![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Properties of living things? |
Order, regulation, energy processing, growth & development, reproduction, response to the environment, evolutionary adaptation |
7 things |
|
|
Difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? |
The presence of membrane-bound organelles |
|
|
|
Biological diversity; how do we explain difference among organisms? |
The accumulation of heritable changes (variation in DNA sequence) |
|
|
|
What is DNA? Where does variation in DNA sequence come from? |
- Units of inheritance that transmit info from parents & offspring - Controls development & maintenance of organism |
|
|
|
What is a genome? A gene? |
- Genetic material of an organism; complete complement of an organism's genes along with its noncoding nucleic acid sequence - Unit of heredity info consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA |
|
|
|
What is a genotype? What is phenotype? |
- Genetic makeup (set of alleles, DNA sequence) - Physical expression of genes |
|
|
|
Element |
Substance that cannot be broken down physically
|
|
|
|
Compound |
Consists of 2 or more elements |
|
|
|
Atom |
Smallest unit that contains the property of an element |
|
|
|
Neutron |
In nucleus, subatomic particle w/o a charge |
|
|
|
Proton |
In nucleus, subatomic particle with + charge |
|
|
|
Electron |
Negative charge, orbits around nucleus, |
|
|
|
Atomic # |
# of protons (# of electrons = # of protons) |
|
|
|
Mass # |
Sum of # protons & electrons |
|
|
|
Atomic mass |
How much atom mass |
|
|
|
What 4 elements make 96% of living matter? |
CHON (Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen) |
|
|
|
What makes up the other 4% of living matter? |
Ca, P, K, S, Na, Cl, Mg |
|
|
|
What is iodine used for the body? |
- Production of thyroid hormone - Regulate growth & metabolism - Basal metabolic rate, protein synthesis, bone growth, neural maturation |
|
|
|
How do arsenic, lead, & mercury affect the body? |
- Affects energy production in mitochondria; apoptosis; lead to cancer, developmental issues, neural issues, death - Disrupts function by causing by causing production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), more dangerous for children - Disrupt function by causing ROS; destroys protein inside the cells |
|
|
|
What is an isotope? |
Different forms of the same element; difference is by neutrons |
Not to be confused with isomer |
|
|
How do we exploit radioactive isotopes? |
-Unstable forms of an element; have a tendency to lose particles - Used in fossil dating, tracers, diagnostics & imaging |
|
|
|
The importance of electrons? |
- They store potential energy - They bring about chemical bonding - When a molecule is being created, the electron that's doing it |
|
|
|
The different bonds of molecules? |
- Covalent- (strong bonds, interaction between electrons) - Non- covalent- (weak, bindings to be reversible) |
|
|
|
Different non-covalent bonds? |
- Ionic- highly electronegative molecule takes an electron from another molecule - Hydrogen- allows different molecules to interact w/ each other; oxygen & hydrogen - Van de Waals- Very short distances any two atoms show a weak bonding interaction - Hydrophobic- Forced together minimize the disruptive effects of hydrogen bonds |
HIVH (acronym) |
|
|
Why are non-covalent bonds used in many molecule interactions? |
Shows the feature of molecules (shape of molecules) |
|
|
|
Why is molecule shape important? What does it determine? |
- Shape is determined by where the atom's electron orbitals are positioned - Shape determines function |
|
|
|
What is meant by equilibrium? |
When the rate of one reaction is equal to the other |
|
|
|
What are the 4 macromolecules? |
- Protein - Nucleic acids - Carbohydrates - Lipds |
PNCL (acronym)
Park "N" climb left |
|
|
What are the 4 ways carbon skeletons can vary? |
- Length - Branching - Presence of rings - Double bond position |
|
|
|
What hydrophobic and hydrophilic mean and what determines each? |
- Substances that are nonionic & non polar; no water affinity - Has affinity for water |
|
|
|
What are isomers? Will their function be the same? |
