![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
130 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Botany |
the scientific study of plants; also called plant biology
|
|
|
What is a plant?
|
- an organism that is green and photosynthetic
- cell wall composed of cellulose -multicellular body -can control water loss -have strengthening tissue -can reproduce by means of microscopic, drought-resistant spores |
|
|
microbiology |
study of bacteria
|
|
|
mycology
|
study of fungi
|
|
|
phycology
|
study of algae
|
|
|
bryology
|
study of mosses
|
|
|
Kingdom
|
a broad taxonomic category made up of related phyla; many biologist currently recognize six kingdoms of living organism
Plantae Animalia Protista Fungi Archaea Bacteria |
|
|
Domain
|
a taxonomic category that includes one or more kingdoms
Archaea Eubacteria Eukarya |
|
|
Spontaneous Generation |
living organism could develop from nonliving or decomposing matter |
|
|
Prokayotic
|
cells lacking a nucleus
|
|
|
Eukaryotic
|
cells containing a nucleus
|
|
|
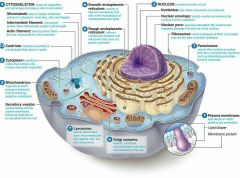
Organelles
|
membrane-bound bodies found within eukaryotic cells
|
|
|
Cell Wall
|
surrounds protoplasma (contains all living cell components)
- Also contain matrix of hemicellulose, pectin and glycoproteins |
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
consists of all cellular components between the plasma membrane and the nucleus
|
|
|
Cytosol |
fluid within cytoplasm containing organelles
|
|
|
Cellulose |
Main Structure component of cell walls |
|
|
What is first produced when new cell walls are formed? |
Middle Lamella |
|
|
These are derived from primary walls by thickening and inclusion of lignin. |
Secondary Walls |
|
|
Plamodesmata |
Fluids and dissolved substances can pass through primary walls of adjacent cells.
-Cytoplasmic Strands Extending Between Cells |
|
|
Plasma Membrane |
Composed of phospholipids arranged in two layers, with proteins interspersed throughout.
-Some proteins extend across the entire width, while others and embedded to the outer surface. |
|
|
Nucleus |
bound by two membranes, which together constitutes the nuclear envelope. |
|
|
Nucleoplasm |
fluid packed with short fibers, and contain larger bodies. |
|
|
Nucleoli |
composed primarily of RNA |
|
|
Chromatin Strands |
coil and become chromosomes |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
facilitates cellular communication and materials channeling. -Enclosed space consisting of a network of flattened sacs and tubes forming channels throughout the cytoplasm.
|
|
|
Ribosomes |
Composed of two subunits composed of RNA and proteins.
- have no bounding membranes may be distributed on outer surface (rough ER) - associated with protein synthesis |
|
|
Smooth ER |
devoid of ribosomes and is associated with lipid secretion. |
|
|
Dictyosomes |
Often bound by branching tubules that originate from the ER. - involved in the modification of carbohydrates attached to proteins synthesized and packed in the ER.
|
|
|
What are assembled within Dictyosomes and collected in small vesicles?
(migrate to plasma membrane and secrete contents to the outside. |
Polysaccharides |
|
|
What are the most conspicuous plastids? |
Chloroplasts - contain stroma and grana |
|
|
Stroma |
enzyme filled matrix |
|
|
Grana |
made up of thylakoids (contain chlorophyll) |
|
|
What are additional plastids found in many plants? |
Chromoplasts and Leucoplasts Amyloplast and Elaioplasts |
|
|
Mitochodria |
Releases energy produced from cellular respiration.
- Inward membrane forms numerous folds - increase surface area available to enzymes in the matric fluid. |
|
|
Microbodies |
small, spherical bodies with a single membrane, distributed throughout the cytoplasm which contain specialized enzymes.
- Perixosomes - Glyoxysomes |
|
|
Perizosomes |
Serve in photorespiration |
|
|
Glyoxysomes |
Aid in converting fat to carbohydrates |
|
|
Vacuoles |
In mature cells, 90% of volume may be taken up by central vacuoles bounded by vacuolar membranes (tonoplasts).
Filled with cell sap which helps maintain pressure within the cell.
Also frequently contains water-soluble pigments. |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
intricate network of microtubules and microfilaments |
|
|
Microtubules |
control the addition of cellulose to the cell wall |
|
|
Microfilaments |
play a major role in the contraction and movement of cells in multicellular animals.
