![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two major divisions of the skull?
|
Neurocranium and splanchnocranium
|
|
|
Name the bones that comprise the brain case. Which of these bones are unpaired?
|
Occipital bone (unpaired)
Parietal bone Frontal bone Sphenoid bone (unpaired) Temporal bone Ethmoid bone (unpaired) |
|
|
Name the facial bones of the skull.
|
Incisive bone
Nasal bone Maxillary bone Palatine bone Vomer bone Pterygoid bone Nasal conchae Zygomatic bone Lacrymal bone |
|
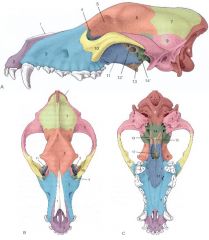
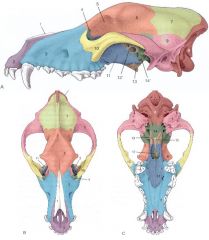
Identify:
1, 2, 3, 4 |
1. Nasal bone
2. Incisive bone 3. Maxillary bone 4. Lacrimal bone |
|
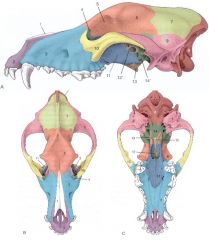
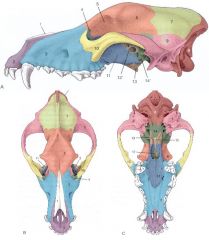
Identify:
10, 11, 13, and 15 |
10. Zygomatic bone
11. Palatine bone 13. Pterygoid bone 15. Vomer bone |
|
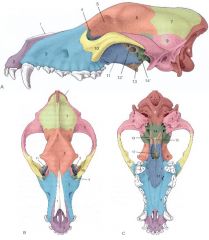
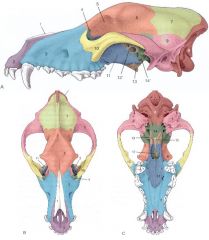
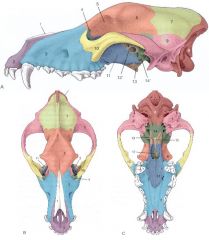
Identify:
6, 7, and 8 Which are unpaired? |
6. Frontal bone
7. Parietal bone 8. Occipital bone (unpaired) |
|
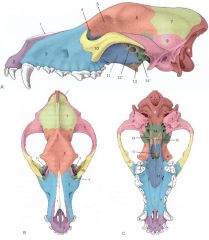
Identify:
9, 12, and 14 (not 12' or 14') Which are unpaired? |
9. Temporal bone
12. Presphenoid bone 14. Basisphenoid bone |
|
|
Describe the skull shape of the following breeds:
Greyhound Golden Retriever English Bulldog |
Dolichocephalic
Mesaticephalic Brachycephalic |
|
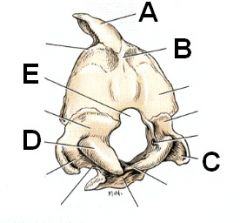
Identify A - E
Which structure should be readily palpable? |
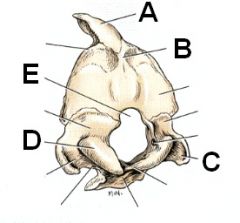
A. Interparietal bone
B. External occipital protuberance (readily palpable) C. Paracondylar (Jugular) process D. Occipital condyle E. Foramen magnum |
|
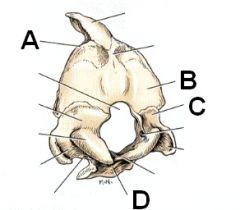
Identify A - D
|
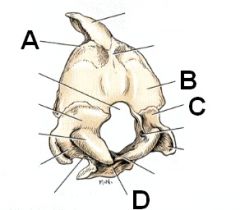
A. Nucchal crest
B. Supraoccipital bone C. Exoccipital bone D. Basioccipital bone |
|
|
What muscle inserts on the basioccipital region of the occipital bone?
|
Longus capitis m.
|
|
|
What courses through the foramen magnum?
|
Spinal cord
Accessory n. Basilar a. |
|
|
What muscle originates on the jugular process of the occipital bone? What is its function?
|
Digastricus m.
Opens jaw. |
|
|
Which bones fuse to form the occipital bone?
|
Basioccipital, exoccipital, and supraoccipital bones
|
|
|
T or F:
The interparietal bone fuses with the occipital bone prenatally to form the external sagittal crest. |
False, fool, but close...
