![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
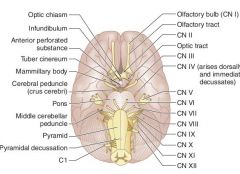
Take a minute to look at this.
|
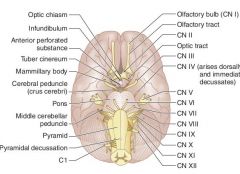
JUST LOOK AT IT!
|
|
|
Which of the cranial nerves pass near the pons?
|
V
VI VII |
|
|
Which are the CNs that lie medially at the brainstem?
|
III
VI XII 3(x2) = 6 (x2) = 12 |
|
|
What are the function of the medial cranial nerves?
|
Motor
|
|
|
What's the function of the pineal gland?
|
Melatonin secretion
Circadian rhythms |
|
|
What information is processed at the superior colliculi?
|
Conjugate vertical gaze
Your eyes are above your eyes; the superior colliculus is above the inferior colliculus |
|
|
What information is processed at the inferior colliculi?
|
Auditory information
Your eyes are above your eyes; the superior colliculus is above the inferior colliculus |
|
|
What is parinaud syndrome?
|
Paralysis of the conjugate vertical gaze due to a lesion in the superior colliculi
|
|
|
What are the structures that are on the dorsum of the midbrain?
|
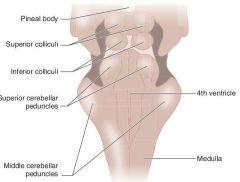
Pineal body
Superior colliculi Inferior colliculi |
|
|
What are the cranial nerves?
|
Olfactory
Optic Oculomotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abducens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Accessory Hypoglossal |
|
|
What is the function of CNI?
|
Smell
|
|
|
Which is the only CN which doesn't have thalamic relay to the cortex?
|
CNI
|
|
|
What is the function of CNII?
|
Sight
|
|
|
What is the function of CNIII
|
Eye movement: SR, IR, MR, IO
Pupillary constriction Accomodation Eyelid opening |
|
|
What are the components of pupillary constriction?
|
Sphincter pupillae
Edinger-Westphal nucleus Muscarinic receptors |
|
|
What is the function of CNIV?
|
Eye movement
|
|
|
What is the function of CNV?
|
Mastication
Facial sensation Somatosensation from the anterior 2/3 of tongue |
|
|
What is the function of CNVI?
|
Eye movement (LR)
|
|
|
What is the function of CNVII?
|
Facial movement
Taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue Lacrimation Salivation Eyelid closing Stapedius muscles i nthe ear |
|
|
What salivary glands are controlled by CNVII?
|
Submandibular
Sublingual The branch of CNVII to the stapedius goes through the parotid gland but no innervation occurs |
|
|
What muscle that controls eyelid closing does CNVII innervate?
|
Orbicularis oculi
|
|
|
What is the function of CNVIII?
|
Hearing
Balance |
|
|
What is the function of CNIX?
|
Taste
Somatosensation from posterior 1/3 of tongue Salivation Monitoring carotid body and sinus chemo- and baroreceptors Stylopharyngeus |
|
|
What sailvary gland is innervated by CNIX?
|
Parotid
|
|
|
What's the action of the stylopharyngeus?
|
Elevation of pharynx, larynx
|
|
|
What is the function of CNX?
|
Taste from the epiglottic region
Swallowing Palate elevation Midline uvula Talking Coughing Thoracoabdominal viscera Monitoring aortic arch chemo- and baroreceptors |
|
|
What is the function of CNXI?
|
Head turning
Shoulder shrugging |
|
|
What is the function of CNXII?
|
Tongue movement
|
|
|
What's the mnemonic for if CNs are sensory or motor or both?
|
Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter Most
|
|
|
What are the CN nuclei contained in the midbrain?
|
III
IV |
|
|
What are the CN nuclei contained in the pons?
|
V
VI VII VIII |
|
|
What are the CN nuclei contained int he medulli?
|
IX
X XII |
|
|
What are the CN nuclei contained in the spinal cord?
|
XI
|
|
|
What type of information is captured by the lateral CN nuclei?
|
Sensory
On the aLar plate |
|
|
Where in the brainstem are the CN nuclei located?
|
Tegmentum portion of the brainstem
|
|
|
What are the different reflexes mediated by the cranial nerves?
|
Corneal
Lacrimation Jaw jerk Pupillary Gag |
|
|
What's the afferent component of the corneal reflex?
|
V1 ophthalmic (nasociliary branch)
|
|
|
What's the afferent component of the lacrimation reflex?
|
V1
|
|
|
What's the afferent component of the jaw jerk reflex?
|
V3
|
|
|
What's the afferent component of the pupillary reflex?
|
II
|
|
|
What's the afferent component of the gag reflex?
|
IX
|
|
|
What's the efferent component of the corneal reflex?
|
VII (temporal branch: orbicularis oculi)
|
|
|
What's the efferent component of the lacrimation reflex?
|
VII
|
|
|
What's the efferent component of the jaw jerk reflex?
|
V3 (motor - masseter)
|
|
|
What's the efferent component of the pupillary reflex?
|
III
|
|
|
What's the efferent component of the gag reflex?
|
X
|
|
|
What are the different nuclei of the vagus nerve?
|
Nucleus solitarius
Nucleus ambiguus Dorsal motor nucleus |
|
|
What information is carried at the nucleus solitarius?
|
Visceral Sensory information (taste, baroreceptors, gut distension)
|
|
|
What information is carried at the nucleus ambiguus?
|
Motor innervation of the pharynx, larynx, and upper esophagus
aMbiguus = Motor |
|
|
What information is carried at the dorsal motor nucleus?
