![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
205 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
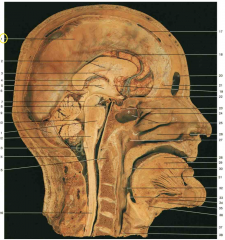
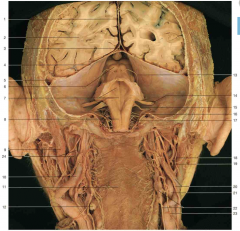
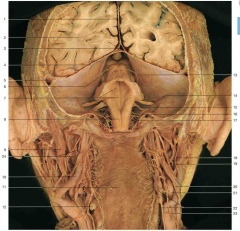
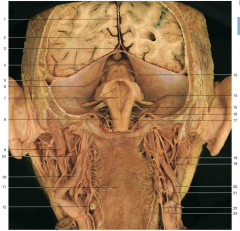
Identify 1 (yellow circle). What layer is this structure made of?
|
1 is the falx cerebri, which is made up of dura mater
|
|
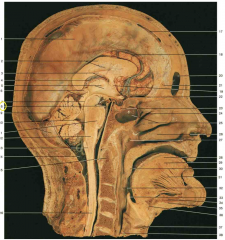
Identify 8 (2 parts). The top arrow is pointing to a brain structure, the bottom arrow to an artery. Name both.
|
top: mamillary body; bottom: basillar artery (note it running just anterior to the pons)
|
|
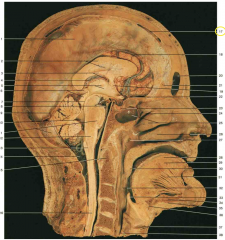
What is the space shown by 17 (yellow circle)?
|
superior sagittal sinus
|
|
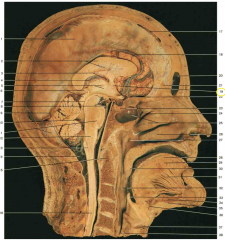
Identify the structure shown by 19 (yellow circle).
|
anterior commissure
|
|
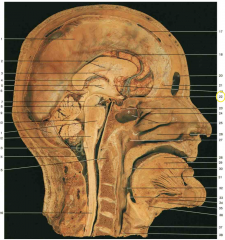
Identify the structure shown by 22 (yellow circle).
|
optic chiasm
|
|
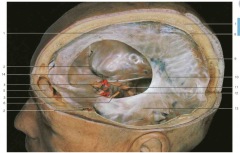
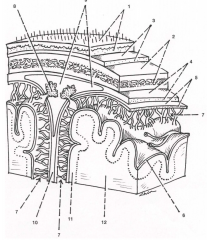
Compare the following anatomical image with the cartoon on the following page.
|
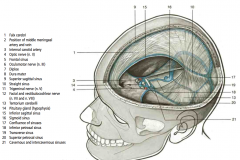
Note: the numbers correspond between the front and back slide.
|
|
|
Within which space do the cerebral arteries usually run?
|
subarachnoid space
|
|
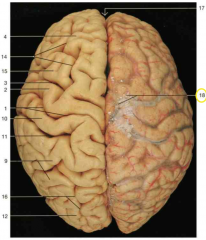
What layer of covering is seen on the right hemisphere of the brain (right side of the image)? What structures are shown by 18 (yellow circle)?
|
arachnoid (and pia) mater are covering the right hemisphere of this brain. 18 is showing the arachnoid granulations.
|
|
|
What major brain structure passes through the tentorial notch?
|
the brainstem
|
|
What is the name of structure 4?
|
tentorium cerebelli
|
|
Identify nerve 13. What would result from a lesion of this nerve?
|
trochlear nerve; lesion of CN IV would lead to inability to depress the adducted eye (presenting as diplopia when walking down stairs)
|
|
What structure of the midbrain is shown in 6?
|
inferior colliculi
|
|
|
At what level of the brainstem is the trochlear nerve nuclei found?
|
the midbrain at the level of the inferior colliculus
|
|
Use this slide to test yourself.
|
Answers.
|
|
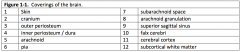
What foramen is identified by A and what passes through it? What foramen is identified by B and what passes through it?
|
A: cribriform foramena (olfactory nerve); B: hypoglossal canal (hypoglossal nerve)
|
|
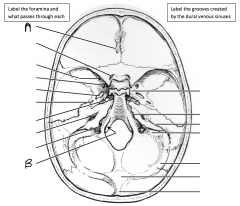
What foramen is identified by A and what passes through it? What foramen is identified by B and what passes through it? What is the space found within C? What is the bone identified by arrow D?
|
A: optic canal (optic nerve); B: superior orbital fissure (oculomotor, trochlear, occipital branch of trigeminal (V1), abducens); C: pituitary fossa (i.e. sella turcica); D: clivus
|
|
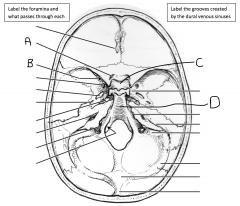
What foramen is identified by A and what passes through it? What foramen is identified by B and what passes through it? What foramen is identified by C and what passes through it?
|
A: foramen rotundum (maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve, V2); B: foramen ovale (mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve, V3); C: foramen spinosum (middle meningeal artery)
|
|
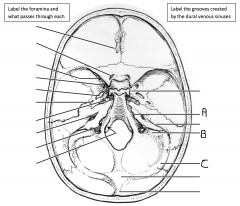
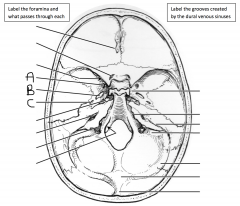
Identify the groove indicated by A. Identify the groove indicated by B. Identify the groove indicated by C.