- Compounds wight the same molecular formula, but different structures - No, since they have different properties |
Not to be confused with isotopes |
|
|
Types of isomers? |
- Structural- differ in the covalent arrangements of atoms - Cis-trans- differ in the spatial arrangements due to inflexibility of double bonds -Enantiomers- mirror images of each other & differ in shape due to presence of an asymmetric carbon |
|
|
|
Functional groups & their roles |
- Provide function 1. Provide shape & structure 2. Reactivity 3. Solubility |
|
|
|
ID functional groups |
- Hydroxyl group (-OH) - Carboxyl group (-COOH) - Sulfhydral group (-SH) - Methyl group (-CH3) - Carbonyl group (-C=O) - Amino group (-NH2) - Phosphate group (-OPO3 2-) |
|
|
|
What is a polymer? |
Long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks linked by covalent bonds |
|
|
|
Dehydration vs. Hydrolysis |
- Loss of a water molecule; two molecules covalently bonded to each other - Reverse of the dehydration reaction; break bonds using water |
|
|
|
Classification of sugars |
- Alpha glucose (same side) - Beta glucose (opposite side) |
|
|
|
Roles of polysaccharides? |
- Storage material - Building material for structures that protect the cell or whole organism |
|
|
|
What are lipids? |
- Diverse group of hydrophobic molecules - Mix poorly w/ water - Large biological molecules that doesn't include true polymers
|
|
|
|
What is a triglyceride? |
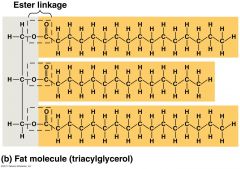
- Three fatty acids joined to glycerol by an esther linkage - Covalent bonds |
|
|
|
Saturated vs. Unsaturated |
- No double bonds between carbon atoms composing a chain; many hydrogen atoms of possible are bonded; w/ hydrogen - One or more double bonds; one fewer hydrogen atom on each double- bonded carbon; cis double bonds; kink in hydrocarbon chain
|
|
|
|
Functions of fats (triglycerides, phospholipids) |
- Energy storage; store long term food in reserves in adipose cells |
|
|
|
Membrane structure & cholesterol |
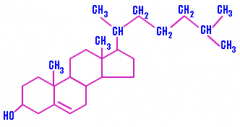
- Steroids - Four fused rings - Distinguished by the particular chemical groups attached to this ensemble of rings |
|
|
|
Protein structure |
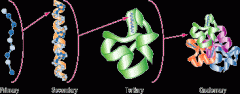
Four levels: - Primary- protein is its sequence of amino acids - Secondary- A coil called alpha helix and a folded structure called a beta pleated sheet - Tertiary- Overall shape of a polypeptide; functional 3-D shape - Quaternary- When 2 or more polpeptide chains form one macromolecule |
|
|
|
Amino acid structure; classification of amino acids |
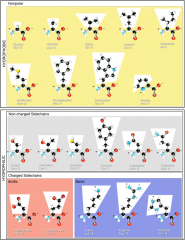
- Organic molecule that has both an amino group and a carboxyl group - Four classes: Hydrophobic (non polar side chains), hydrophilic (polar side chains), acidic (negatively charge), basic (positively charge) |
|
|
|
What is a peptide bond? |
Covalent bond between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on another; formed by a dehydration reaction - Length depends on protein - Sequence depends what the protein will be
|
|
|
|
What reactions make or break peptide bonds? |
- Broken by hydrolysis, made by dehydration |
|
|
|
Sequence, structure, and function of peptide relationship |
- Determines what the protein will be - Side chains create function |
|
|
|
Physical properties that determine protein structure? |
- Physical & chemical conditions - Alterations in pH, salt concentration, temperature, pressure, or other environmental factors |
|
|
|
What is denaturation |
Process which a protein loses its native shape due to the disruption of weak chemical bonds & interactions, thereby becoming biologically inactive - In DNA it is the separation of the two strands of the double helix |
|
|
|
What is a chaperonin and what does it do? |
- Protein molecules that assist in the proper folding of other proteins - Keep the polypeptide segregated from the bad influences in the cytoplasmic environment while it folds spontaneously |
|
|
|
Define nucleic acid, nucleotide, & gene |
- Polymers made of monomers & two types= DNA & RNA - Composed of three parts: phosphate group, sugar group, & nitrogenous base - Gene- unit of inheritance |