While the interparietal bone does fuse with the occipital bone prenatally, the sagittal crest is made up of parts of the parietal and interparietal bones. |
|
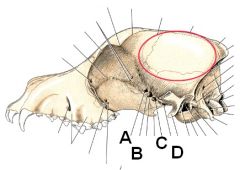
Identify A - D
ID the circled area. What muscle originates here and what is its function? |
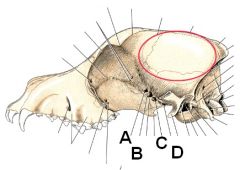
A. Optic canal
B. Orbital fissure C. Rostral alar foramen D. Caudal alar foramen Temporalis m. originates from the temporal fossa. Function - close jaw. |
|
|
What bony structure divides the cerebrum from cerebellum? Which bone or bones is this structure formed by?
|
Tentorium osseum is formed by parietal and occipital bones
|
|
|
What are the three parts of the temporal bone? Which houses the inner ear? Which is the strongest?
|
Squamous, petrous, and tympanic portions.
Petrous houses inner ear AND is the strongest. |
|
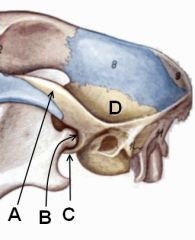
Identify these parts of the temporal bone.
|
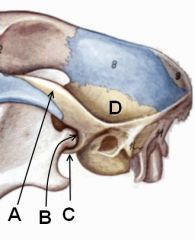
A. Zygomatic process
B. Mandibular fossa C. Retroarticular process D. Squamous part of temporal bone. |
|
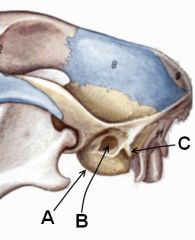
Identify these parts of the temporal bone. What muscle or muscles attach at C?
|
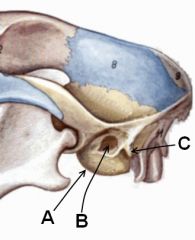
A. Tympanic bulla
B. External acoustic meatus C. Mastoid process Cleidomastoideus and sternomastoideus mm. insert here. |
|
|
Which processes serve as attachment points for the orbital ligament?
|
Zygomatic process of the frontal bone and the frontal process of the zygomatic bone.
|
|
|
What bone or bones form the zygomatic arch? What muscle or muscles originate here?
|
Temporal process of the zygomatic bone, zygomatic process of the temporal bone
Masseter m. origin. |
|
|
Which bones form the orbital margin?
|
Frontal, zygomatic, and lacrimal bones.
|
|
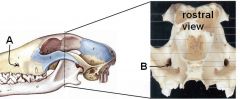
Identify A and B. What canal is formed by these? What courses through this canal?
|
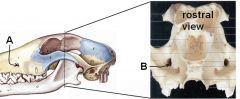
A. Infraorbital foramen
B. Maxillary foramen A + B = infraorbital canal infraorbital a. and n. course through here |
|
|
T or F:
The maxillary bone contains alveoli for all upper teeth in sheep. |
I'll bet you said false and, if I was talking about dogs, you'd be right! Sheep have no upper incisors and thus no alveolar sockets! In dogs, the upper incisors are within the incisive bone.
|
|
|
Which bones form the hard palate?
|
Maxillary bone (palatine processes)
Incisive bone Palatine bone |
|
|
Which bone(s) form the nasal aperture?
|
Incisive and nasal bones
|
|
|
What are the parts of the sphenoid bone? Which foramena are found in each region?
|
Presphenoid bone:
Optic canal Basisphenoid bone: Oval foramen, round foramen, alar canal |
|
|
What structure does the pituitary "sit" in?
|
Hypophyseal fossa right near the turkish saddle (sella turcica)
|
|
|
What portion of the ethmoid bone contributes to the bony nasal septum?
|
Perpendicular plate
|
|
|
Which bone separates the cranial and facial regions of the skull?
|
Ethmoid bone
|
|
|
Which bone or bones form the pterygopalatine fossa? What muscle(s) originate here?
|
Maxillary bone
Palatine bone Zygomatic bone Pterygoid bone Sphenoid bone Pterygoid mm. originate here |
|
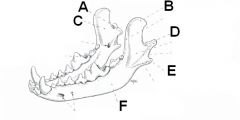
Identify the parts of the mandible
|
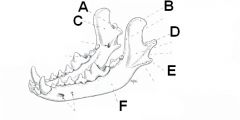
A. Condyloid process
B. Coronoid process C. Ramus of mandible D. Mandibular notch E. Angular process F. Body of mandible |
|
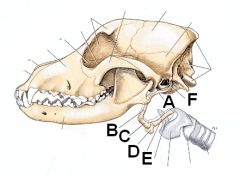
ID the parts of the hyoid
|
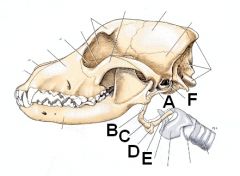
A. Stylohyoid
B. Epihyoid C. Ceratohyoid D. Basihyoid E. Thyrohyoid F. Tympanohyoid cartilage |