|
A: groove of superior petrosal sinus; B: groove of sigmoid sinus; C: groove of transverse sinus
|
|
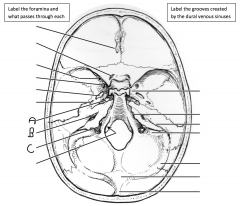
What foramen is identified by A and what passes through it? What foramen is identified by B and what passes through it? What foramen is identified by C and what passes through it?
|
A: foramen lacerum (nothing, the internal carotid artery enters the skull AT the foramen lacerum); B: internal auditory meatus (facial, vestibulocochlear nerve); C: jugular foramen (glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory nerve)
|
|
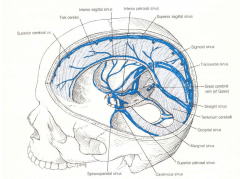
Review the dural venous sinuses
|
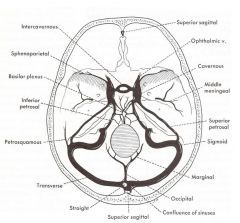
And from above
|
|
|
What fissure completely separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum? What dural structure occupies this fissure?
|
transverse (horizontal) fissure; tentorium cerebelli
|
|
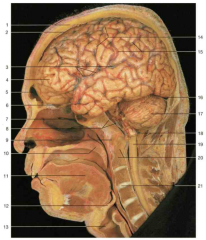
Identify the lateral sulcus.
|
Number 3 on the image
|
|
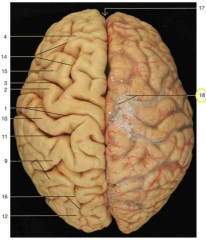
Identify number 1.
|
central sulcus
|
|
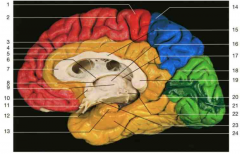
What is the name of the sulcus identified by number 18 (yellow circle)? What two lobes does it separate?
|
parieto-occipital sulcus (divides the parietal and occipital lobes on the medial surface of the brain)
|
|
|
What is the name of the sulcus that divides the superior parietal lobe from the inferior parietal lobe on the lateral surface of the brain?
|
intraparietal sulcus
|
|
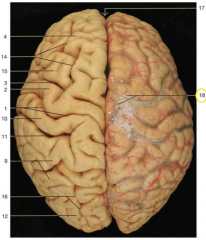
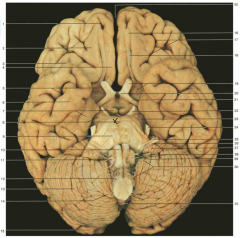
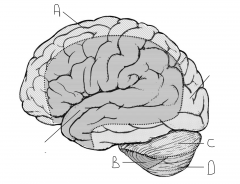
Identify the lobes of the brain in this image (4)
|
Frontal lobe: 4; Parietal lobe: 9; Occipital lobe: 12. Note: the temporal lobes are inferior and hard to see on this superior aspect image.
|
|
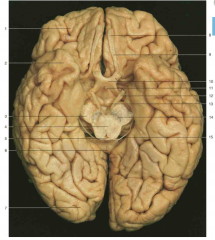
Identify the lobes of the brain in this image (3)
|
Frontal lobe: 1; Temporal lobe: 2; Occipital lobe: 7. Note: the parietal lobes are superior and hard to see on this inferior aspect image.
|
|
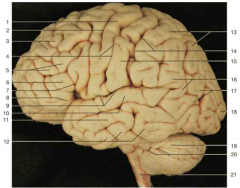
Identify number 1.
|
precentral gyrus
|
|
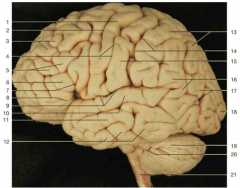
Identify number 3.
|
superior frontal gyrus
|
|
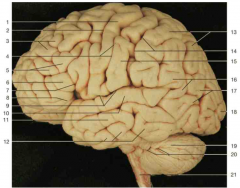
Identify number 5.
|
middle frontal gyrus
|
|
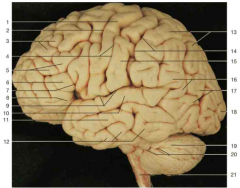
Identify number 6.
|
inferior frontal gyrus
|
|
|
What two regions can the inferior frontal gyrus be divided into and what is the relative location of each?
|
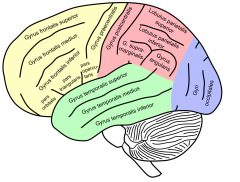
opercular area, triangular area. Note: the lab manual does not include the third area, orbital.
|
|
|
What two regions is the inferior parietal lobule divided into?
|
angular gyrus, supramarginal gyrus
|
|
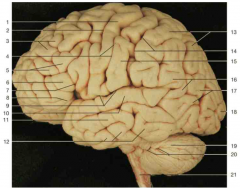
Identify number 10.
|
superior temporal gyrus
|
|
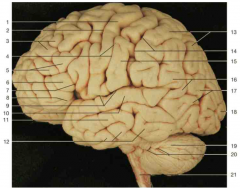
Identify number 11.
|
middle temporal gyrus
|
|
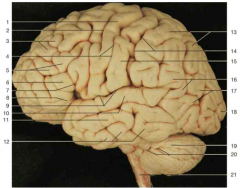
Identify number 12.
|
inferior temporal gyrus
|
|
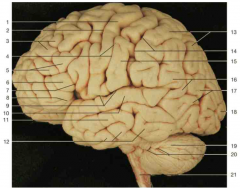
Identify number 16.
|
supramarginal gyrus
|
|
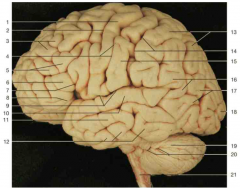
Identify number 17.
