4 covalent bonds with other elements or carbon molecules to from long chain molecules or ring like structures (called carbon skeleton) |
|
|
Sugar and starches are ____________ |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
Name 3 classes of carbohydrates and 2 functions of carbohydrates |
3 Classes: 1. Monosaccharides (only have one carb molecule) 2. Disaccarides (have two molecules) 3.Polysacchardies (have many molecules)
2 Functions: 1. Carbs are a major source of cellular fuel 2. Carbs are structural molecules (e.g. ribose sugars in RNA and deoxyribose sugars in DNA) |
|
|
What is the generic formula formula of carbohydrates? |
Carbs contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, so: (CH2O)n is the structural formula |
|
|
Name 5 monosaccharides that are important to the body |
* Ribose
|
|
|
Label the chemical structure of each of the 5 monosaccharides |
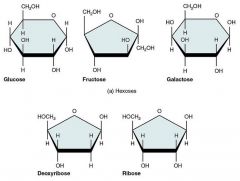
|
|
|
What sugars (monosaccharides) make up the 3 disaccharides: sucrose, lactose, maltose? |
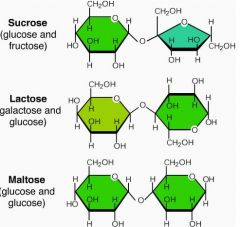
|
|
|
Which is the glucose storage molecule of plants? Of animals? Are polysaccharides very soluble? |
Starch (made by plants) and glycogen (made by animals) are polymers that store glucose (only).
Polysaccharides are not very soluble. |
|
|
What elements are included in lipids? Are lipids water-soluble? |
ipids contain C, H, O. However, they contain much lower numbers of oxygen (as compared to carbs). and sometimes have phosphorous.
Lipids are insoluble in water. |
|
|
What are the four major types of lipids found in the body? |
1. Neutral Fats or Triglycerides, 2. phospholipids, 3. steroids, and 4. eicosanoids |
|
|
What is the basic structure of a triglyceride? |
Triglycerides are neutral fats - solid fats and liquid oils.
They are composed of three fatty acids that are three long hydrocarbon chains (CHn) witlh a carboxy acid (COOH-) end. Which is bonded to glycerol, a three carbon sugar alcohol. |
|
|
What are three functions of triglycerides? |
Large amounts of energy are stored in the many bonds of long hydrocarbon chains Form fatty layers that provides insulation & protection from trauma Aids in fat soluble vitamin absorption. |
|
|
Phospholipids are ________ and this property allows them to be used as building blocks for cellular membranes. |
Phospholipids are __modified triglycerides__ and this property allows them to be used as building blocks for cellular membranes. (the head is “polar” aka water loving, the tail is “nonpolar” aka hydrophobic) |
|
|
Name 4 types of steroids that are important in the body |
1. Bile Salts (synthesized from cholesterol)
|
|
|
Which steroid is the basis for all steroids formed in the body? |
Cholesterol |
|
|
Label the basic chemical structure of cholesterol |
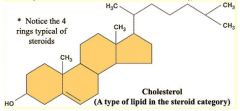
|
|
|
Prostaglandin is an _____________ |
Prostaglandin is an ____eicosanoid___ |
|
|
Name 4 roles prostaglandins play in body functions |
1. Inducing labor contractions
|
|
|
Which proteins transport fats in blood? |
Lipoproteins |
|
|
How many different amino acids are there? |
20 |
|
|
Protein polymers are created by forming _________ bonds between the _______ and _______ ends of two adjacent amino acids. |
Protein polymers are created by forming ___peptide____ bonds between the ___carboxyl (COOH-)__ and __amino (NH2+)__ ends of two adjacent amino acids. |
|
|
What are the four levels of structure for a protein? |
Primary - The sequence of amino acids form the polypeptide chain Secondary - The primary chain forms alpha helices (spirals) and beta-pleated sheets - held together by hydrogen bonds Tertiary - Superimposed on secondary structure alpha helices and/or beta sheets folded up to form a compact globular molecule held together by intra-molecular bonds Quarternary - two or more polypeptide chains each with its own tertiary structure, combine to form a functional protein. |
|
|
Name 2 major types of proteins? |
Fibrous proteins - strand like, water insoluble and stable (e.g keratin, elastin, collegen)
