![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the muscles of mastication and what are their actions?
|
Digastricus m. - open jaws
Masseter m. Temporalis m. Lateral pterygoid m. Medial pterygoid m. - all close jaws |
Hint: there are 4 that close and one that opens
|
|
|
What nerve(s) innervate the muscles of mastication?
|
Trigeminal (CNV)
Facial (CNVII) - caudal belly of digastricus |
More than one...
|
|
|
What embryologic origin do the muscles of mastication have?
|
All from 1st pharyngeal arch EXCEPT for caudal belly of digastricus (2nd pharyngeal arch)
|
The muscle with the different innervation also has the different embryological origin
|
|
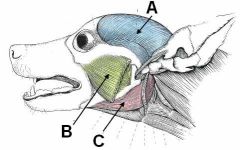
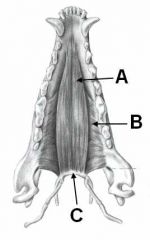
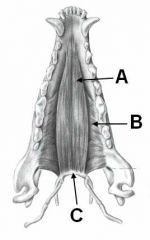
ID these muscles AND provide the origin, insertion and innervation.
|
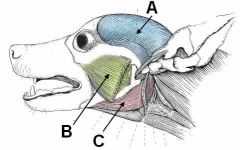
A - Temporalis m.; Temporal fossa to coranoid process of mandible; mandibular n. of CNV
B - Masseter m.; zygomatic arch to masseteric process of mandible; mandibular CNV C - Digastricus; jugular process to ventromedial border of mandible; mandibular CNV and CNVII |
|
|
|
T or F:
The only branch of the trigeminal n. (CNV) with motor innervation is the mandibular branch. |
True!
All three branches have provide sensory innervation but the mandibular branch is also motor. |
|
|
|
T or F:
Only carnivores and sheep have two heads to the masseter m. while all others have three heads. |
False. It's the other way around...
|
|
|
|
T or F:
The digastricus inserts more rostrally on cats than in dogs which explains why cat bites have a greater pressure per unit area than dogs. |
False! While the digastricus does insert farther rostrally, it has nothing to do with bite pressure! This insertion allows cats to open their mouths wider!
|
|
|
|
Which is larger; the medial or lateral pterygoid muscle?
|
Medial is larger and stronger!
|
|
|
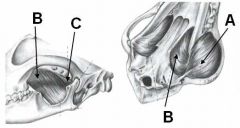
ID these muscles and provide the origin, insertion, and innervation.
|
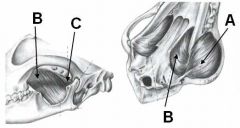
A - Masseter m.; zygomatic arch to masseteric fossa
B - Medial pterygoid m.; pterygopalatine fossa to medial angular process of mandible C - Lateral pterygoid m.; ventral to alar canal to medial surface of mandibular condyle All innervated by mandibular n. of CNV |
|
|
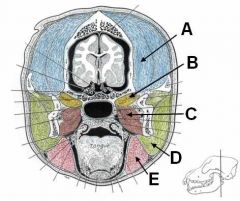
Yarrrrr! What be these muscles of mastication?
|
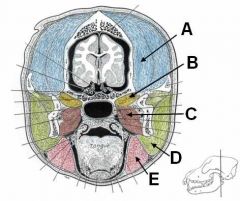
A - Temporalis m.
B - Lateral pterygoideus m. C - Medial pterygoideus m. D - Masseter m. E - Digastricus m. |
|
|
|
What are the intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
|
Proper lingual mm.
|
Only one name...
|
|
|
What are the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
|
Styloglossis m.
Hyoglossis m. Genioglossus m. |
Yarrr...thar be 3...
|
|
|
What is the innervation for all muscles of the tongue?
|
Hypoglossal n. (CN XII)
|
This nerve exits the hypoglossal foramen...
|
|

What muscle or muscles is Bill the cat using to give you the Bronx Cheer?
|

Proper lingual mm. - major action (protrudes tongue and allows for fine lingual motion)
Genioglossus m. draws tongue forward. |
|
|
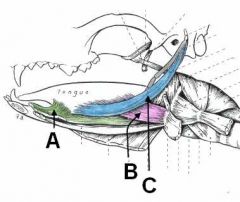
ID these muscles of the tongue and provide their action
|
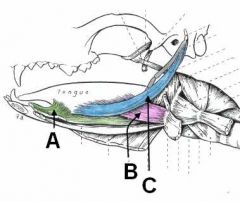
A - Genioglossus m. - depress tongue, draw tongue forward, curl tip down (rostral fibers)
B - Hyoglossus m. - retract and depress tongue C - Styloglossus m. - retract tongue |
|
|
|
What is the muscle fiber orientation of the proper lingual mm.?
|
Dorsal longitudinal
Ventral longitudinal Transverse Vertical |
|
|
|
What are the functions of the hyoid apparatus?
|
Suspension of the larynx (attaches it to skull)
Anchors tongue |
|
|
|
What are the functions and innervations of the hyoid muscles?
|
Involved in swallowing, retching, and lapping.
Innervated by various cervical and cranial nn. |
|
|
|
Which muscles draw the hyoid caudally?
|
Sternohyoideus m.
Sternothyroideus m. Thyrohyoideus m. |
|
|
|
Which muscles draw the hyoid cranially?
|
Geniohyoideus m.
Mylohyoideus m. |
|
|
|
Which muscle has an effect on the hyoid apparatus without directly inserting or originating on any hyoid bones?
|
Sternothyroideus m.
|
Remember - laryngeal cartilages are attached to the hyoid!
|
|
|
Which cranial nerves innervate hyoid muscles?
|
CNV, CNVII, CNXII, CNIX
|
|
|
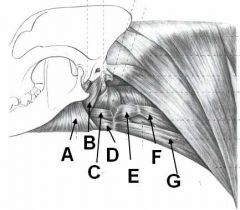
ID these muscles!
|
A - Mylohyoideus m.
B - Styloglossus m. C - Hyoglossus m. D - Geniohyoideus m. E - Thyrohyoideus m. F - Sternothyroideus m. G - Sternohyoideus m. |
|
|
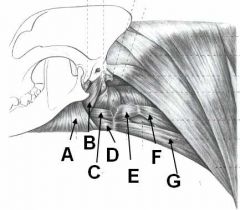
ID THIS!!!
|
A - Geniohyoideus m.
B - Mylohyoideus m. C - Basihyoid bone |
|
|
|
What is the action of the stylohyoideus m.?
|
Raises basihyoid bone
|
Hint: it inserts on the basihyoid
|
|
|
What is the action of the ceratohyoid m.?
|
Decrease angle between the thyrohyoid and ceratohyoid bones.
|
|
|
|
Which pharyngeal structures are close when swallowing?
|
Jaws close
Intrapharyngeal ostium closes Glottis closes |
|