|
angular gyrus
|
|
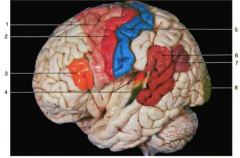
Identify the area highlighted for number 3.
|
Broca’s area (speech motor area)
|
|
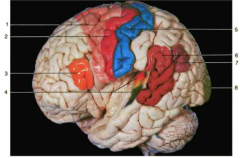
Identify the area highlighted for number 6.
|
Wernicke’s area (speech sensory area)
|
|
|
In which larger gyrus is Broca’s area located: superior frontal gyrus, middle frontal gyrus, inferior frontal gyrus?
|
inferior frontal gyrus
|
|
Identify number 12. (Hint: on the lateral aspect of the brain, this structure would be located on the superior surface of the superior tempura gyrus, buried in the lateral fissure)
|
transverse temporal gyrus (this is the primary auditory cortex)
|
|
|
What is the name of the region of the parietal lobe located above the intraparietal sulcus?
|
superior parietal lobule
|
|
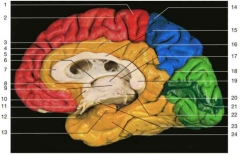
Identify number 21.
|
calcarine sulcus
|
|
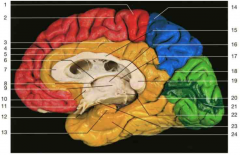
Identify number 18.
|
parieto-occipital sulcus
|
|
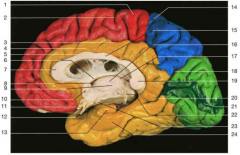
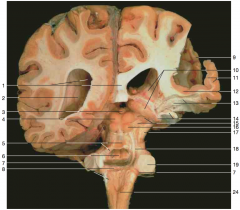
dentify space 8.
|
interventricular foramen (of Monroe)
|
|
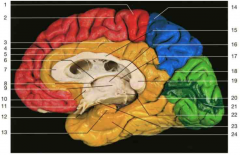
Identify number 24 and number 13.
|
24: parahippocampal gyrus; 13: uncus
|
|
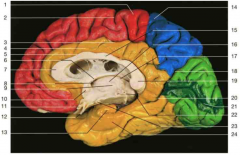
dentify number 12. Where does this structure terminate?
|
infundibulum; terminates at the pituitary gland
|
|
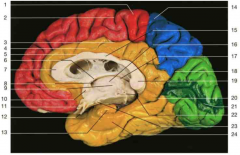
dentify number 11.
|
optic chiasm
|
|
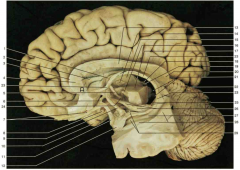
Identify A. Be specific.
|
rostrum of the corpus collosum
|
|
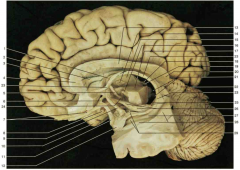
Identify number 1.
|
body of the fornix
|
|
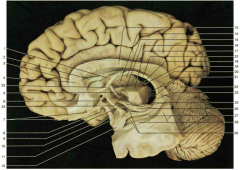
Identify number 2. What is a good landmark for this structure?
|
septum pellucidum; located between the fornix and the corpus collosum genu
|
|
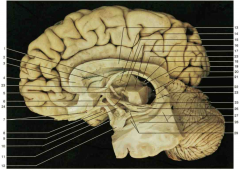
Identify number 4. Be specific.
|
genu of the corpus collosum
|
|
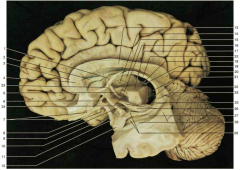
Identify number 7.
|
olfactory bulb (front) and tract (back)
|
|
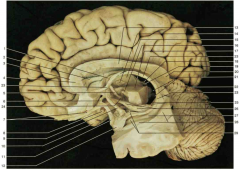
Identify number 13. Be specific.
|
body of the corpus collosum
|
|
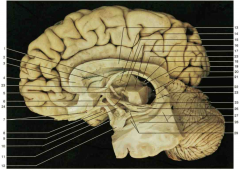
Identify number 19.
|
pineal body
|
|
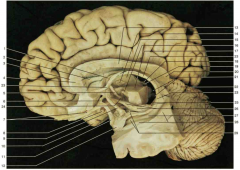
Identify number 20.
|
splenium of the corpus collosum
|
|
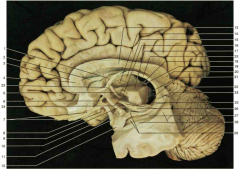
Identify the gyrus in the space identified by number 27.
|
parahippocampal gyrus
|
|
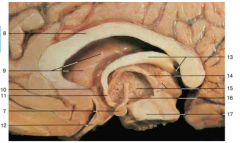
Identify the space of 9.
|
lateral ventricle
|
|
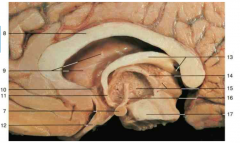
Identify number 10.
|
anterior commissure
|
|
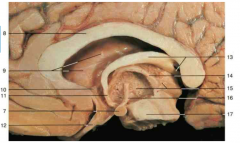
Identify number 7.
|
mamillary body
|
|
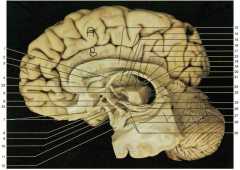
Identify gyrus A. Identify gyrus B.
|
A: superior frontal gyrus. B: cingulate gyrus
|
|
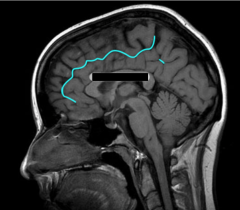
Identify this sulcus.