-appear to play a role in cytoplasmic streaming. |
|
|
Meristems |
Permanent region of active cell division. |
|
|
Apical Meristems |
Found at the tip of roots and shoots -increase in length as the apical meristems produce new cells (primary growth)
|
|
|
Apical Meristem |
1) Protoderm 2) Ground Meristem 3) Procambium |
|
|
Protoderm |
Epidermis (dermal tissue system) |
|
|
Ground Meristem |
Ground tissue (parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma) Ground tissue system |
|
|
Procambium |
Primary xylem and primary phloem (vascular tissue system) |
|
|
Primary Meristems |
Primary Tissues |
|
|
Lateral (Secondary) Meristems |
Produce tissues that increase the girth of roots and stems
* Secondary Growth - Vascular Cambium - Cork Cambium |
|
|
Vascular Cambium |
Produces secondary tissues that function primarily in support and conduction (thin cylindrical cells)
|
|
|
Cork Cambium |
Lies outside vascular cambium just inside the outer bark. |
|
|
Simple tissues |
- Parenchyma *Aerenchyma *Chlorenchyma -Collenchyma -Sclerenchyma |
|
|
Parenchyma |
composed of parenchyma cells. tend to have large vacuoles and many contain various secretions. |
|
|
Aerenchyma |
Parenchyma tissue with extensive connected air spaces. |
|
|
Chlorenchyma |
Parenchyma cells containing chloroplasts |
|
|
Collenchyma |
Containing living cytoplasm and may live an extended time. - provide flexible support for organs - unevern thick primary walls (pectin) |
|
|
Sclerenchyma |
Cells with thick, tough, secondary walls, normally impregnated with lignin.
Sclereids FIbers |
|
|
Sclereids |
Stone Cells |
|
|
Fibers |
Contain Lumen (textiles) |
|
|
Complex Tissues |
made up of two or more cell types -Xylem -Phloem -Epidermis -Periderm |
|
|
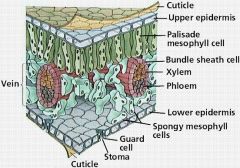
Xylem |
chief conducting tissue for water and minerals absorbed by the roots.
-Vessels -Tracheids - Rays |
|
|
Vessels |
made of vessel elements (only found in flowering plants)
-long tubes open at each end |
|
|
Tracheids |
tapered at the ends with pits that allow water passage between cells |
|
|
Rays |
lateral conduction |
|
|
Phloem |
conducts dissolved food materials produced by photosynthesis throughout the plant.
- Sieve Tube
- Companion Cells |
|
|
Sieve Tube Members |
Large, cylindrical -Sieve Plates - porous region
(advanced cell type, alive and fully functioning, better control, may want sugar to go on one direction) |
|
|
Companion Cells |
Narrow, tapered sieve cells/ albuminous cells
(accompany sieve cells, lack nucleus for sieve cell may speed transport of the sugar) |
|
|
Epidermis |
outermost layer of cells.
(mostly one cell type, but can have some scattered cells) ie: root cap and root hair. |
|
|
What does the Epidermis secrete on the surface of the outer walls? |
Fatty Substance called the cutin |
|
|
What does the root epidermal cell produce? |
root hairs |
|
|
What do leave have that is bordered by pairs of guard cells? |
Stomata |
|
|
Periderm |
constitutes outer bark. |
|
|
What is the periderm primarily composed of ? |
cork cells |
|
|
The cytoplasm of cork cells usually secrete a waterproof substance found in the roots. What is it called? |
Suberin |
|
|
Lenticels |
some parts of cork cambium form loosely arranged pockets of parenchyma cells that protrude through the surface of the periderm. |
|
|
Secretory Cells and Tissue |
May function individually or as part of a secretory tissue. -Flower Nectar -Citrus Oils -Glandular hair mucilage -Latex |
|
|
Epiphyte |
plants that grow on other plants |
|
|
Angiosperms |
Flowering Plants (most abundant) |
|
|
Gymnosperms |
-Seeds not enclosed in ovaries. -Sporophyte is the dominant generation -Seeds exposed on modified leaves that usually form cones. |
|
|
Bryophytes |
- non vascular land plants - mosses, liverworts and hornworts - typically ground hugging plants |
|
|
Monocot |
strap like leaves, parallel veins, fibrous roots, one cotyledon, never woody |
|
|
Eudicot |
broad leaf (petiole), netted veins, palmate veins, 4 to 5 parts, tap root, 2 cotyledon, can be woody. |
|
|
Cotyledon |
usually die quickly and drop off |
|
|
Cell Theory |
all living organisms are composed of one or more cells. |
|
|
Cellulose |
the chief structural polymer in plant cell walls, is a polysaccharide |
|
|
When a seed germinates, the embryo's ____ grows out and develops into the first root. |
Radicle
(may develop into taproot of adventitious roots) |
|
|
Dicotyledonous Plants |
taproot with branch roots |
|
|
Monocotyledonous Plants |
adventitious roots that develop a fibrous root system. |
|
|
Root Cap |
thimble - shaped mass of parenchyma cells covering each root tip.
- protects tissue from damage - function in gravity perception |
|
|
Region of Cell Division |
composed of apical meristem in the center of the root tip.
- most cell division occurs at the edge of the inverted cup - shaped zone |
|
|
Region of Elongation |
cells become several times their original length. - vacuoles merge |
|
|
Region of Maturation |
most cells differentiate into various distinctive cell types. -root hairs form * absorb water and minerals and adhere tightly to soil particles. - thin cuticle. |
|
|
What forms a mutualistic association with plant roots? |
Mycorrhizae
-fungus is able to absorb and concentrate phosphorus much better than it can be absorbed by the root hairs.
