![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
At the foramen magnum the brainstem is continuous with |
Spinal cord |
|
|
At the tentorial notch, the brainstem is continuous with |
Diencephalon |
|
|
Where are cranial nerve nuclei located |
In the tegmentum |
|
|
Posterior half of the brainstem is called the |
Tegmentum |
|
|
Posterior to the 4th ventricle is the |
Tectum |
|
|
The tectum is small except for |
Colliculi in midbrain |
|
|
Anterior corticospinal tract is responsible for |
control of axial muscles |
|
|
Lateral corticospinal tract is responsible for |
control of limbs, fine control of movements of the hand. |
|
|
Where do fibres in the anterior corticospinal tract decussate |
At spinal level of exit |
|
|
Where do fibres int he lateral corticospinal tract decussate |
Medullary pyramids |
|
|
Two components of the posterior column |
Nucleus gracilis, nucleus cuneatus |
|
|
In the PCML pathway, which part of the thalamus to fibres enter |
Ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) |
|
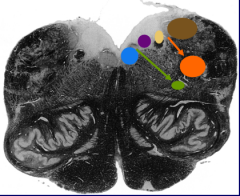
What is the blue nucleus |
Hypoglossal nucleus |
|
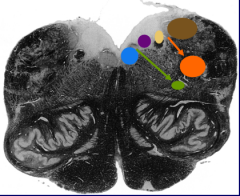
What is the green nucleus |
Nucleus ambiguus |
|
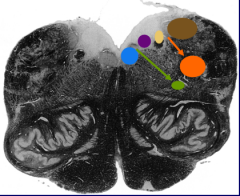
What is the purple nucleus |
Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus nerve |
|
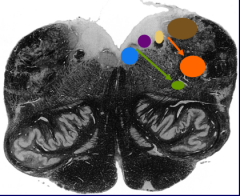
What is the yellow nucleus |
Nucleus of the solitary tract |
|
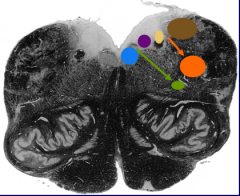
What is the orange nucleus |
Spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve |
|
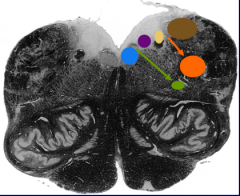
What is the brown nucleus |
Vestibular nuclei |
|
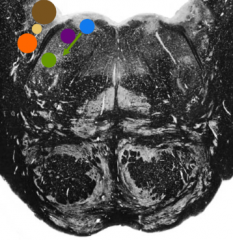
What is the blue nucleus |
Abducens nucleus |
|
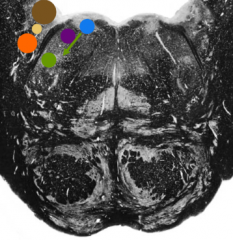
What is the green nucleus |
Facial nucleus |
|
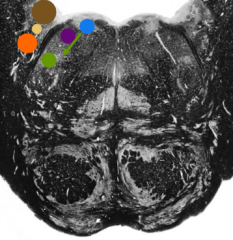
What is the purple nucleus |
Superior salivary nucleus |
|
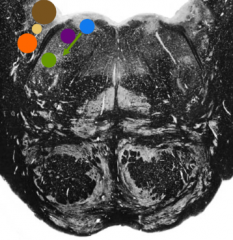
What is the brown nucleus |
Vestibular nuclei |
|
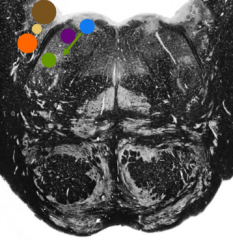
What is the yellow nucleus |
Nucleus of solitary tract |
|
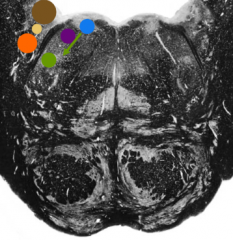
What is the orange nucleus |
Spinal trigemninal nucleus |
|
|
What are the three trigeminal nuclei |
Mesencephalic, chief sensory, spinal trigeminal nucleus. |
|
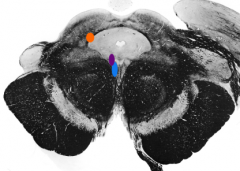
What is the orange nucleus |
Mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus |
|
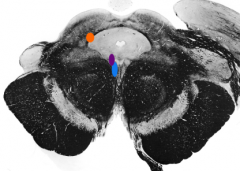
What is the purple nucleus |
Edinger-Westphal nucleus |
|
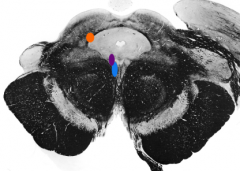
What is the blue nucleus |
Oculomotor nucleus |
|
|
Where is the reticular formation |
In the tegmentum |
|
|
Functions of the reticular formation |
Visceral regulation (cardio, resp, swallowing, vomiting), Motor functions (eye movements and central pattern generators), Sensory functions (modulation of pain pathways), Regulation of attention and conciousness. |
|
|
Blood supply to medulla |
Anterior spinal artery, Vertebral arteries, PICA |
|
|
Blood supply to pons |
Pontine branches of basilar artery |
|
|
Blood supply of midbrain |
Basilar artery, Superior cerebellar, Posterior cerebral. |