|
cingulate sulcus
|
|
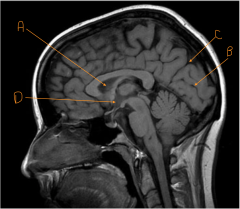
Identify A.
|
septum pellucidum
|
|
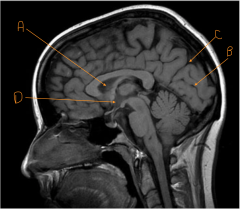
Identify the line carved out by B.
|
calcarine sulcus
|
|
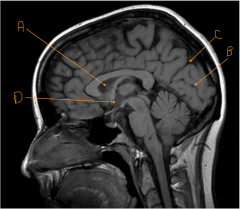
Identify the line carved out by C.
|
parieto-occipital fissure
|
|
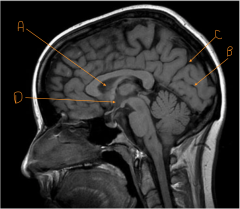
Identify D.
|
hypothalamus
|
|
Identify number 8 (the part without the X).
|
cerebral peduncle
|
|
|
List the four cranial nerves involved in speech, along with their respective roles.
|
i) CN V3 (movement of the jaw). ii) CN VII (movement of muscles of facial expression). iii) CN X (muscles of palate, pharynx, larynx). iv) CN XII (intrinsic/extrinsic muscles of the tongue)
|
|
|
Damage to which cranial nerve would cause the following (include side of damage): weak, hoarse voice with sagging left soft palate.
|
left CN X
|
|
|
Damage to which cranial nerve would cause the following (include side of damage): deviation of tongue to left upon protrusion.
|
left CN XII
|
|
|
Damage to which cranial nerve would cause the following (include side of damage): when asked to “show his teeth” the patient’s mouth pulls to the left side.
|
right CN VII
|
|
|
Damage to which cranial nerve would cause the following (include side of damage): loss of taste on posterior right side of tongue.
|
right CN IX
|
|
|
Which cranial nerves are involved in the afferent and efferent reflex arms for: blinking on irritation of cornea.
|
afferent: CN V1; efferent: CN VII
|
|
|
Which cranial nerves are involved in the afferent and efferent reflex arms for: pupillary constriction on exposure to light.
|
afferent: CN II; efferent: CN III
|
|
|
Which cranial nerves are involved in the afferent and efferent reflex arms for: gagging on stimulation of tonsillar region.
|
afferent: CN IX; efferent: CN X
|
|
|
Which cranial nerves are involved in the afferent and efferent reflex arms for: salivation on smelling warm chocolate chip cookies.
|
afferent: CN I; efferent: CN IX
|
|
|
Which structures pass through the cavernous sinus (6)?
|
CN III, CN IV, CN V1, CN V2, CN VI, internal carotid artery
|
|
|
What are the three coverings surrounding the spinal cord?
|
from deep to superficial: pia, arachnoid, dura mater
|
|
|
From where do the ventral rootlets emerge (be specific).
|
ventrolateral sulci
|
|
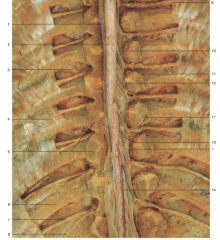
Identify number 13. What meningeal layer are these extensions part of?
|
denticulate ligaments; part of pia mater
|
|
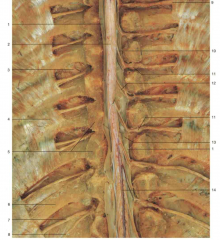
Identify artery number 14.
|
anterior spinal artery
|
|
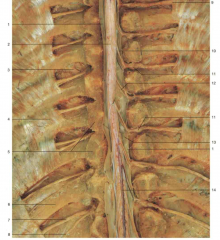
Identify number 1.
|
dura mater
|
|
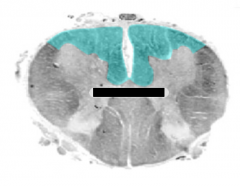
Identify the shaded area. What two sulci/fissures create this area?
|
ventral faniculus, created by the ventral median fissure and ventrolateral sulcus
|
|
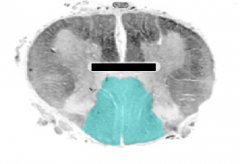
Identify the shaded area. What two sulci/fissures create this area?
|
dorsal faniculus, created by the dorsal median sulcus and dorsolateral sulcus
|
|
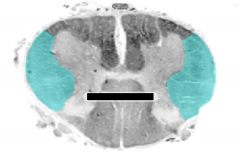
Identify the shaded area. What two sulci/fissures create this area?
|
lateral faniculus, created by the ventrolateral sulcus and the dorsolateral sulcus
|
|
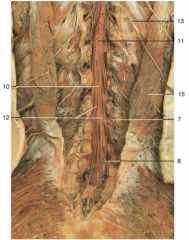
Identify number 11.
|
conus medullaris
|
|
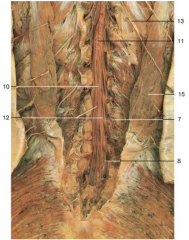
Identify number 12.
|
cauda equina
|
|
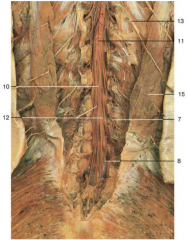
Identify number 10. Be specific.
|
filum terminale interna
|
|
|
What are the two regions of the filum terminale? At what vertebral level do they change?
|
filum terminale interna, filum terminale externa; they change at S2 where the dural sac terminates
|
|
|
What vertebral level is adjacent to the conus medullaris of the adult spinal cord?
|
L2
|
|
|
What vertebral level is adjacent to the lower limit of the dural sac?
|
S2
|
|
|
What is the name of the intervening space within the dural sac?