2. Globular proteins - compact, spherical, water-soluble and sensitive to environment changes (e.g. antibodies, hormones, molecular chaperones) |
|
|
Fibrous proteins are also known as ______ proteins |
STRUCTURAL |
|
|
Which protein is the single most abundant protein? and what type is it? |
Collagen a fibrous protein |
|
|
Name four important types of globular proteins |
1. Enzymes
|
|
|
What is the most important role of molecular chaperones? |
Ensure quick and accurate folding and association of proteins. |
|
|
_______ are biological catalysts that ________ the activation energy to _______ the speed of a reaction. |
__Enzymes__ are biological catalysts that ____lower___ the activation energy to ___increase___ the speed of a reaction. |
|
|
A holoenzyme consists of two parts: an __________ and a ________. |
A holoenzyme consists of two parts: an __apoenzyme (protein)_____ and a __cofactor (metal ion) or coenzyme (a B complex vitamin)____. |
|
|
What is the largest molecule in the body? |
DNA! |
|
|
What is DNA's building block? What 3 components is it composed of? |
DNA is made up of the nucleotide “building block”, which is composed of the following three components: 1. Phosphate Group |
|
|
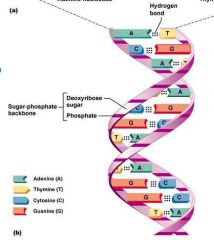
What are the 4 bases of DNA? What are the 2 base pairs of DNA? |
4 bases of DNA are: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
The 2 pairs they make are: A-T and G-C, held together by hydrogen bonds
|
|
|
DNA replicates ________cell division, ensuring ________ |
DNA replicates ___before____cell division, ensuring _____genetic continuity__ |
|
|
What are the 4 bases of RNA? What are the 2 RNA base pairs |
4 bases of RNA are: Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
The 2 pairs they make are: A-U and G-C, |
|
|
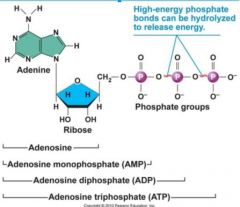
How does the structure of ATP compare to that of the adenine nucleotide of RNA? |
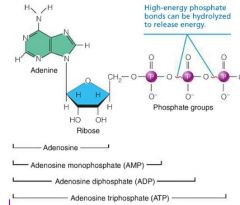
ATP - Adenosine Triphosphate, contains RNA nucleotide w/ two additional phosphate groups.
|
|
|
What is the main function of ATP? |
ATP is the primary energy-transferring molecule in cells and it provides a form of energy that is immediately usable by all body cells. |
|
|
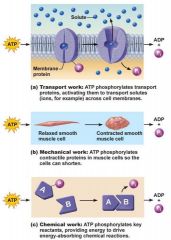
What are the three types of work performed by ATP? |
Transport Work - ATP phosphorylates transport proteins, activating them to transport solutes (e.g. ions) across cell membranes Mechanical work - ATP phosphorylates contractile proteins in muscle cells so the cells can shorten Chemical work - ATP phosphorylates key reactants, providing energy to drive energy-absorbing chemical reactions. |
|
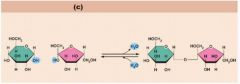
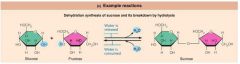
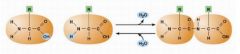
Label the dehydration of sucrose and its breakdown by hydrolysis:
|
|
|
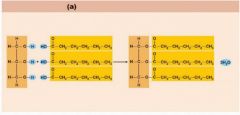
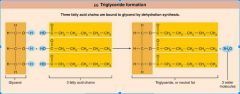
Label the triglyceride:
|
|
|
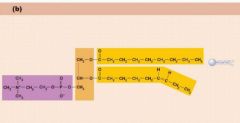
Label the phospholipid:
|

|
|
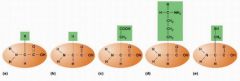
Label the structure of amino acids:
|

|
|
Label the dehydration and hydrolysis of amino acids:
|
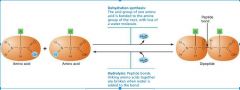
|
|
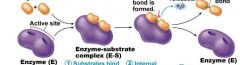
Label the process of Enzymes:
|
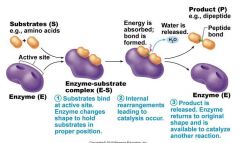
|
|
|
Identify the Primary and Secondary Structure of Proteins |
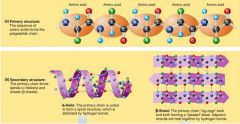
|
|
|
Identify the Tertiary Structure of a Protein |
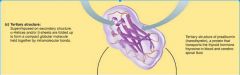
|
|
|
Identify the Quarternary Structure of a Protein |
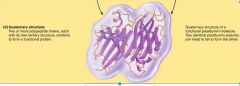
|
|
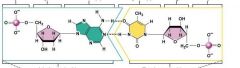
Identify the nucleotides structure in DNA |
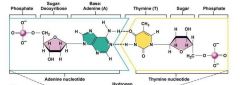
|
|
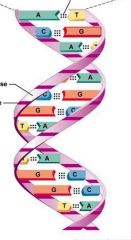
Identify the structures of the DNA double helix:
|
|
|
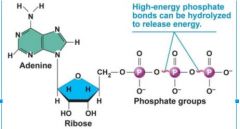
Identify the structure of ATP:
|
|
|
|
What are the three types of work ATP performs? |
|