* absorption of water and nutrients. - plant offers sugars and amino acids |
|
|
Root Nodules |
Few species of bacteria produce enzymes that can convert nitrogen into nitrates and other nitrogenous substances readily absorbed by roots. |
|
|
Hygroscopic Water |
Physically bound to soil particles and is unavailable to plants. |
|
|
Gravitational Water |
Drains out of pore spaces after a rain |
|
|
Capillary Water |
Water held against the force of gravity in soil pores. |
|
|
Field Capacity |
Water remaining in the soil after drainage by gravity |
|
|
Permanent Wilting Point |
Rate of water absorption insufficient for plant needs |
|
|
Available Water |
Soil water between field capacity and the permanent wilting point. |
|
|
What causes some minerals to become less available?
-add nitrogenous fertilizers |
Alkalinity |
|
|
What may inhibit growth of nitrogen - fixing bacteria.
-add calcium or magnesium pounds com |
Acidity |
|
|
Vascular Cambium |
Produces wood and inner bark Two types of cells in vascular cambium
1. Fusiform initials 2. Ray initials |
|
|
Periderm |
-cork -cork cambium -parenchyma |
|
|
Rhizomes
|
Horizontal stems that grow belowground
thin or thick bulky distinct nodes ie. ginger |
|
|
Runners
|
Horizontal stems that generally grow along surface
ie. strawberry |
|
|
Stolons
|
Produced beneath the surface of the ground and tend to grow in different direction
ie. strawberry |
|
|
Bulbs
|
Large buds surrounded by numerous fleshy leaves, with a small stem at the lower end.
ie. onion |
|
|
Corms
|
Resemble bulbs, but composed almost entirely of stem tissue.
ie. crocus |
|
|
Cladophylls
|
Flattened, leaf - like stems
ie. cactus |
|
|
Thorns
|
sharp and pointed + stiff
ie. honey locust |
|
|
Tendrils
|
coil on contact as they form
ie. grape |
|
|
What are the two most important characteristics in commercial wood? |
Density Durability |
|
|
Knots |
bases of lost branches covered by new annual rings produced by the cambium of the trunk. |
|
|
Lipids |
fatty or oily substance that are mostly insoluble in water because they have no polarized components |
|
|
Parts of a Cell
|
|

|
Plant Tissue
|
|
|
Leaf Diagram
|
|
|
Leaves are attached to a plant in one of three leaf arrangements. Which of the following is not one of those arrangements?
a) whorled b) spiraled c) alternate d) opposite |
b) spiraled
|
|
|
Leaf veins are usually arranged in a pattern. Which of the following is not one of the primary patterns given?
a) Palma tell b) Pinnately c) Parallel d) Cruciate |
d) Cruciate
|
|
|
What is a pulvinus?
a) tip of a root b) structure within the seed c) swelling at base of leaf |
c) swelling at base of leaf
|
|
|
What plastic is abundant in the potato?
|
amyloplast
|
|
|
Twiner
|
grow around a support
ie. morning glory |
|
|
Tuber
|
enlarged tip of a rhizome
ie. white potato |
|
|
Stem Major Function
|
supports and vascular connections from root to shoot
|
|
|
Your friend grows African violets, and you knock one of her prized specimens off the shelf on to the floor. It breaks into many separate pieces. Though you feel bad, your friend tells you not to worry. What could be the reason for your friend’s behavior?
• African violet leaves form adventitious roots, so she can reproduce an entire plant easily.
• She knows that African violets are really not worth very much.
• Only African violets that are ready to die will shatter into separate leaves. |
African violet leaves form adventitious roots, so she can reproduce an entire plant easily. |
|
|
Endodermal cells are most similar in function to
• a colander. • a pasta maker. • an airport security station. • an answering machine. |
an airport security station |
|
|
As part of a study of plant secondary compounds, you produce genetically modified alfalfa plants that do not grow as well as control plants. When you uproot the plants, you find that the roots on the GM alfalfa are smooth, whereas the control roots have bumps on their surface. What is a logical explanation for this result?
• You caused the plants to overexpress a bacteriocidal compound. • Your plants had severely curtailed flavonoid production, so nodules didn’t form. • You caused the plants to overexpress ubiquitin. |
Your plants had severely curtailed flavonoid production, so nodules didn’t form. |
|
|
You take a core sample along the diameter of a threeyear-old tree. In what order will you see the layers within?
• vascular cambium, primary phloem, primary xylem, secondary xylem, primary phloem
• secondary phloem, primary phloem, vascular cambium, primary xylem, secondary phloem
• primary phloem, primary xylem, vascular cambium, secondary xylem, primary phloem
• primary phloem, secondary phloem, vascular cambium, secondary xylem, primary xylem |
Primary phloem, secondary phloem, vascular cambium, secondary xylem, primary xylem |
|
|
Cell cycle – cells divided and go through an orderly series of events. Usually divided into |
* Interphase * Mitosis *Prophase * Metaphase *Anaphase *Te lophase |