|
lumbar cistern (part of the subarachnoid space)
|
|
|
Name three things that occupy the subarachnoid space.
|
CSF, blood vessels, nerves
|
|
|
What meningeal layer forms the filum terminale interna?
|
pia mater, covered in spinal dura and arachnoid meninges
|
|
|
What meningeal layer forms the filum terminale externa?
|
pia mater, fuses with investing dura mater
|
|
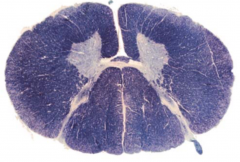
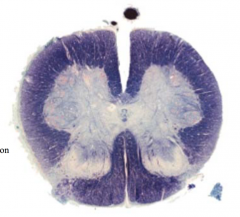
From which spinal level was the following section taken?
|
upper cervical; there is a distinction between fasciculus gracilis/cuneatus (cervical region), but not incredibly prominent ventral horn enlargement so not lower cervial
|
|
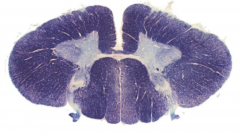
From which spinal level was the following section taken?
|
lower cervical; there is a distinction between fasciculus gracilis/cuneatus (cervical region) with ventral horn expansions
|
|
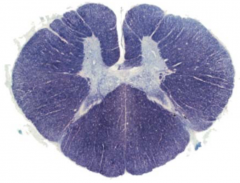
From which spinal level was the following section taken?
|
thoracic
|
|
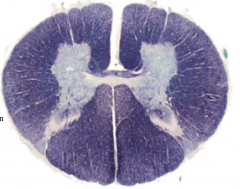
From which spinal level was the following section taken?
|
lumbar level through the lumbosacral enlargement
|
|
From which spinal level was the following section taken?
|
low sacral level
|
|
|
In which spinal segments can the lateral horns be seen? What sorts of neurons are found there?
|
from T1 to L2 (while they exist in S2 to S4, they can’t be seen because they are engulfed by the lumbosacral enlargements). They are occupied by preganglionic autonomic neuronal cell bodies
|
|
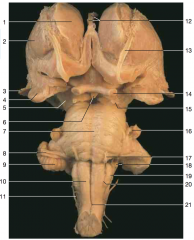
Is this an anterior or posterior view of the brainstem? How do you know?
|
anterior; Belly of the pons, majority of cranial nerves coming out of anterior brainstem
|
|
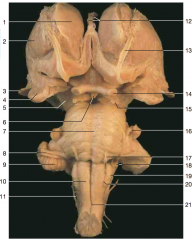
Identify number 1.
|
caudate nucleus
|
|
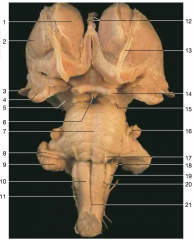
Identify number 2.
|
putamen (or lentiform nucleus)
|
|
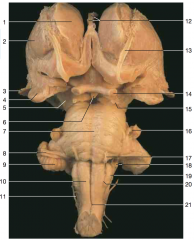
Identify number 5.
|
cerebral peduncle
|
|
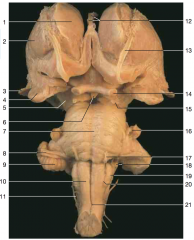
Identify number 6.
|
infundibulum
|
|
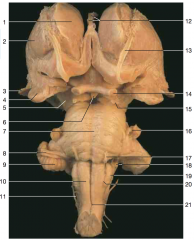
Identify number 7.
|
(belly of the) pons
|
|
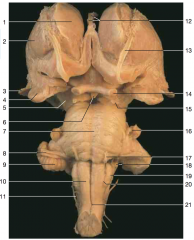
Identify nerve number 8.
|
CN VII, and CN VIII
|
|
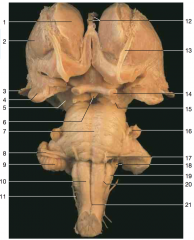
What part of the cerebellum is shown by number 9.
|
flocculus
|
|
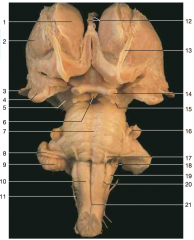
Identify number 10.
|
pyramids
|
|
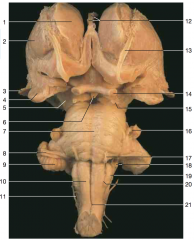
Identify nerve number 11.
|
accessory (CN XI)
|
|
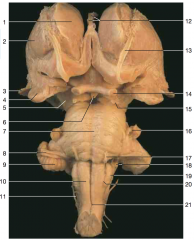
Identify number 19.
|
inferior olive
|
|
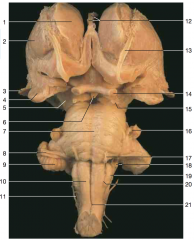
Identify nerve number 18.
|
CN IX, and CN X (Note: choroid plexus from the fourth ventricle can often be seen just beneath these nerves)
|
|
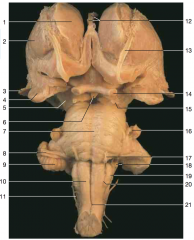
Identify nerve number 17.
|
abducens nerve CN VI
|
|
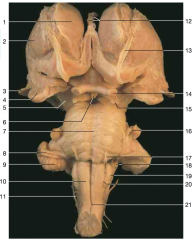
Identify nerve number 16.
|
trigeminal nerve CN V
|
|
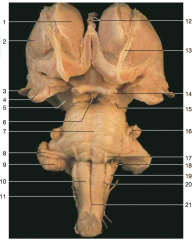
Identify nerve number 15.
|
CN III
|
|
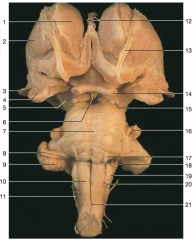
Identify nerve number 14.