|
Autonomic (PS) fibers to the heart, lungs, and upper GI
|
|
|
What are the cranial nerves that involve the nucleus solitarius?
|
VII
IX X |
|
|
What are the cranial nerves that involve the nucleus ambiguus?
|
IX
X |
|
|
What are the cranial nerves that involve the dorsal motor nucleus?
|
X
|
|
|
How does CNI exit the skull?
|
Cribriform plate
|
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the optic canal?
|
CNII
Ophthalmic artery Central retinal vein |
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the superior orbital fissure?
|
CN: III, IV, V1, VI
Ophthalmic vein Sympathetic fibers |
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the foramen rotundum?
|
CN V2
|
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the ovale?
|
CN V3
|
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the foramen spinosum?
|
Middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the internal auditory meatus?
|
CNVII, VIII
|
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the jugular foramen?
|
CN: IX, X, XI
Jugular vein |
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the hypoglossal canal?
|
CNXII
|
|
|
What structures exit the skull through the foramen magnum?
|
Spinal roots of CNXI
brainstem Vertebral arteries |
|
|
What is the cavernous sinus?
|
A collection of venous sinuses on either side of the pituitary
|
|
|
What structures drain into the cavernous sinus?
|
Eye
Superficial cortex |
|
|
Where does the cavernous sinus empty into?
|
Internal jugular vein
|
|
|
What structures pass through the cavernous sinus?
|
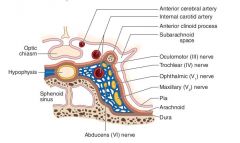
CN: III, IV, V1, V2, VI (extraocular muscles + V1, V2)
Postganglionic sympathetic fibers Cavernous portion of the internal carotid artery |
|
|
What structure is located above the cavernous sinus?
|
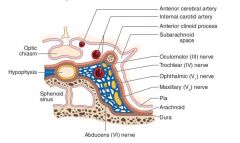
Optic chiasm
|
|
|
What is cavernous sinus syndrome?
|
Opthalmoplegia and decreased conreal and maxillary sensation with normal vision
|
|
|
What are causes of cavernous sinus syndrome?
|
Mass effect
Fistula Thrombosis |
|
|
What happens if there's a CNV motor lesion?
|
Jaw deviates toward the side of the lesion due to the unopposed force from the opposite pterygoid muscle
|
|
|
What happens if there's a CNX lesion?
|
Uvula deviates away from the side of the lesion
Weak side collapses and the uvula points away |
|
|
What happens if there's a CNXI lesion?
|
Weakness turning the head to the contralateral side of hte lesion
Shoulder droop on the side of the lesion |
|
|
What's the action of the left SCM?
|
Helping to turn the head to the right
|
|
|
What happens if there's a CNXII lesion?
|
Tongue deviates toward the side of the lesion due to weakened tongue muscles on the affected side
Lick your wounds! |
|
|
What are the different types of hearing loss?
|
Conductive
Sensorineural Noise-induced |
|
|
What are the tests used to distinguish between the different types of hearing loss?
|
Rinne test
Weber test |
|
|
If someone has conductive hearing loss, what will the Rinne test result be?
|
Abnormal: bone > air
|
|
|
If someone has conductive hearing loss, what will the weber test result be?
|
Localizes to the affected ear
|
|
|
If someone has sensorineural hearing loss, what will the rinne test result be?
|
Normal: air>bone
|
|
|
If someone has sensorineural hearing loss, what will the weber test result be?
|
Localizes to the unaffected ear
|
|
|
What cells are damaged in noise-induced hearing loss?
|
Sterocilliated cells in the organ of Corti
|
|
|
What frequenceis of hearing are lost in noise-induced hearing loss?
|
High frequency hearing loss first
|
|
|
What is a cause of acute noise-induced hearing loss?
|
Tympanic membrane rupture
|
|
|
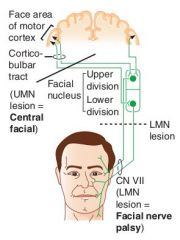
What is severed in an upper motor neuron lesion of the face?
|
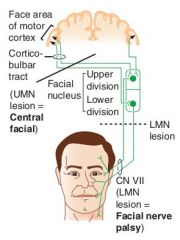
Lesion of motor cortex
Lesion of connection between the cortex and the facial nucleus |
|
|
What are the findings in an UMN lesion of the face?
|
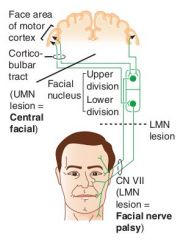
Contralateral paralysis of the lower face
Forehead spared |
|
|
Why is the forehead spared in an UMN lesion of the face?
|
Bilateral UMN lesion of the forehead
|
|
|
What are the physical findings in a LMN lesion?
|
Ipsilateral paralysis of the upper AND lower face
|
|
|
What damage occurs in facial nerve palsy?
|
Complete destruction of the facial nucleus itself
Destruction of the branchial efferent fibers from the facial nucleus |
|
|
What are the physical findings in facial nerve palsy?
|
Peripheral ipsilateral facial paralysis with inability to close eye on the involved side
|
|
|
What's the prognosis from facial nerve palsy?
|
Gradual recovery
|
|
|
What are the causes of facial nerve palsy?
|
AIDS
Lyme disease Herpes simplex Herpes zoster Sarcoid Tumors Diabetes |
|
|
What are the muscles of mastication?
|
Masseter
teMporalis Medial pterygoid M's munch |
|
|
What muscle opens the jaw?
|
Lateral pterygoid
Lateral lowers |
|
|
What is the innervation of the muscles of mastication?
|
V3
|