|
|
|
Difference between DNA & RNA |
- DNA: forms double helix, backbones run antiparallel, strings move in opposite direction, A=T; G(triple bond)C - RNA: single stranded, ribose instead of deoxyribose, G(triple bond)C; A=U |
|
|
|
Know purines and pyramidines |
- Large, w/ a six-membered ring fused to a fire-membered ring; adenine (A) and guanine (G) - One six-membered ring of carbon & nitrogen atoms; cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U)
|
|
|
|
What is a phosphodiester linkage? |
- In DNA & RNA, linkage between 3' carbon atoms of one sugar molecule & 5' carbonator of another; deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA - Strong covalent bond |
|
|
|
What does antiparallel mean? |
Two sugar-phosphate backbones run in opposite 5'->3' directions from each other |
|
|
|
What is complimentary base pairing? |
- A base sequence & the other strand is the predictable counterpart of the other |
ex. 5'- AGGTCCG-3' 3'- TCCAGGC-5' |
|
|
Role of nucleic acids? |
- Allow for transmission of inheritable traits to offspring -DNA provides directions for its own replication ~unique emergent property |
|
|
|
What is central dogma? |
- Two-step process, transcription and translation, by which the info in genes flows into proteins: DNA->RNA->Protein - Transcription of an RNA copy of a segment of DNA |
|
|
|
What feature do ALL cells have? |
Cell membrane, cytosol, DNA, & ribosomes |
|
|
|
What does surface area-to-volume ratio place a limit on the size of cells |
*refer to study guide |
|
|
|
Explain the structure & function of the nucleus |
- Contains most of the cell genes & most conspicuous organelle - Nuclear envelope- Double membrane structure outer membrane continuous w/ ER - Pore- regulate large molecules that move in and out - Nuclear lamina- strengthens the membrane |
|
|
|
What do ribosomes do in cells? What types of macromolecules are ribosomes constructed from? Difference between free & bound ribosomes? |
- Responsible for creating protein; outside of ER or nuclear envelope (bound ribosomes) - Ribosomal RNA & Protein/polypeptides - Free ribosomes: Suspended in the cytosol; most proteins made function within the cytosol - Bound ribosomes: Attached to the outside of the ER or nuclear envelope; make proteins that are destined for insertion into membranes or to export from cell like secretion |
|
|
|
List all organelles whose membranes are considered part of the endomembrane system. What functions does the EMS serve for the cell? |
- Nuclear envelope; endoplasmic reticulum; golgi apparatus; lysomes; perxisomes; plasm membrane - Regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell |
|
|
|
Summarize the structure & function of the RER and the golgi apparatus |
- Closest to nucleus; covered w/ ribosomes; membrane factory for the cell; grow in place by adding membrane proteins & phospholipids to its membrane; makes membrane phospholipids - Has cis (largest outer radius) & trans (closest to cell membrane); modifies products of the ER; manufactures certain macromolecules; protein modification; creation of polysaccharides- modifications of polysaccharides |
|
|
|
Describe functions performed by SER |
Farther from nucleus; create lipids (lipid synthesis); detoxification; metabolize certain amount of carbs; calcium storage
|
|
|
|
Functions of lysosomes in the cell |
- Phagocytosis- takes things from external environment (digesting food) - Autophagy- when larger parts of cell wear out, recycles its nutrients to make new organelles - fuses with the food vacuole & digests the molecules |
|
|
|
Summarize the functions of each of the 3 types of vacuoles- central, contractile, and food |
- Central: major role in the growth of plant cells; holds reserves of important organic compounds; disposal site for metabolic by products; protects against predators - Food vacuole: contains food from outside of the cell; formed by phagocytosis; forms by budding in from the cell membrane - Contractile: Pumps excess water out of the cell; maintaining a suitable concentration of ions and molecules inside the cell; offsets osmosis by pumping water out of the cell |
|