|
optic nerve (Note: optic tract is closer to the brainstem than the optic nerve)
|
|
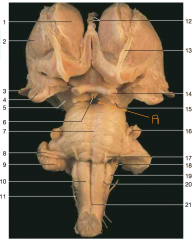
Identify space A.
|
interpeduncular fossa
|
|
|
What is a name for the junction of the pons with the medulla and cerebellum?
|
cerebellopontine angle
|
|
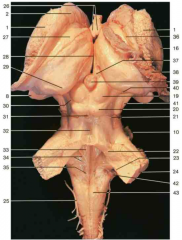
Identify number 2.
|
head of caudate nucleus
|
|
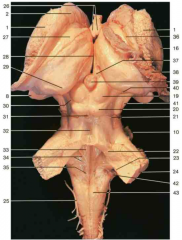
Identify space 28.
|
third ventricle
|
|
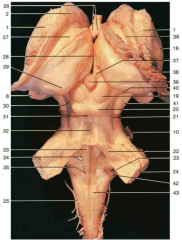
Identify number 29. Be specific.
|
pulvinar of the thalamus
|
|
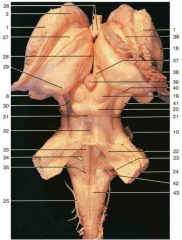
Identify number 19.
|
superior colliculus
|
|
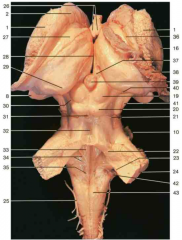
Identify number 20.
|
inferior colliculus
|
|
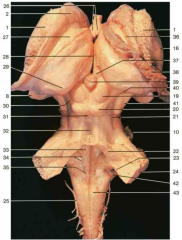
Identify number 24.
|
middle cerebellar peduncle
|
|
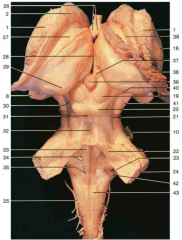
Identify number 22.
|
superior cerebellar peduncle
|
|
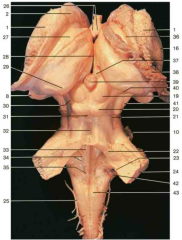
Identify number 23.
|
inferior cerebellar peduncle
|
|
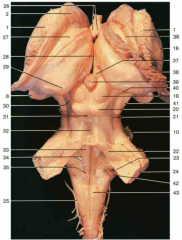
Identify number 39.
|
pineal body
|
|
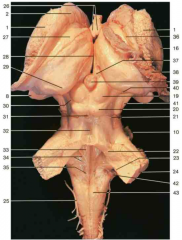
Identify number 40.
|
medial geniculate body
|
|
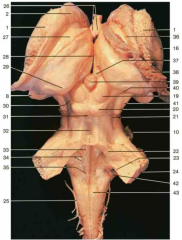
Identify nerve number 21.
|
trochlear nerve CN IV
|
|
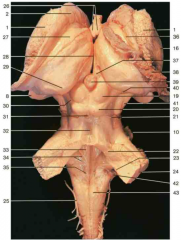
Identify the triangular structure at 35.
|
vagal trigone below hypoglossal trigone
|
|
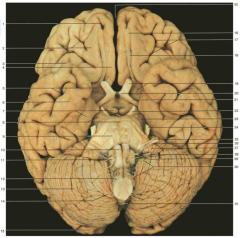
Identify nerve number 25.
|
CN VII
|
|
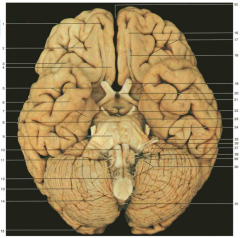
Identify nerve number 26.
|
CN VIII
|
|
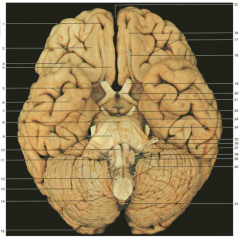
Identify nerve number 28.
|
CN IX and CN X
|
|
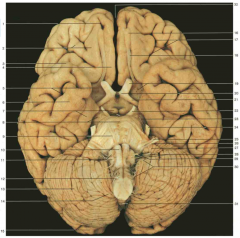
Identify nerve number 29.
|
CN XII
|
|
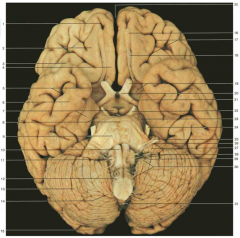
Identify nerve number 30.
|
CN XI
|
|
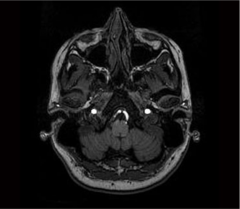
What brainstem level is shown in this MRI?
|
closed medulla
|
|
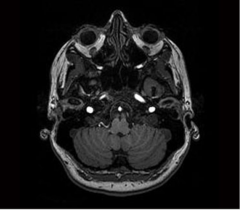
What brainstem level is shown in this MRI?
|
open (rostral) medulla
|
|
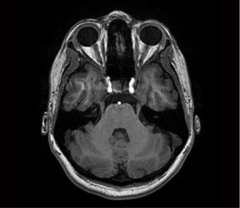
What brainstem level is shown in this MRI?
|
caudal pons
|
|
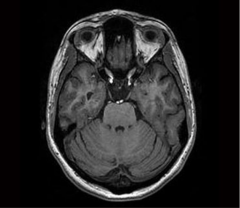
What brainstem level is shown in this MRI?
|
midpons
|
|
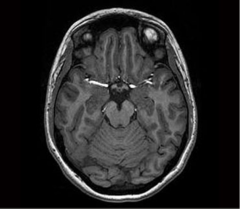
What brainstem level is shown in this MRI?
|
caudal midbrain (level of inferior colliculus)
|
|
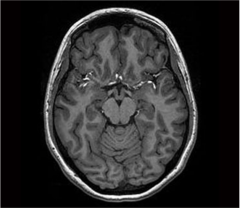
What brainstem level is shown in this MRI?
|
rostral midbrain (level of superior colliculus)
|
|
|
What cranial nerve(s) exit at the level of the rostral midbrain?
|
CN III only
|
|
|
What cranial nerve(s) exit at the level of the caudal midbrain?
|
CN IV only
|
|
|
What cranial nerve(s) exit at the level of the midpons?
|
CN V only
|
|
|
What cranial nerve(s) exit at the level of the caudal pons?
|
CN VI, VII, VIII
|
|
|
What cranial nerve(s) exit at the level of the open medulla?
|
CN IX, X, XII
|
|
|
What cranial nerve(s) exit at the level of the closed medulla?
|
none
|
|
|
What structures in the brain are supplied by the anterior choroidal artery (3)? From which major artery does the anterior choroidal branch?
|
optic tract, posterior limb of internal capsule and the parahippocampcal gyrus; internal carotid artery
|
|
|
What regions are supplied by the middle cerebral artery? Through what fissure/sulcus does this artery run?
|
superolateral surface of the cerebral hemispheres, temporal pole; runs through the lateral fissure
|
|
|
What artery supplies blood to the medulla?
|
vertebral artery
|
|
|
What structures are supplied by the posterior cerebral artery (4)?
|
inferior surface of cerebral hemisphere, occipital lobe, midbrain, thalamus
|
|
|
What structure is supplied by the posterior communication artery?
|
anterior portions of the diencephalon
|
|
|
What artery supplies the pons?
|
basilar artery
|
|
|
What structure is supplied by the superior cerebellar artery?
|
superior surface of the cerebellum
|
|
|
What anatomical structure is supplied by the anterior spinal artery?
|
the anterior part of the spinal cord
|
|
|
What structure is supplied by the posterior spinal arteries?
|
dorsolateral sulcus of spinal cord
|
|
|
What artery supplies the middle cerebellar peduncles?
|
anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
|
|
|
What artery supplies the inferior surface and posteriormedial portions of the cerebellum?
|
posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
|
|
|
What regions are supplied by the anterior cerebral artery?
|
medial surface of frontal and parietal lobes
|
|
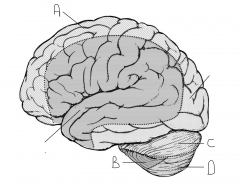
Which artery supplies region A.
|
anterior cerebral artery
|
|
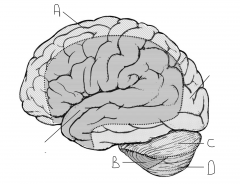
Which artery supplies region B.
|
AICA
|
|
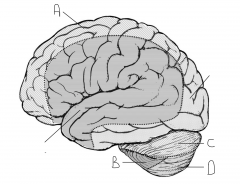
Which artery supplies region D.
|
PICA
|
|
Which artery supplies region C.
|
superior cerebellar artery
|
|
|
From which major artery does the AICA usually split?
|
basilar artery
|
|
|
From which major artery does the PICA usually split?
|
vertebral artery
|
|
|
From which major artery does the superior cerebellar artery usually split?
|
basilar artery (right before the PCA)
|
|
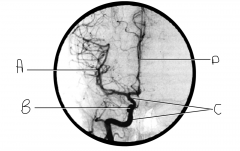
What artery is injected with contrast? What view is this?
|
internal carotid; AP view
|
|
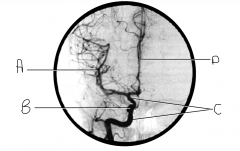
Identify artery A.
|
MCA
|
|
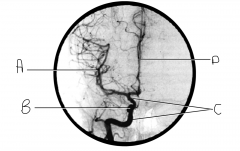
Identify structure B.
|
carotid siphon
|
|
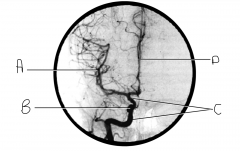
Identify artery C.
|
internal carotid artery
|
|
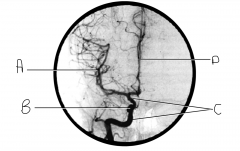
Identify artery D.
|
ACA
|
|
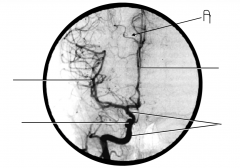
Identify artery A.
|
pericallosal artery
|
|
What artery is injected with contrast? What view is this?
|
internal carotid; lateral view
|
|
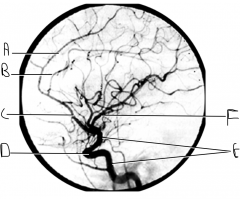
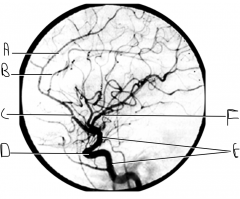
Identify artery A.
|
callosomarginal artery
|
|
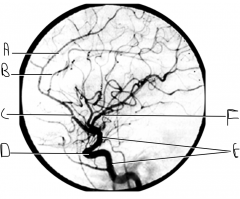
Identify artery B.
|
pericallosal artery
|
|
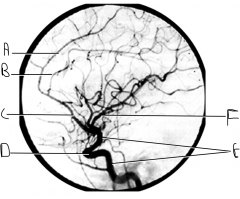
Identify artery C.
|
ACA
|
|
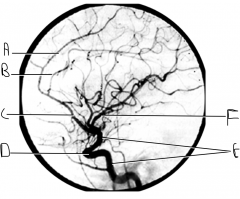
Identify structure D.
|
carotid siphon
|
|
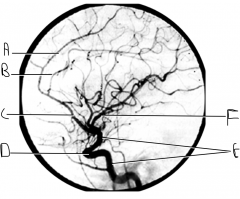
Identify artery E.
|
ICA
|
|
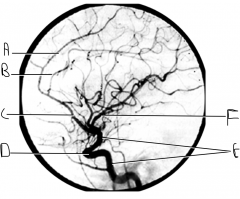
Identify artery F.
|
MCA
|
|
What artery is injected with contrast? What view is this?
|
vertebral artery; AP view
|
|
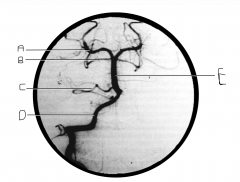
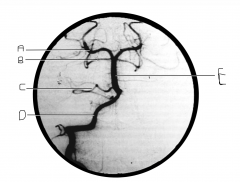
Identify artery A.
|
PCA
|
|
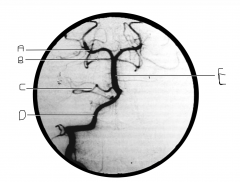
Identify artery B.
|
superior cerebellar artery
|
|
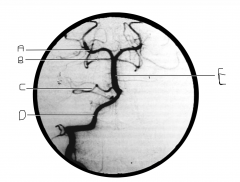
Identify artery C.
|
AICA
|
|
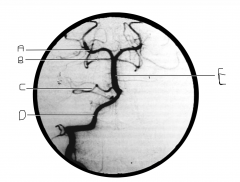
Identify artery D.
|
vertebral artery
|
|
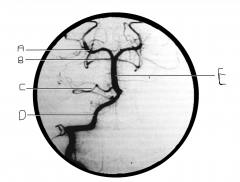
Identify artery E.
|
basilar artery
|
|
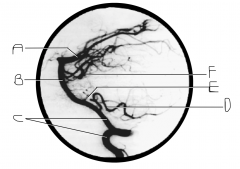
What artery is injected with contrast? What view is this?
|
vertebral artery; lateral view
|
|
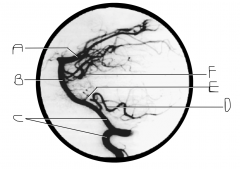
Identify artery A.
|
PCA
|
|
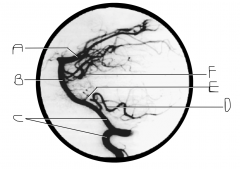
Identify artery B.
|
basilar artery
|
|
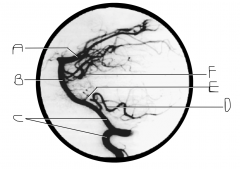
Identify artery C.
|
vertebral artery
|
|
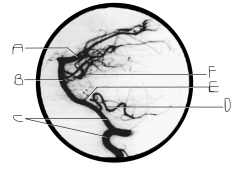
Identify artery D.
|
PICA
|
|
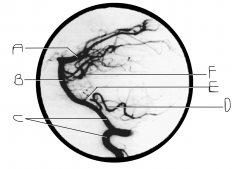
Identify artery E.
|
AICA
|
|
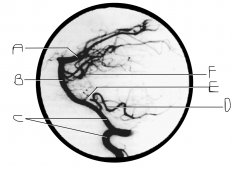
Identify artery F.
|
superior cerebellar artery
|
|
|
What structure passes between the PCA and the superior cerebellar?
|
CN III
|
|
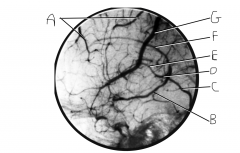
What does this image depict?
|
venogram or cerebral veins and dural venus sinuses
|
|
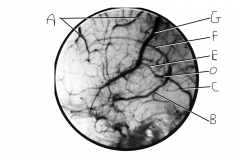
Identify vein A.
|
superior cerebral veins
|
|
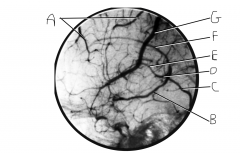
Identify vein B.
|
basal vein (of Rosenthal)
|
|
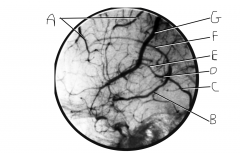
Identify vein C.
|
straight sinus
|
|
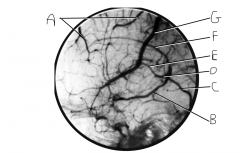
Identify vein D.
|
great cerebral vein of Galen
|
|
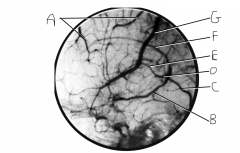
Identify vein E.
|
internal cerebral vein
|
|
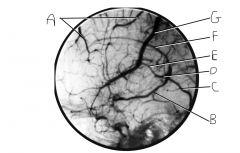
Identify vein F.
|
inferior sagital sinus
|
|
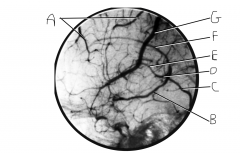
Identify vein G.
|
superior anastomotic vein (on FN, this is still called superior cerebral veins along with A)
|
|
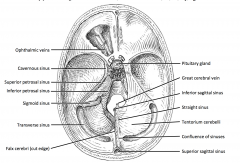
Compare the cartoon showing the dural venous sinuses.
|
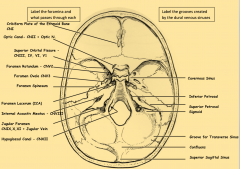
With the dry skull showing the grooves and foramen
|
|
|
You examine a left carotid angiogram from the lateral view and find the posterior cerebral artery filled with contrast in addition to the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. How can you explain these findings?
|
large left posterior communicating artery in this patient
|

